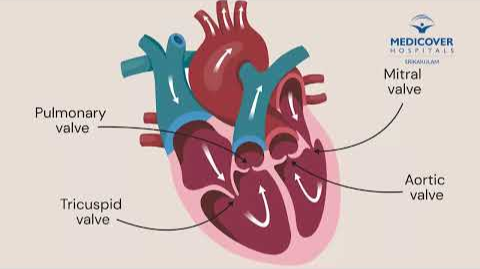
What is a Heart Transplant?
A heart transplant is a life-saving surgery in which a failing or damaged heart is replaced with a healthy heart from a deceased organ donor. It is considered only when all other treatments for severe heart disease have been tried and are no longer effective.
This procedure is for people with end-stage heart failure a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Without a transplant, survival is limited. For those who qualify, a new heart can restore strength, improve quality of life, and extend life expectancy.
Thanks to advances in surgery, organ preservation, and anti-rejection medications, heart transplant success rates have improved over time. Most recipients go on to live active, fulfilling lives for many years after surgery.
Can A Heart Be Transplanted?
Yes, a heart can be successfully transplanted. While it is one of the most complex surgeries performed, it has become a standard treatment for end-stage heart failure.
The donor heart must come from a person who has been declared brain-dead but whose heart is still beating and healthy. The donor must be matched to the recipient by blood type, body size, and other factors to reduce the risk of rejection.
Once the donor heart is available, the surgery typically takes 4 to 6 hours. The patient is placed on a heart-lung machine during the procedure, which keeps oxygen-rich blood flowing through the body while the old heart is removed and the new one is sewn in.
Thousands of heart transplants are performed worldwide each year, and survival rates continue to improve.
Who Performed The First Heart Transplant?
The first successful human-to-human heart transplant was performed by Dr. Christiaan Barnard in Cape Town, South Africa, on December 3, 1967. He transplanted the heart of a young woman who died in an accident into Louis Washkansky, a 54-year-old man with severe heart failure.
Mr. Washkansky lived for 18 days after the surgery. While short by today's standards, the operation proved that heart transplantation was possible and sparked rapid advances in transplant medicine.
Since then, improvements in immunosuppressive drugs, infection control, and surgical techniques have dramatically increased survival and quality of life for transplant recipients.
What Are The Types Of Heart Transplants?
There are several types of heart transplant procedures, chosen based on the patient's condition and needs.
- Orthotopic heart transplant: This is the most common type. The diseased heart is removed and replaced with the donor heart in the same position. It is used in most adult and pediatric cases.
- Heterotopic heart transplant (piggyback' transplant): In rare cases, the new heart is placed beside the old one, allowing both hearts to work together. This may be considered if the donor heart is slightly smaller or if the lungs are healthy but the heart is weak. It is rarely performed today.
- Domino transplant: In select cases, a patient receiving a heart-lung transplant can donate their still-functioning heart to another recipient. This is uncommon and only possible under very specific conditions.
- Heart-lung transplant: When both the heart and lungs are severely damaged such as in cystic fibrosis or pulmonary hypertension both organs may be transplanted together.
Your heart transplant team will determine which approach is best for your situation.
4 to 6 hours
Surgery Duration
General Anesthesia
Anesthesia Used
1 to 3 Weeks
Hospital Stay
3 to 6 weeks
Full Recovery Timeline

What Are The Indications For A Heart Transplant?
Heart transplant surgery is recommended only for people with end-stage heart failure who are not responding to medications, lifestyle changes, or other treatments. It is considered when the heart is so damaged that it can no longer pump blood effectively and life expectancy is limited without a new heart.
Common indications include severe shortness of breath even at rest, frequent hospitalizations for heart failure, poor heart function on imaging tests, and inability to perform basic daily activities. This surgery is not an option for mild or moderate heart disease, it is reserved for life-threatening, irreversible conditions.
What Conditions Does A Heart Transplant Treat?
Heart transplant surgery treats severe, irreversible heart conditions that lead to advanced heart failure.
These include:
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Enlargement and weakening of the heart, often caused by genetics, infections, or alcohol, leading to heart failure.
- Ischemic Cardiomyopathy: Damage from severe coronary artery disease, resulting in weakened heart function and heart failure.
- Congenital Heart Disease: Heart defects present from birth that, if untreated or unmanageable, may require a transplant.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Irreversible damage to heart valves, causing impaired blood flow and heart failure despite treatment.
- Restrictive/Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Rigid or thickened heart muscle that restricts proper function and can lead to heart failure.
- Severe Arrhythmias: Life-threatening irregular heartbeats not controlled by medication or devices, causing heart failure.
- Failed Previous Heart Surgery: Heart failure resulting from complications or failure of past surgeries like bypass or valve replacements.
When Would A Doctor Recommend Heart Transplant Surgery?
A doctor may recommend heart transplant surgery when:
- Symptoms of heart failure continue despite maximum medical therapy
- You are frequently admitted to the hospital for fluid overload or unstable heart function
- Your ejection fraction is very low (typically below 25%) and not improving
- You have life-threatening arrhythmias that cannot be controlled with devices or drugs
- You are unable to walk short distances or complete daily tasks due to fatigue or breathlessness
Referral to a transplant center often happens before you become critically ill. Early evaluation allows time for testing, listing, and support while waiting for a donor heart.
Why Is Heart Transplant Surgery Done?
Heart transplant surgery is done to save lives and improve quality of life in people with irreversible heart failure. Without it, survival is limited. With it, many people live for years with improved strength, energy, and breathing.
The goal is to replace a failing heart with a healthy donor heart so blood can be pumped effectively through the body. Most recipients are able to return to meaningful activities, reduce symptoms, and enjoy a better quality of life.
While lifelong follow-up and anti-rejection medications are required, the procedure offers a second chance for those with no other options.
How Should I Prepare Before a Heart Transplant?
Preparing for a heart transplant involves both medical readiness and lifestyle adjustments to ensure the best outcomes. Your healthcare team will guide you through:
- Medical Stabilization: Managing existing heart failure symptoms and optimizing medications.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol, eating a heart-healthy diet, and staying as active as possible.
- Mental Health Support: Undergoing psychological evaluation to ensure emotional readiness and coping strategies.
- Planning Ahead: Arranging caregiver support, time off from work, and understanding the financial aspects of transplant care.
- Education: Learning about the surgery, recovery expectations, medications, and long-term follow-up.
What Tests Are Done Before a Heart Transplant Surgery?
Before being placed on the transplant waiting list, you'll undergo a detailed heart transplant evaluation. This includes:
- Blood composition: Evaluates red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and blood chemistry to look for anemia, infections, or other issues that could affect surgery or recovery.
- Immune system testing: Helps doctors predict how your immune system may respond to a donor heart and identify the best donor match.
- Kidney function: Urinalysis and blood tests measure how well your kidneys are working, since strong kidney function is essential before and after transplant.
- Heart Function Tests: Echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization, or stress testing to evaluate how well your heart is working.
- Imaging: Chest X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs to check for other conditions that could affect surgery.
- Other Evaluations: Dental checkups, cancer screenings, and mental health assessments to ensure no hidden risks.
Should I Stop Eating, Drinking, or Taking Medicines Before a Heart Transplant?
Your doctor will provide specific instructions, which may include:
- Fasting: No food or drink for several hours before surgery once a donor heart becomes available.
- Medications: Some medicines may need to be paused, adjusted, or continued depending on your health status. Always follow your transplant team's guidance.
- Emergency Readiness: Keep a hospital bag packed and be ready to go immediately once you are called for surgery.
How is a Heart Transplant Procedure Performed?
A heart transplant is a life-saving procedure for people with severe heart disease. Here's a simple, step-by-step guide to how this procedure is performed, using clear and friendly language fit for your hospital website.
Preparing for Surgery
- Before anything starts, you'll meet with a team of experts who will explain the risks and answer your questions. It's normal to feel nervous; many people do.
- You'll get tests like blood work and scans to check your health and make sure you're ready for the operation.
- Once a suitable donor heart becomes available, you'll be prepared for surgery, often with very little notice, as timing is critical.
Going Into Surgery
- You'll be given General anesthesia, so you'll sleep deeply and feel no pain.
- Doctors carefully clean the surgical area and connect you to monitors for safety, so your team can keep a close eye on things while you're resting.
Removing Your Heart
- Skilled surgeons carefully remove your damaged heart. Don't worry-all your most important veins and arteries are kept safe and protected.
- Your body is connected to a special machine called a heart-lung bypass machine. This keeps your blood flowing and your body supplied with oxygen while the operation is happening.
Placing the Donor Heart
- The new heart is gently stitched into place. All the major blood vessels are carefully connected one by one.
- Your doctor checks that everything fits perfectly before letting blood begin to flow through the new heart.
Restarting the Heart
- Your surgical team uses gentle, controlled electric stimulation to help your new heart start beating for the first time in your body. This can be an emotional moment!
- Once your heart is beating, the team checks for any bleeding or leaks and makes sure everything is secure and working well.
Closing the Surgery
- The last step is closing your chest incision. Doctors carefully stitch up the area and place dressings to promote healing.
- You'll go to a specialized recovery area, where nurses and doctors will closely watch over you. Don't hesitate to ask for help or share how you are feeling they're there to support you.
The entire procedure generally takes 4 to 6 hours, though it can be longer in complex cases.
Who Performs a Heart Transplant Procedure?
Heart transplant surgery is performed by a specialized team of medical professionals, which includes:
- Cardiothoracic Surgeons: Lead the transplant operation and perform the removal and implantation of the heart.
- Cardiac Anesthesiologists: Manage anesthesia and monitor vital functions during surgery.
- Perfusionists: Operate the heart-lung bypass machine that maintains circulation while the heart is replaced.
- Transplant Cardiologists: Supervise patient selection, donor matching, and medical management before and after surgery.
- Specialized Nurses & Support Staff: Provide critical intraoperative and postoperative care.
What Should I Expect Immediately After The Heart Transplant Procedure?
Right after surgery, you will be taken to the intensive care unit where you will be closely monitored. You will still be on the ventilator and asleep for the first few hours. Once you wake up, the breathing tube will be removed, usually within 24 to 48 hours.
You may have:
- Tubes in your chest to drain fluid
- A catheter in your bladder to measure urine output
- Wires or patches to monitor your heart rhythm
- Pain or discomfort at the incision site, which will be managed with medication
Medical staff will check your vital signs, new heart function, and blood work frequently. You will also have regular echocardiograms and, in the early weeks, heart biopsies to check for signs of rejection.
Most patients stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 weeks, depending on how quickly they heal and whether any complications arise.
You will begin moving around as soon as possible often sitting up the day after surgery and walking within a few days. Early movement helps prevent blood clots and speeds recovery.
When Can I Return To Normal Activities After A Heart Transplant?
Recovery timelines vary, but in general:
- First Few Weeks: Focus is on wound healing, regaining energy, and frequent medical monitoring.
- 3 to 6 Months: Many patients are able to return to work, school, light exercise, and normal daily routines.
- Long Term: Strenuous exercise, heavy lifting, and high-stress activities are reintroduced gradually under your doctor's guidance.
Participation in cardiac rehabilitation is strongly recommended to safely rebuild strength and endurance.
Are Lifestyle Changes Required After Recovery?
Yes. Long-term success after a heart transplant depends on consistent lifestyle changes, including:
- Medication Adherence: Take all immunosuppressants and prescribed medicines exactly as directed.
- Diet: Follow a heart-healthy diet low in salt, saturated fats, and processed foods.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity approved by your cardiologist.
- Avoid Infections: Practice good hygiene and avoid exposure to sick individuals, as medications weaken your immune system.
- Quit Smoking & Alcohol: Essential to protect your new heart and overall health.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling can support long-term well-being.
With proper care, most patients enjoy a significantly improved quality of life and long-term survival.
What Are the Benefits of a Heart Transplant?
For people with severe heart failure, a heart transplant offers the best chance for long-term survival and improved quality of life.
Most recipients experience:
- A significant improvement in energy and ability to breathe
- Reduced or complete relief from symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling
- The ability to return to daily activities, work, and hobbies
- Longer life expectancy many live 10 to 15 years or more after transplant
- Improved heart function and overall health
While it is not a cure, a heart transplant gives a second chance at life. Most patients say their quality of life is much better after surgery than it was before.
What Are the Risks and Complications of a Heart Transplant?
While heart transplantation offers major benefits, it also carries serious risks. Common complications include:
- Organ rejection: The immune system may attack the donor heart despite immunosuppressive therapy.
- Infections: Weakened immunity from anti-rejection drugs increases the risk of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
- Graft failure: Problems with how the donor heart connects and functions in the recipient's body.
- Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy (CAV): A unique type of coronary artery disease that can damage the new heart over time.
- Kidney disease or failure, often related to long-term medication use.
- High blood pressure (hypertension) and osteoporosis from medication side effects.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms may occur after surgery.
- Neurologic complications such as stroke, seizures, or delirium.
- Mental health effects: Depression, anxiety, or difficulty adjusting after transplant
What Are the Side Effects of a Heart Transplant?
After surgery, it is normal to have temporary side effects from anesthesia, healing, and medications.
You may experience:
- Pain or discomfort at the incision site
- Fatigue during the first few weeks
- Swelling in the legs or abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Trouble sleeping
- Mood changes or emotional ups and downs
Many of these improve as your body heals. However, some side effects come from long-term use of anti-rejection drugs, such as:
- Weight gain
- Increased hair growth or acne
- Tremors or shaky hands
- High blood sugar or diabetes
- Increased risk of certain cancers
Your care team will help you manage these side effects with dose adjustments, lifestyle changes, or other treatments.
What is Cost of a Heart Transplant in India?
The cost of a heart transplant varies depending on several factors. On average, it ranges between Rs. 20,00,000 to Rs. 35,00,000. This estimate usually covers pre-surgery evaluation, the transplant procedure, and immediate post-operative care.
However, there are additional long-term expenses that can significantly increase the overall cost, such as lifelong medications, follow-up appointments, and treatment of possible complications.
Factors Affecting the Heart Transplant Cost
- Hospital and Surgeon Expertise: The reputation of the hospital and the experience of the transplant team play a major role in determining costs.
- Location: Costs can vary between cities. Major metropolitan areas may have higher charges compared to smaller cities.
- Patient's Health Condition: The patient's overall health before surgery and their recovery needs after the transplant can affect the expenses, especially if intensive care or extended hospitalization is required.
- Additional Costs: Long-term costs such as anti-rejection medications (immunosuppressants), rehabilitation, follow-up visits, and treatment for complications are not always included in the initial package but are necessary for lifelong care.