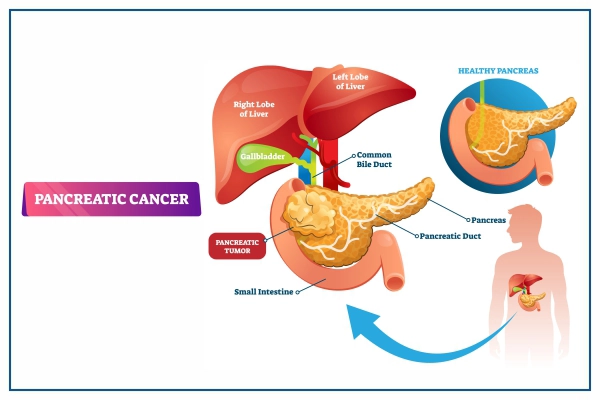
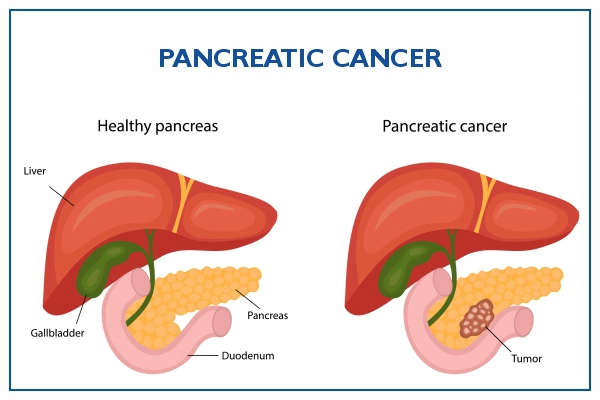
What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Pancreatic cancer occurs when unhealthy cancer cells develop and multiply within the tissues of the pancreas. It is difficult to diagnose pancreatic cancer at an early stage since the cancer has no specific signs and symptoms. Due to this, many cancers are diagnosed at an advanced stage when the illness is in its severe form, providing limited treatment options.
The pancreas is a part of the digestive system. It is a body organ present in the abdomen. The pancreas performs two important functions:
- Exocrine function that facilitates digestion
- Endocrine function that controls blood sugar levels
- Exocrine tumours: Exocrine tumors originate in glands, such as the pancreas or sweat glands. They can be benign or malignant and require proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Neuroendocrine tumors: Neuroendocrine tumors arise from hormone-producing cells. They can occur in various organs, with symptoms dependent on their location.
What symptoms of pancreatic cancer are present?
Pancreatic cancer is rarely detected in its initial stage when the treatment is easy. This happens because symptoms are not noticeable unless they have spread throughout the body. The pancreatic cancer symptoms are -
- Backache caused by abdominal discomfort
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Stools that are light-colored
- Itching sensation on the skin
- Dark urine
- Yellow pigmentation of the skin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Difficult to control diabetes
- Blood clots
- Weakness
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhen To See The Doctor?
Consult your primary care doctor if you experience any unexplained symptoms that are worrying you. There are many other health problems that can cause these symptoms, therefore your doctor may recommend a few diagnostic tests to check for other health conditions and also for pancreatic cancer. If pancreatic cancer is confirmed, you will be referred to an oncologist or gastroenterologist for further pancreas treatment.
Consult our oncologist or gastroenterologist for more information and adequate treatment for pancreatic cancer.
What are the Causes & Risk Factorsof Pancreatic Cancer?
Pancreatic cancer's cause remains elusive, though smoking and genetic mutations pose risks. DNA mutations in pancreatic cells lead to abnormal growth, forming tumours. Left untreated, these cells can spread, originating from duct cells (pancreatic adenocarcinoma) or neuroendocrine cells (neuroendocrine tumors).
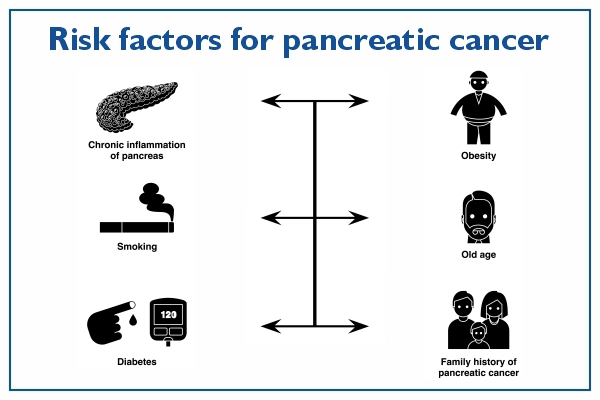
Risk factors
The risk factors for pancreatic cancer are:
Other possible risk factors include:
- Excess coffee consumption
- Physical inactivity
- High intake of red meat
- More consumption of soft drinks
How is pancreatic cancer Diagnosis?
Tests to diagnose pancreatic cancer are as follows:
- Blood test - This test is done to examine the overall health and monitor the functioning of liver and kidneys. Blood samples are taken to check the levels of tumour markers, such as CA-19-9. High tumour marker levels may indicate the presence of pancreatic cancer.
- Ultrasound test - This test uses soundwaves to generate images of pancreas and its surrounding structures. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) with endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can be done to diagnose pancreatic malignancies. This procedure is also used to collect a tissue sample for a biopsy test.
- CT scan: CT scan This imaging test is used to diagnose pancreatic carcinoma. It also helps to detect the spread of the cancer to the nearby organs or lymph nodes.
- PET scan or positron emission tomography: The scan is useful in detecting distant metastasis of pancreatic cancer disease.
- MRI scan magnetic resonance imaging: MRI scan uses magnetic waves to detect cancer-related to the pancreas. MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is done to inspect the pancreatic and bile ducts.
- Tissue sampling tests: This test includes fine-needle aspiration (needle biopsy), laparoscopy, and endoscopy.
Imaging tests:
How is pancreatic cancer treated?
Surgery: The pancreatic cancer surgery involves eliminating all or a part of the pancreas. It also depends on the location and size of the pancreatic tumour.
Different surgical procedures are carried out depending on the purpose of the surgery. They are -
- Laparoscopy : During this procedure, the oncologist surgeon will find out if the cancer has metastasized to the nearby organs in the abdomen. If metastasis has occurred then the procedure to remove the primary pancreatic tumour is not done.
-
Surgical procedures to remove the pancreatic malignant tumour :
- Whipple procedure: It is also known as a pancreaticoduodenectomy. This surgery is done if the malignancy is present only in the head of the pancreas. Whipple procedure is an extensive surgery and should be done by an experienced pancreatic surgeon only.
- Distal pancreatectomy: This operative procedure is preferred if the tumour is present on the left side of the pancreas tail. In this operation the surgeon takes out the tail and body of the pancreas, and the spleen.
- Total pancreatectomy: This procedure is recommended if the cancer has spread completely in the pancreas or is present in various parts of the organ.
- Chemotherapy : It is a drug therapy that is used to destroy malignant cells. In advanced pancreatic cancer chemotherapy can be effective to control tumour progression, reduce symptoms and prolong survival.
- Radiation therapy (radiotherapy) : The radiation therapy can be used after surgery or it is given along with chemotherapy and is known as chemoradiation or chemoradiotherapy.
- Supportive (palliative) care : It is specific medical care that aims to provide relief from pain and other disease symptoms. Palliative care focuses to help cancer patients and their families have a better quality of life.
Pancreatic Cancer Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover Hospitals, we have the most trusted team of oncologist surgeons and gastroenterologists working together to provide excellent healthcare services to our patients. With the use of latest equipment and the most advanced diagnostic procedures, we evaluate the patient’s condition and diagnose them at the earliest to initiate the treatment on time because in cancer treatment, timely action is vital for recovery. Our team also adopts a multi-disciplinary approach for treating pancreatic cancer and its related complications with the active participation of medical experts from different specialties. We provide world-class healthcare services at affordable costs in all our departments to offer our patients high-quality treatment outcomes and satisfactory experiences.
