| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
|
Meet the respective specialist based on your symptoms |
Eat fatty and fried foods |
|
Take prescribed medicines regularly |
Follow fad diet plan |
|
Consume alcohol |
|
|
Avoid taking other medicines without prescription |
Skip the doctor appointment |
|
Get adequate sleep and maintain a healthy lifestyle |
Eat artificial sweeteners and food colours |
Autoimmune Disease: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
The immune system is made up of specialized cells and chemicals that work together to fight bacteria and viruses causing infections. However, when the immune system mistakenly starts attacking the body’s own tissues, autoimmune conditions occur. Autoimmune conditions can be classified into two types: organ-specific autoimmune disease and non-organ-specific disorders.
Organ-specific autoimmune disease affects just one organ, while non-organ-specific conditions impact multiple organs or systems in the body.
There are around 80 different autoimmune disorders, with severity ranging from mild to severe, depending on which organ is affected and the level of damage. Autoimmune deficiency may also develop in some cases, weakening the body’s natural defense system.
Women are generally more prone to autoimmune diseases than men, especially during their reproductive years, possibly due to the role of sex hormones in these conditions. While the symptoms of autoimmune diseases can be managed with proper treatment, there is still no complete cure for these disorders.
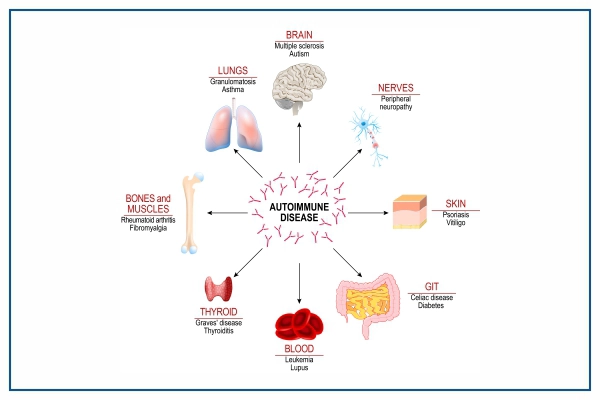
Types of Autoimmune Disease
Autoimmune disorders can affect almost any organ or system in the body. There are about 80 different types of autoimmune disorders. Some of the autoimmune disorders are
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus)
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionWhat are the Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases?
The signs of autoimmune disease can vary, but common autoimmune disease symptoms include:
- Muscle pain, joint pain or weakness
- Fever
- Insomnia, weight loss, heat intolerance or rapid heartbeat
- Recurrent rashes or hives, sun sensitivity, and a butterfly-shaped rash over the nose and cheeks.
- Hair loss or white patches on the skin or inside the mouth
- Dry mouth, eyes or skin
- Tingling in the feet or hands and numbness
- Difficulty in concentrating
- Abdominal pain, blood or mucus in the stool, or diarrhoea
- Mouth ulcers
- Blood clots
- Multiple miscarriages
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and management.
When to see a doctor?
See a doctor if you have symptoms of an autoimmune disease. You might need to visit a specialist, depending on your disease type.
- Rheumatologists for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune disorders such as Sjögren's syndrome and SLE.
- Gastroenterologists for GI disorders such as Celiac disease and Crohn's disease.
- Endocrinologists for conditions related to glands such as Graves' disease.
- Dermatologists for skin disorders such as psoriasis.
If you’re looking for the best immunologist in India, they can provide the expertise you need to manage your condition. You can also search for an autoimmune disease doctor near you. Experienced doctors at Medicover can help you receive the right treatment and management for various autoimmune diseases and their symptoms.
What are the Causes of Autoimmune Disease?
Doctors are uncertain what causes the immune system to malfunction. However, some people are more likely than others to develop an autoimmune disease. Certain autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis and lupus, are inherited. Not every family member will have the same disease, but they will inherit a vulnerability to an autoimmune disorder. Because the prevalence of autoimmune illnesses is increasing, scientists suspect that environmental factors such as infections and exposure to chemicals or solvents may be responsible.
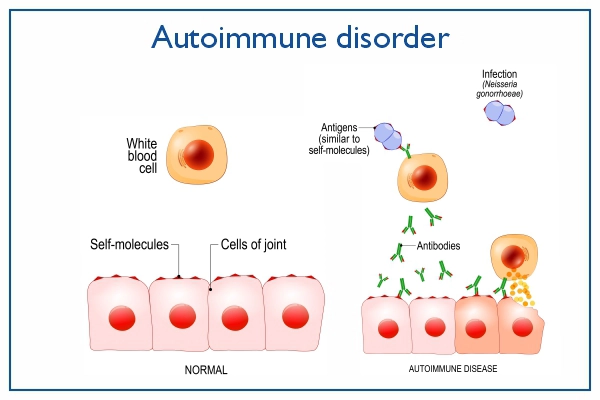
What are the Autoimmune Disease Risk factors?
Autoimmune disorders can affect anyone, but specific conditions induce the risk. The risk factors for the various types of autoimmune disorders vary. However, some common factors include
- Genetics: Certain autoimmune diseases run in families. A person may be born with genes predisposing them to a condition, but they may not acquire it until they are exposed to a combination of triggers.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as sunlight, certain chemicals, and viral or bacterial infections, can all impact the formation of autoimmune diseases
- Gender: Due to hormonal factors, women are more likely to develop more autoimmune disorders than men, except for Ankylosis Spondylitis which is more common in men than women.
- Hormones: Autoimmune illnesses are more common throughout the reproductive years. Some diseases tend to be influenced by major hormonal changes such as pregnancy, delivery, and menopause, for better or worse.
- Infection: Some disorders seem to be triggered or worsened by certain infections.
What are the Autoimmune Disease Complications?
Autoimmune disease complications can be serious or even fatal. The severity of complications is usually based on the type of autoimmune disease and the individual patient. Autoimmune disease complications can include:
- Blindness
- Bleeding and blood clots
- Joint and bone damage
- Cancer
- Other autoimmune disorders might develop.
- Infections that occur frequently, such as pneumonia and bronchitis
- Cardiovascular disease and blood vessel damage
- Neuropathy, paralysis, seizures, and stroke are all examples of nervous system problems.
- Adhesions
- Organ damage and failures, such as liver and kidney failure
- Pancreatitis
- Complications during pregnancy
How to get an Autoimmune Disease Diagnosed?
Most autoimmune disorders cannot be diagnosed with a single test and a high degree of suspicion is needed to correlate the symptoms. To diagnose patients, the doctor will use a combination of tests, a review of the symptoms, and a physical examination, especially if multiple organs or systems are affected. Methods of diagnosis may vary depending on the disease. They commonly include
Autoimmune Disease Treatment
Treatments can’t cure autoimmune diseases, but they can control the overactive immune response and bring down inflammation or at least reduce pain and inflammation. Drugs used to treat these conditions include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce inflammation and pain
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. They are sometimes used to treat an acute flare of symptoms
- Pain-killing medications such as paracetamol and codeine
- Immunosuppressant drugs to inhibit the activity of the immune system
- Physical therapy to encourage mobility
- Treatment for the deficiency, for example, insulin injections in the case of diabetes
- Surgery to treat bowel blockage in the case of Crohn's disease
How to Prevent Autoimmune Disease?
To prevent autoimmune disease, it's important to focus on a few key habits. First, maintain a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. Regular exercise is crucial to keep your body fit and reduce inflammation. Managing stress is also very important, as chronic stress can trigger autoimmune responses. Make sure you get proper sleep because it helps in strengthening your immune system. Avoid smoking, as it increases the risk of autoimmune diseases. Lastly, try to minimize exposure to environmental toxins, as these can affect your immune health.
While there is no guaranteed autoimmune disease cure, these steps can significantly help with autoimmune disease prevention and support overall health.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Do’s and Don’ts
Psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, disease, rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel Hashimoto's hypothyroidism appear to be unrelated at first glance. As they have different impacts on different parts of the body. However, they have one thing in common, they are all autoimmune disorders. The food you consume, the lifestyle you lead, and the way you respond and manage a condition have a significant impact on your overall health. If you have an autoimmune condition, following these dos and don'ts will help you manage it.
Autoimmune Disease Care at Medicover
At Medicover Hospitals, we have the most trusted group of doctors and healthcare professionals who are skilled at providing the best medical treatment to patients with compassion and care. To diagnose most common autoimmune disorders, our diagnostic department is equipped with advanced technology and equipment.
Our excellent team of specialists, including rheumatologists, gastroenterologists, dermatologists, and other experts, uses a systematic, multi-disciplinary approach to identify and treat autoimmune diseases. With great precision, they provide targeted treatments for these conditions, ensuring desirable results and better outcomes for our patients.
Still have questions? Speak with our experts now!
040-68334455Frequently Asked Questions
How important is it to remove waste matter from the body in managing autoimmune diseases?
Proper waste removal is crucial in managing autoimmune diseases as it helps reduce inflammation and prevent the accumulation of toxins that can exacerbate symptoms. Adequate hydration, fibre-rich foods, and regular exercise can aid in efficient waste elimination and support overall health.
Can I live a normal life with autoimmune disease?
Yes, many people with autoimmune diseases can live a normal life with proper treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and symptom management. Early diagnosis and regular care play a key role in managing the condition effectively.
Is autoimmune disease serious?
It can be serious depending on the type and how it affects different organs in your body. Some autoimmune diseases can cause long-term damage if left untreated, but with the right care, symptoms can often be controlled, and the condition managed.
Are autoimmune diseases cancerous?
Autoimmune diseases themselves are not cancerous, but some types, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, may increase the risk of developing certain cancers over time. Regular check-ups are important for monitoring any potential risks.
What kind of doctor is best for autoimmune disease?
A rheumatologist is typically the best doctor to treat autoimmune diseases, as they specialize in immune system disorders. Depending on the disease, other specialists like dermatologists or endocrinologists may also be involved.
What is the autoimmune diet?
The autoimmune diet focuses on foods that help reduce inflammation and promote healing, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It often involves avoiding gluten, dairy, and processed foods, while emphasizing whole, nutrient-dense foods to support the immune system.
