What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory, noncontagious skin disease caused by immune system disorder. It results in raised, red, itchy plaques on areas such as the hands, knees, elbows, legs, back, and scalp due to accelerated skin cell growth.
Psoriasis skin disease can be localised or widespread. It is a common, chronic skin disorder with no treatment. It appears in cycles and shows up for a few weeks or months, then slows down or enters remission.
What are the Signs & Symptoms of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis symptoms are not the same for everyone. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Red scaly, white patches
- Small scaling spots mostly in children
- Dry, cracked skin
- Burning, itching or soreness
- Pitted or cracked nails
- Joint pain
- Stiff joints
- Itching sensation
Types of Psoriasis Based on Location on Body
There are five types of psoriasis based on the locations on body
- Genital psoriasis It is a common type of psoriasis skin disorder. Many people experience this type of psoriasis. It is observed on the skin in the genital area or on the inner and upper thighs
- Scalp psoriasis It also indicates Psoriatic arthritis (PsA), as many people exhibit both symptoms together. Scalp psoriasis symptoms appear like fine scaling which may appear like dandruff, thick pink plaques that cover the entire scalp.
- Facial psoriasis It mainly occurs on the eyebrows, the skin between the nose and the upper lip, and on the forehead and hairline. Psoriasis on the face is usually mild in nature.
- Inverse psoriasis It affects the skin folds of the body. It is observed in the buttocks, groin, and under the breasts. Fungal infections may induce this type of psoriasis. Inverse psoriasis results in smooth patches of red skin that intensifies with friction and sweating.
- Psoriasis on hands, feet, and nails manifests as scaling on palms and soles, accompanied by pitted and cracked nails, and often causes difficulties in daily activities.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionTypes of Psoriasis based on Aetiology
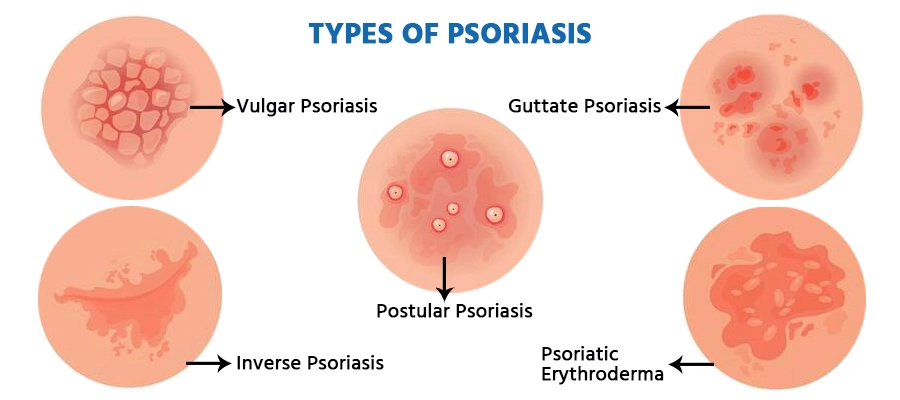
- Guttate psoriasis, caused by streptococcal infection, manifests as small, scaly red papules, commonly in children and young adults.
- Pustular psoriasis presents with yellow, pus-filled lesions known as pustules. It can be generalised, affecting many body parts, or localised, found on smaller areas like palms and soles.
- Plaque psoriasis shows raised inflamed, red patches with a silvery-white coating. It can be tender, itchy, and painful, typically appearing on the back, elbows, knees, and scalp.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis, though rare, causes severe redness and shedding of skin layers in large sheets. It can be life-threatening, with symptoms including severe itching, pain, changes in heartbeat, fever, dehydration, and alterations in nail texture.
What are the Causes of Psoriasis Skin Disease?
Psoriasis causes are still unclear, but it is sure that our immune system and genetic factors play a significant role.
Common psoriasis trigger factors are;- Skin injury
- Streptococcal infections
- Cold weather and dry conditions
- Stress factors
- Genetic predisposition
- Obesity
- More alcohol consumption
- Medications for high blood pressure
- Medications like antimalarial drugs and lithium

What are the Risk factors that Develop Psoriasis Disease?
The risk factors for psoriasis disease are -
- Family history Psoriasis disease can pass on from one generation to another. If your parents have this disease then the chances of you getting it increases
- Stress As stress greatly impacts your immunity, high-stress levels may increase your risk of psoriasis.
- Smoking Tobacco smoking increases the risk of psoriasis but it also escalates the intensity of the disease. Smoking can also play a trigger factor in the initial development of the disease.
What are the Complications of Psoriasis Skin Disease?
Psoriasis skin disease can induce other complications, such as -
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Eye problems like conjunctivitis, uveitis and blepharitis
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Certain autoimmune illnesses, such as sclerosis, celiac disease, and the inflammatory bowel disease called Crohn's disease
- Mental health problems, such as depression and low self-esteem
How is Psoriasis Disease Diagnosed?
- Dermatologists will diagnose psoriasis based on the patient’s medical history.
- Examine the affected part of the skin, including skin, scalp and nails.
- Collect a small skin sample (biopsy) for microscopic examination to determine the type of psoriasis and rule out other disorders.
- A blood test is recommended to rule out any other health conditions relating to the development of psoriasis.
How Treatment is Done for Psoriasis Skin Disease?
Psoriasis cure focuses on stopping the skin cells from growing and get rid of scales from the skin. The treatment option depends on the severity of the psoriasis disease.
Topical therapy -
- Corticosteroids These medicines are commonly used to treat mild to moderate psoriasis disease. Corticosteroids are available in many forms such as ointments, lotions, creams, sprays, gels, foams, and shampoos. Mild psoriasis ointments are used for for sensitive areas, like skin folds, face and large patches. Topical corticosteroids can be applied during flares, and on alternate days to manage remission.
- Vitamin D analogues The synthetic form of vitamin D, such as calcipotriene and calcitriol decreases skin cell growth, thus minimizing the intensity of psoriasis symptoms.
- Retinoids The synthetic form of vitamin A is known as Retinoid. The retinoid used to cure psoriasis is called tazarotene. Tazarotene is unsafe during pregnancy or breastfeeding or if you intend to become pregnant.
- Calcineurin inhibitors These include such as tacrolimus ointment and pimecrolimus cream. These medicines can treat Plaque psoriasis and Inverse psoriasis. They reduce plaque buildup and inflammation. These medicines are not recommended for prolonged use due to the risk of skin cancer or lymphoma. They are also not safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Salicylic acid The synthetic form of vitamin A is known as Retinoid. The retinoid used to cure psoriasis is called tazarotene. Tazarotene is unsafe during pregnancy or breastfeeding or if you intend to become pregnant.
- Coal tar It effectively cures plaque-type psoriasis and scalp psoriasis. It reduces itching and swelling. Coal tar can be prescribed alone or in combination with other medicines. It is considered safe for long-term use.
- Goeckerman therapy It is a therapy to manage moderate to severe forms of plaque psoriasis. It works by using a combination of crude coal tar and artificial ultraviolet radiation. Goeckerman therapy is a unique form of light therapy.
- Anthralin Anthralin is a psoriasis cream to decelerate skin cell growth. Anthralin takes off scales and makes skin smoother. It is not recommended on the face or genitals. Anthralin causes skin irritation, and it stains easily. It's applied for a short period of time and then cleaned off.
Light therapy
Phototherapy or light therapy is a first-line treatment to cure moderate to severe psoriasis. In this, the skin is exposed to ultraviolet light. It is done under medical supervision.
- Sunlight Short duration of sunlight exposure (heliotherapy) might improve psoriasis, at least temporarily. Sunlight consists of ultraviolet light, consisting of UVA and UVB rays. The UVB rays slow psoriasis growth rate.
- UVB broadband Specific doses of UVB broadband light from an artificial light source can cure psoriasis that doesn't improve with topical treatments. Few side effects observed are itching, redness, and dry skin. Use moisturizers regularly to ease your discomfort.
- UVB narrowband UVB narrowband phototherapy is more effective in managing psoriasis than UVB broadband treatment. It's recommended two or three times a week to improve the skin. Prolonged usage of Narrowband UVB phototherapy may lead to severe and long-lasting burns.
- Psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) PUVA therapy comprises psoralen and UVA. PUVA is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for psoriasis. The psoralen is taken before the skin is exposed to UVA. It is an aggressive treatment to manage severe cases of psoriasis.
- Excimer laser It is a form of phototherapy, a strong UVB light that targets only the diseased skin. This laser therapy needs fewer sessions than traditional phototherapy as it contains more powerful UVB light. Excimer laser side effects include redness and blistering.
List of Lifestyle Habit Changes that Aid Quick Psoriasis Recovery
- Bath every day
- Use moisturiser
- Cover the diseased skin
- Use limited sunlight
- Stay away from psoriasis triggers
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Eating nutritious food
- Avoiding smoking
- Stay away from pollution
Consult your dermatologists to choose the right type of shampoo or soap that does not cause any harm to your skin.
What are Do’s and Don’ts to Relieve from Psoriasis Symptoms
Psoriasis is an allergic and highly irritating skin condition that needs to be managed and treated well. Follow its dos and don’ts to relieve the symptoms.
It is possible to relieve psoriasis symptoms by avoiding the trigger factors and taking prescribed medicines on time.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Eat healthy diet | Consume alcohol or smoke |
| Bath every day | Scrath or scrub lesions |
| Apply prescribed moisturiser on your skin | Let skin injuries happen |
| Maintain healthy weight | Get exposed to pollution, dirt, and cold weather |
| Use limited sunlight | Use unreliable skin products |
Psoriasis Care at Medicover Hospitals
Medicover’s dermatology department consists of famous skin specialists who provide specialized care. Our skin specialists are highly experienced in treating many skin problems, such as;
- Skin allergies
- Acne
- Rash
- Ulcers
- Atopic dermatitis
- Psoriasis, etc.
