What is Heart Bypass Surgery?
Heart bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is a medical procedure that has become a lifesaver for many individuals suffering from severe heart disease.
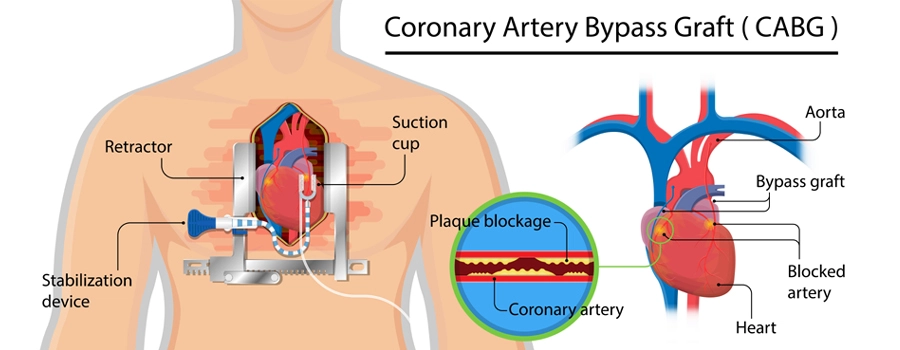
Bypass surgery is a surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD). In this condition, the blood vessels that supply oxygen to the heart become narrowed or blocked. This narrowing can lead to chest pain (angina) or heart attacks.
During the surgery, a surgeon creates new pathways for blood to flow to the heart muscle by using healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body or artificial grafts. By doing this, the surgery bypasses the blocked or narrowed arteries, allowing the blood to reach the heart muscle more easily.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhat is Open Heart Surgery?
Open heart surgery is used to treat blockages in the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. The surgery involves creating a new path for blood to flow around the blocked or narrowed artery using a healthy blood vessel.
This healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of the body, such as the chest, leg, or arm. This new blood vessel is called a graft. The surgery is called open because the surgeon has to open the chest and temporarily stop the heart to perform the procedure.
Different Types of Heart Bypass Surgery
There are different types of heart bypass surgeries depending on how many arteries are blocked and need to be bypassed. The most common types are:
- Single bypass surgery : If one artery is blocked, one graft is used to avoid it.
- Double bypass surgery : If two arteries are blocked, two grafts are used to bypass them.
- Triple bypass surgery : In this procedure, three arteries are blocked, and three grafts are used to bypass them. It is also known as 3-bypass surgery.
- Quadruple bypass surgery : In Quadruple bypass surgery, if four arteries are blocked, four grafts are used to bypass them. It is also called 4-bypass surgery.
- Quintuple Bypass Surgery : In this procedure, five grafts are utilised to bypass five blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It is also known as 5-bypass surgery.
- Sextuple Bypass Surgery : Here, six grafts are created to bypass six blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It is also known as 6-bypass surgery.
Difference Between Bypass Surgery and Open Heart Surgery
The major difference between bypass and open heart surgery is that surgery procedure. In contrast, open heart surgery is a general term that covers many different procedures, including bypass surgery on the heart.
| Open Heart Surgery | Bypass Surgery |
|---|---|
| Open heart surgery refers to any surgery that involves opening the chest and exposing the heart. | Bypass Surgery or Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is a procedure that restores blood flow to the heart when the coronary arteries are blocked or narrowed. |
It may be done to repair or replace a damaged heart valve by:
|
The surgeon takes a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, such as the leg or chest, and attaches it to the heart, bypassing the blocked artery. |
| Heart surgery is one of the most common types of open heart surgery, but not all open heart surgeries are bypass procedures. | It creates a new route for oxygen-rich blood to reach the heart muscle. |
What is the Bypass Surgery Procedure?
CABG or coronary surgery, is a sophisticated and life-saving surgical technique that treats CAD by making new routes for blood to reach the heart muscle. Here is a detailed overview of the bypass surgery procedure;
- Anesthesia : The patient is put under general anesthesia for comfort and safety.
- Incision : A vertical incision in the chest is made, and the sternum is divided to access the heart.
- Graft Harvesting : Healthy blood vessels (grafts) are taken, typically from the leg or chest.
- Bypassing Arteries : Grafts are attached, rerouting blood flow around blocked coronary arteries.
- Restarting the Heart : The heart is restarted, resuming normal function.
- Closing the Chest : The sternum is closed, and the chest incision is sutured.
Patients usually spend several days in the hospital for recovery and post-operative care, with the full recovery period varying from person to person.
Precautions Before Bypass Surgery
- Quit smoking right away if you do, as it can raise the chances of infection and problems.
- Talk to the surgeon about which drugs to keep or stop taking, especially those that can alter blood clotting, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or some supplements.
- When you return home, have someone with you, as you will need assistance with food and chores for four to six weeks.
- Don’t eat or drink anything after midnight on the night before surgery, as this can avoid nausea and vomiting during and after the surgery.
- Follow any other directions given by the doctor or care team, such as doing all necessary tests by the due date, resting and eating protein-rich foods, and packing a bag with essential items for the hospital stay.
Precautions After Bypass Surgery
- Strictly follow the doctor’s instructions and take the medications as prescribed.
- Do breathing and coughing exercises for 4 to 6 weeks to avoid lung infections.
- Walk two to three times a day and slowly increase the time and intensity of physical activity.
- Eat a diet that is good for the heart, low in saturated fat, salt, and sugar, and high in fibre, fruits, and vegetables.
- Keep a healthy body weight and prevent obesity.
- Stop smoking and stay away from secondhand smoke.
- Manage high blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Lower stress and practice relaxation methods such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Don’t remove, scrub, rub, or apply lotion or powder on the incisions until they heal fully.
- Don’t swim, take baths, or expose the incisions to sunlight until they recover fully.
- Don’t lift heavy objects, drive, or do hard activities for at least six weeks after the surgery.
- Get medical help if you have chest pain, shortness of breath, fever, bleeding, infection, or other problems.
What is the Cost of Bypass Surgery?
The cost of heart surgery in India varies depending on factors such as:
- Geographical location
- The hospital
- The surgeon’s fees
- Type of graft used
- The patient’s overall health.
The average cost of heart surgery in India is approximately INR 95,000 to 4,50,000. However, the total expense may vary depending on conditions such as:
- The number of arteries that need to be bypassed
- The type of graft used (artery or vein)
- The method of surgery (on-pump or off-pump)
- The duration of hospital stay and recovery
- The complications and risks involved
- The insurance coverage and medical tourism options
India has gained recognition as a destination for medical tourism due to its quality healthcare services and affordability. The cost of heart surgery in India is significantly lower compared to many Western countries.
Patients worldwide often travel to India to receive high-quality medical care at a fraction of the cost they would incur in their home countries.
What is the Recovery Procedure After Bypass Surgery?
The recovery time varies from person to person, but most patients can expect to spend several days in the hospital. During this time, they are closely monitored for any complications.
The complete recovery process may take several weeks to a few months, and it involves;
- Cardiac rehabilitation
- Dietary modifications
- A gradual return to normal activities.
However, some general guidelines for the CABG surgery recovery time process are:
Hospital Stay (5 to 7 days)
The patient is closely monitored for complications and receives medications and treatments. Tubes and wires are removed before the patient leaves the hospital.
Home Recovery (7 to 10 days)
The patient follows the healthcare team’s instructions, such as:
- Taking medications
- Changing dressings
- Checking for infection
- Avoiding strenuous activities
The patient also makes lifestyle changes, such as
- Quitting smoking
- Eating healthy
- Managing stress
- Controlling blood pressure
- Cholesterol
- Blood sugar levels
The patient does not drive, lift heavy objects, or have sexual intercourse for 4 to 6 weeks.
Cardiac Rehabilitation (for several weeks or months)
- The patient joins a program with supervised exercise, education, counselling, and support.
- It helps the patient recover physically and emotionally, improve fitness, reduce future heart risk, and enhance quality of life.
Full Recovery (12 weeks or longer)
- The patient follows up with the cardiologist regularly and reports any new or worsening symptoms.
- The patient continues to take medications and follow lifestyle modifications.
What are the Dietary Considerations to Follow After Bypass Surgery?
Following CABG surgery, patients must pay attention to their diet. Foods to avoid after coronary bypass surgery include:
- High-fat foods
- Processed meats
- Full-fat dairy products
- High-sodium foods
- Sugary foods
- Beverages
- Hydrogenated and trans-fat products
- Excessive caffeine consumption
- Avoid alcohol, such as beer, wine, liquor, and cocktails.
A heart-healthy diet is typically recommended to maintain cardiovascular health that is rich in:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
To maintain a healthy diet after CABG surgery, one should follow these guidelines:
- Eat healthy foods low in fat, salt, sugar, and refined grains and high in fibre, protein, and omega-3s.
- These foods will help your body heal and prevent complications.
- Drink enough fluids, but not with meals, to avoid dehydration and dumping syndrome.
- Eat small, frequent meals, limit portions, and take supplements as prescribed.
In conclusion, bypass surgery or CABG is a critical medical intervention for those with coronary artery disease. Understanding the procedure, costs, risks, and recovery process is important for individuals considering this surgery.
Whether in the United States, India, or elsewhere, the decision to undergo CABG surgery should be carefully considered and made in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Ready to take control of your health journey? Book your appointment now and start your path towards wellness today!
Book an AppointmentFrequently Asked Questions
Bypass surgery, commonly known as coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, is one medical procedure to improve heart blood flow. This treatment is usually performed on patients with limited or obstructed coronary arteries, which can impede oxygen and blood flow to the heart muscle.
During the procedure, your blood may be diverted to a heart-lung bypass machine. This machine circulates blood and oxygen throughout your body, taking over your heart and lungs.
The average length of a coronary artery bypass graft procedure is 3 to 6 hours. However, the number of blood vessels being attached will determine how long it takes.
It will take you between six and twelve weeks to fully recover once you are released from the hospital.
Medicover hospitals provide international-standard patient-centric care for heart bypass surgeries in India, with some of the top cardiologists.
