
Nurses and Nursing Care Services at Medicover Hospitals
Nurses are integral members of the healthcare team, providing essential care and support to hospital patients. This abstract provides an overview of different categories of Nurses at Medicover Hospital, highlighting their roles, responsibilities, and areas of expertise.
Understanding these categories is essential for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals seeking nursing care.
OPD Nurse
OPD nurses perform various tasks, including:
- Assessing patient needs
- Triaging patients
- Conducting preliminary examinations
- Assisting with diagnostic tests and medical procedures
- Administer medications
- Educate patients about their conditions and treatment plans
- Provide emotional support and counselling
In addition to patient care, OPD nurses contribute to efficiently managing the outpatient department. They help with:
- Scheduling appointments
- Maintain medical records
- Ensure infection control practices
- Facilitate effective communication among patients, healthcare providers, and support staff
OPD nurses also play a role in health education and preventive care, promoting healthy lifestyles and disease prevention in the community.
Ward or Staff Nurse
Staff nurses form the largest group of nursing professionals. They are responsible for:
- Assessing
- Planning
- Implementing
- Evaluating patient care
RNs work in diverse healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community health centers. Their roles range from providing direct patient care to coordinating and managing healthcare teams.
The Staff Nurse is the first-level professional nurse in the hospital setup. Therefore, by appearance and word, she will always be professional. They are skilled and give expert bedside care to the patients.
Ward nurses execute special technical duties in areas like operation theatres, intensive care units, and highly dependent units. She also acts as a ‘de facto’ sister when the situation arises in the ward or department.
ICU Nurse
ICU Nurses possess advanced education and training. They have the role of helping to diagnose illnesses and provide primary and specialized healthcare services. They often work independently or collaboratively with physicians, offering various services across various specialities.
ICU nurses possess diverse skills, including:
- Clinical expertise
- Critical thinking
- Effective communication
- Empathy
They are trained to handle complex medical procedures, emergencies, and end-of-life care while emotionally supporting patients and their families.
Nurses establish therapeutic relationships, recognizing the importance of holistic care that addresses not only physical health but also psychological, social, and cultural factors. They are crucial in promoting health and preventing diseases, emphasizing patient education and community outreach.
BMT /KTP /LTP - Transplant Nurse
A transplant nurse is a healthcare professional who specializes in caring for patients undergoing:
Transplant nurses play a vital role in the management of patients receiving bone marrow transplants or undergoing other bone marrow-related procedures. They demonstrate resilience, adaptability, and dedication to patient care.
Operating Theater Nurses
Operating theatre nurses are responsible for ensuring
- The sterility of the operating theatre
- Organizing surgical instruments and supplies
- Preparing the patient for surgery
They work closely with surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other healthcare professionals to prepare and maintain the surgical environment. During procedures, they assist the surgical team by providing
- Instruments
- Managing surgical equipment
- Anticipating the needs of the surgeons
Cath Lab Nurse
A Cath lab nurse, also known as a cardiac catheterization laboratory nurse, is a specialized registered nurse in the cardiac catheterization laboratory, also known as the cath lab. A cath lab is a specialized unit within a hospital where various diagnostic and interventional procedures are performed to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions.
Cathlab nurses play a crucial role in assisting cardiologists and other healthcare professionals during cardiac catheterization procedures. Their responsibilities include:
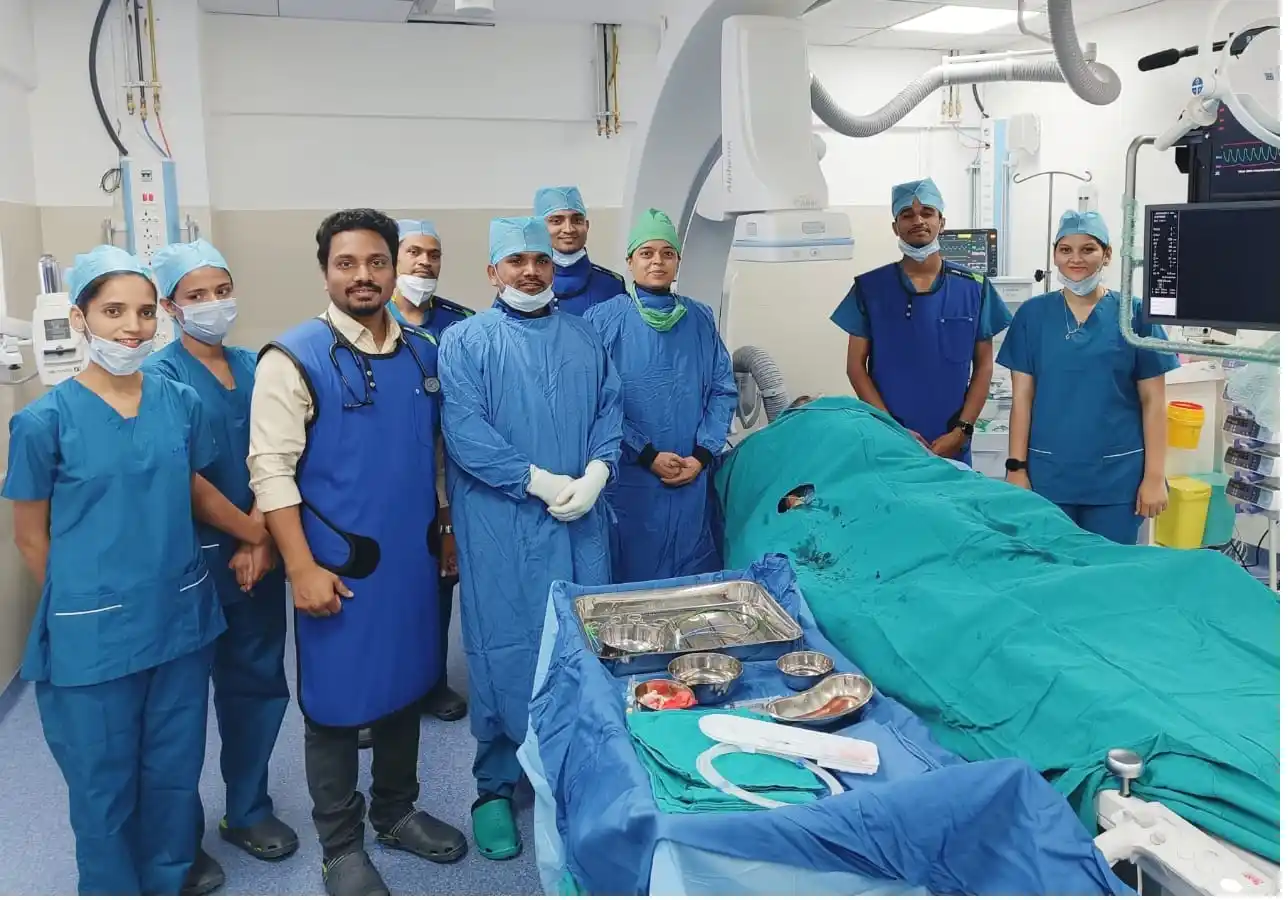
- Patient Assessment: Cath lab nurses assess patients before the procedure, obtaining their medical history and vital signs, and ensuring they are prepared for the catheterization.
- Procedure Preparation: They prepare the catheterization lab by ensuring all necessary equipment, medications, and supplies are available. They also prepare the patient by explaining the procedure and addressing any concerns.
- Patient Monitoring: During the procedure, cath lab nurses closely monitor the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. They are trained to identify and respond to any changes or complications that may arise.
- Medication Administration: Cathlab nurses administer medications as directed by the cardiologist, such as sedatives, analgesics, and anticoagulants, to ensure patient.
Chemo Nurse
A chemo nurse is also known as an oncology nurse or chemotherapy nurse. A registered nurse who specializes in providing care to patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment for cancer. Chemo nurses work closely with oncologists and the healthcare team to administer:
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Monitor patients during treatment
- Provide education and support throughout the process
Some of the key responsibilities of a chemo nurse:
- Patient assessment
- Chemotherapy administration
- Patient monitoring
- Symptom management
- Emotional support and education

Pain Nurse
A pain management nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in assessing, managing, and treating pain in patients. They work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and specialized pain management centers.
Pain nurses collaborate with healthcare teams to:
- Develop comprehensive pain management plans
- Provide holistic care to individuals experiencing acute or chronic pain
The primary responsibilities of a pain nurse are:
- Pain assessment: experience
- Pain management planning
- Medication administration
- Non-Pharmacological interventions
- Patient Education
- Collaborative Care
- Advocacy and Support
Wound Care-Nurse
A wound nurse is a registered nurse with specialized training and expertise in assessing, treating, and managing various types of wounds. They collaborate with healthcare teams to provide optimal wound care for patients and work in different healthcare settings like
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Long-term care facilities
- Home Nurse Services
A few responsibilities of a wound nurse:
- Wound Assessment
- Treatment Planning
- Wound Dressing and Care
- Infection Control
- Patient and Family Education
- Collaboration and Consultation
Nursing Incharge
An incharge nurse plays a crucial role in maintaining effective interdisciplinary communication. They collaborate with physicians, pharmacists, therapists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive and coordinated patient care.
Nurse incharges may also participate in quality improvement initiatives, implementing evidence-based practices and monitoring outcomes to enhance patient care and safety. One of the primary responsibilities of a nurse incharges is to promote patient safety and quality care.
They monitor patient conditions, ensure compliance with care protocols and policies, and address any concerns or issues during their shift. The nurse-in-charge is a resource for nursing staff, providing guidance, support, and clinical expertise when needed


Nursing Supervisors
They are responsible for coordinating and managing nursing units or departments within healthcare facilities. They oversee nursing staff, including registered nurses, licensed practical nurses, and certified nursing assistants, ensuring appropriate staffing levels, scheduling, and assignment of duties
Nursing supervisors provide:
- Guidance
- Support
- Mentorship to nursing staff
- Promoting professional growth and development
Infection Control Nurse
Infection prevention and control nurses are specialized healthcare professionals who play a vital role in preventing and controlling the spread of infections within healthcare settings. They collaborate with healthcare teams to establish and enforce protocols, policies, and best practices to minimize the risk of infections.
Infection control nurses conduct surveillance for infectious diseases, analyze data, and provide recommendations for infection prevention measures. Obtaining their medical history and vital signs and ensuring they are prepared for the catheterization.
Their responsibilities include:
- Procedure Preparation: They prepare the catheterization lab by ensuring all necessary equipment, medications, and supplies are available. They also prepare the patient by explaining the procedure and addressing any concerns.
- Patient Monitoring: During the procedure, cathlab nurses closely monitor the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. They are trained to identify and respond to any changes or complications that may arise.
Medication Administration:
Cathlab nurses administer medications as directed by the cardiologist, such as sedatives, analgesics, and anticoagulants, to ensure patient.
Nurse Educator
Beyond direct patient care, nurses contribute to healthcare through various roles and specialities. Nurse educators train the next generation of nurses, sharing their knowledge and expertise to ensure a skilled workforce.
Nurse educators conduct studies to improve:
- Healthcare practices
- Advance evidence-based care
- Enhance patient outcomes
Nurses and leaders manage healthcare organizations, develop policies, and create supportive environments for nursing staff



Nursing Superintendent
A nursing superintendent, also known as a nursing administrator / Chief Nursing Officer (CNO), is a senior-level nurse executive overseeing and managing a healthcare facility’s nursing department.
Responsibilities of a Nursing Superintendent:
- Ensuring High-quality Patient Care
- Coordinating Nursing Operations
- Nursing practice and standards
- Risk Management and Compliance
- Staff Development and Education
- Professional Advocacy
- Promoting Nursing Excellence
- Strategic Leadership
- Collaboration and Communication
- Nursing Administration
- Quality Improvement and Patient Safety

Nursing Superintendents require advanced nursing degrees and extensive experience in nursing leadership roles. They possess strong leadership, management, and interpersonal skills to effectively collaborate with diverse stakeholders, inspire and motivate the nursing team, and drive organizational goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nurses are indispensable professionals who play a pivotal role in healthcare. They are compassionate, skilled, and dedicated individuals who provide holistic care to patients, promote health and wellness, and advocate for the well-being of individuals and communities.
Nurses possess a wide range of knowledge and expertise, from clinical skills to critical thinking and effective communication. They work collaboratively with interdisciplinary teams to deliver high-quality care and ensure positive patient outcomes.
Nurses are at the forefront of healthcare, whether in hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, or community settings, providing essential services across the lifespan.