What is Type 2 Diabetes?
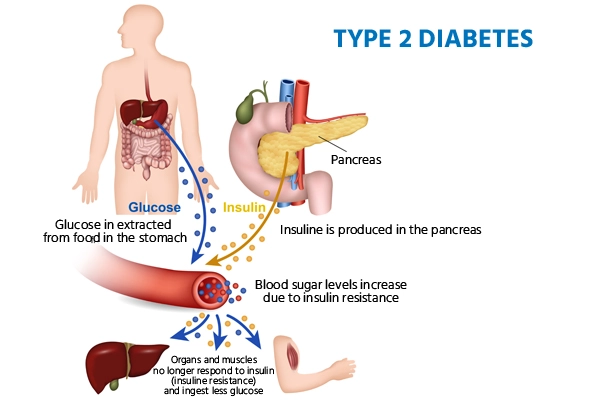
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production.
Our body's energy source, glucose, is regulated by insulin produced by the pancreas; in diabetes, insulin resistance leads to impaired glucose uptake by cells.
When cells don't respond to insulin, the pancreas tries harder by making more, but eventually can't keep up, causing high blood sugar and diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is managed through lifestyle changes, including exercise, healthy eating, and regular check-ups, to maintain control over daily activities.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhat are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
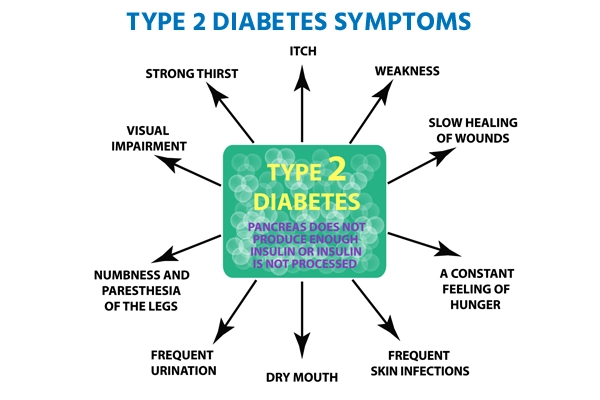
- Vision problems
- Weakness
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Increased thirst
- Increased hunger
- Gum disease
- Slow healing of wounds
- Prone to infections
- Tingling or numbness in your hands or feet
- Unexplained weight loss
What are the types of diabetes?
Diabetes is divided into four types:
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also called juvenile or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar due to the body's inability to produce insulin, often emerging in childhood due to genetic and viral factors.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, affecting 90-95% of diabetics, arises from insulin resistance, leading to difficulty in controlling blood sugar levels, primarily diagnosed in adults.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes, occurring during pregnancy, can impact both mother and baby's health, disappearing post-birth yet elevating the risk of future type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes
Prediabetes signals elevated blood sugar levels below the threshold for type 2 diabetes, yet without lifestyle adjustments, it may progress to full-blown diabetes.
When to see a doctor?
Consult a diabetologist if you notice any diabetes symptoms.
What are the causes of type 2 diabetes?
A number of factors can lead to type 2 diabetes, they are:
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history or genetics
Type 2 diabetes starts with insulin resistance, where cells don't respond to insulin, prompting the pancreas to produce more, but eventually fails, leading to high blood sugar.
What are the risk factors of type 2 diabetes?
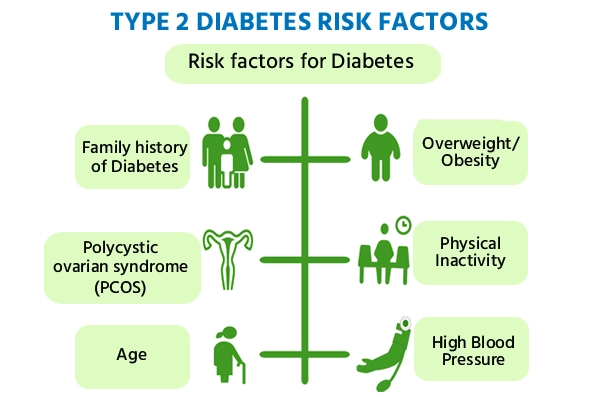
The risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes are:
- Weight gain or obesity
- Family history
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Having prediabetes
- If you are 45 years or older
- Having close relatives with type 2 diabetes
- Had gestational diabetes during pregnancy
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
- Ethnicity - People belonging to Asian, African American, Latino, and Pacific Islander.
How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed after conducting a few blood tests:
- Glycolated hemoglobin testing (A1c) : It is a blood test done to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This test helps to find out about blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
- Fasting plasma glucose test : It is the simplest and quickest method for determining blood glucose levels and diagnosing diabetes. An individual needs to fast and avoid eating or drinking (except water) for 8 to 12 hours before the test.
- Random plasma glucose test : In this test, the blood is drawn at a laboratory at any time. The test is unaffected by whether you have fasted or eaten recently.
- Oral glucose tolerance testing : This test, also called a glucose tolerance test, measures how your body responds to sugar (glucose). It is done to screen for type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
What is the treatment for type 2 diabetes?
The type 2 diabetes cure is not available. But it is possible to control diabetes by adhering to a healthy way of life and taking diabetes medications on time.
Diabetes management can be done by following the below-given methods:
- Daily glucose monitoring with a meter or CGM is essential. Your doctor may prescribe medications, insulin, or injections to manage diabetes effectively.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly to keep yourself healthy. Diet for type 2 diabetes includes:
- Eat healthy : Focus on veggies, whole grains, legumes, and lean proteins.
- Choose fruits wisely : Oranges, berries, and apples are good options.
- Watch out for sugar, fat, and salt : Keep them to a minimum.
- Stick to regular meals : Have breakfast, lunch, and dinner every day.
- Monitor regularly : Check blood sugar,
- blood pressure, and cholesterol as per your doctor's advice.
What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
The diabetes complications are:
- Heart problems
- Neuropathy in limbs
- Kidney disease
- Liver problems
- Eye damage
- Hearing impairment
- Dementia
- Sleep apnea
- Skin problems, including fungal and bacterial infections
What dos and don'ts for type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes means high blood sugar, leading to issues like frequent urination, fatigue, and slow wound healing. Managed with medications and insulin therapy.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Eat meals on time | Smoke or consume alcohol |
| Eat a healthy diet | Eat more sugar and salt in diet |
| Take diabetes medicines properly | Ignore monitoring your blood sugar levels |
| Get regular blood test | Follow a sedentary lifestyle and gain weight |
| Prefer small meals than large meals | Eat a high-fat diet |
Follow tips to control type 2 diabetes for a healthy life and prevent complications.
Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover Hospitals, our expert diabetes team provides top-quality care with a collaborative approach. We offer affordable world-class services for excellent treatment outcomes.
Citations
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21501-type-2-diabetes
https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/type-2
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentFrequently Asked Questions
Type 2 diabetes cannot be cured, but it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and medication.
The frequency of blood sugar monitoring varies depending on individual health needs, but it's typically recommended that levels be checked regularly, as advised by a healthcare provider.
Common medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Yes, unmanaged type 2 diabetes can increase the risk of various health complications, including cardiovascular diseases, kidney problems, nerve damage, and eye issues.
Yes, individuals with type 2 diabetes are often advised to follow a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and portion control are also important.
