What is Osteomyelitis?
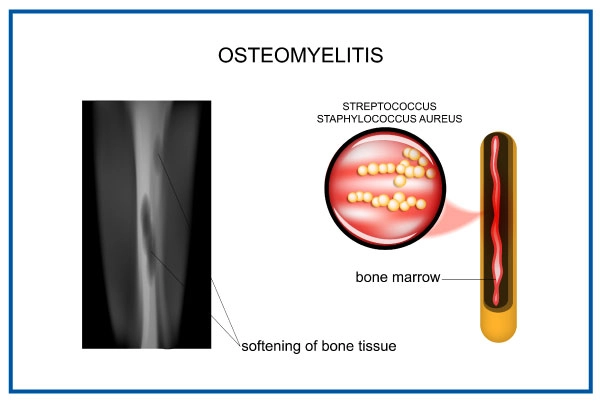
Osteomyelitis (OM) is a bone infection. It is an inflammation or swelling of bone tissue. The infection can spread to a bone by spreading through the blood circulation or from nearby infected tissues. Bone infection can also occur if an injury exposes the bone to germs.
Osteomyelitis can either be acute (of recent onset) or chronic (longstanding). There can be numerous causes of osteomyelitis, which can affect both children and adults.
Types of osteomyelitis:
Acute osteomyelitis
- Haematogenous osteomyelitis : Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis is a common bone infection. It usually affects boys and is generally seen in children. Acute osteomyelitis occurs in areas of high metabolic activity and often infects the distal femoral and proximal tibial metaphysis.
- Direct inoculation osteomyelitis : It is an infection of the bone caused due to inoculation of organisms from trauma, infection or from sepsis initiated by a surgical procedure.
Chronic osteomyelitis:
This type of infection fails to respond to treatment and reappears to stay for a long time. Often, chronic osteomyelitis is polymicrobial, indicating the involvement of more than one infectious agent. It causes bone pain and Brodie's abscess (chronic pyogenic osteomyelitis).
Osteomyelitis symptoms:
The osteomyelitis symptoms include:
- Localised bone pain
- Excessive sweating
- Decreased movement of the affected body part
- The overlying skin patch may be inflamed and red
- Accumulation of pus
- Muscle cramps
- Sudden weight loss
- General malaise
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Chills
When to see a doctor?
Consult your doctor if there is worsening bone pain accompanied by fever. If you notice signs and symptoms of an infection because of a medical condition or a recent operative procedure or injury, book an appointment with a doctor.
Consult our orthopaedic doctors or general physicians for more information and adequate treatment for osteomyelitis.
Osteomyelitis Causes and risks
Osteomyelitis is caused when bacterial infection from nearby infected tissue or an open wound enters the bloodstream and settles in bone, where they grow. Staphylococcus aureus bacteria is responsible for causing this bone infection. Rarely, a fungus or other germ may also cause osteomyelitis.
Risk factors
Bacteria can attack a bone in a variety of ways, such as:
Following are the risk factors for getting osteopenia-
- Blood circulation : Microorganisms from other parts of the body like the lungs in case of pneumonia or from the bladder in a urinary tract infection can enter the bloodstream and pass on to a weakened spot in a bone.
- Injuries : Severe cuts and puncture wounds can introduce pathogens inside the body. If an injury becomes infected, the bacterial germs can advance to a nearby bone. Osteomyelitis can also occur if a severely broken part of a bone sticks out through the skin.
- Surgery : Surgical procedures to repair bone fractures or to replace worn joints can facilitate microorganisms to penetrate a bone. Implanted orthopaedic devices are a risk factor for osteomyelitis.
Osteomyelitis Risk factors include:
The risk factors that may escalate a person’s susceptibility to osteomyelitis are:
- Cancer
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Long-term skin infections
- Poor blood circulation (arteriosclerosis)
- Immune deficiency disorders
- The implantation of prosthetic joints
- Intravenous drug use
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Excessive alcoholism
- Smoking
- HIV or AIDS
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Osteomyelitis Complications
To prevent complications, starting an early treatment, including antibiotic therapy, is necessary. Few complications can arise with untreated or inadequately treated osteomyelitis; they are as follows:
- Brodie's abscess
- Osteonecrosis (bone death)
- Soft tissue inflammation (cellulitis)
- Septicaemia (Sepsis)
- Chronic infection with no response to treatment
- Pathological fractures
- Bone deformity
- Systemic infection
- Squamous cell carcinoma (Skin cancer)
- Sinus tract formation
- Amyloidosis (rare)
Osteomyelitis Diagnosis and Treatment
The orthopaedic doctor will enquire about the patient's medical history and perform a physical examination to diagnose osteomyelitis symptoms.
The doctor may examine the area around the affected bone for any inflammation or tenderness and may recommend a combination of diagnostic tests to determine the condition:
- Blood tests include: Complete blood count (CBC): A complete blood count (CBC) is a blood test to examine the general health and detect various disorders, including infection, anaemia and leukaemia. It’s done to evaluate for increased white blood cells (WBCs) that may indicate an infection.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or Sed rate: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate or sed rate is a blood test that identifies inflammation in the body. The ESR test checks the rate of fall (sedimentation) of RBCs for a given blood sample in a test tube. Increased ESR rate indicates inflammation.
- C-reactive protein (CRP): A c-reactive protein test finds the level of c-reactive protein (CRP) in the blood. The CRP blood test aids in finding out bacterial infections, osteomyelitis infection and inflammation in the body.
- Blood culture test: It is a blood test that looks for germs (such as bacteria or fungi) in the blood.
- Needle aspiration or bone biopsy: Bone biopsy helps for a final diagnosis by separating pathogens directly from the bone lesion. It is a procedure in which bone samples are removed. This is done with the help of a small needle introduced into the affected bone part to determine the presence of cancer or other abnormal cells.
- X-ray test: It is a test to examine internal organs of the body particularly bones and joints. X-rays can reveal bone damage.
- Bone scans or Bone Scintigraphy: A bone scan is a type of nuclear radiology procedure to investigate the bone condition. It is done to identify any chemical and physical changes in the bone and to detect and assess bone infections, for example, osteomyelitis.
- Computerised tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan is a medical imaging procedure that uses computers and rotating X-ray machines to produce images of the body's internal organs. The scan is useful for diagnosing infections like osteomyelitis.
- Magnetic resonance MRI scan: It is a medical imaging diagnostic tool that uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to produce clear pictures of the structures inside the body. It is useful to diagnose osteomyelitis.
- Ultrasound (USG) scan: The scan uses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the body's internal structures. The USG scans are useful for diagnosing acute osteomyelitis.
Osteomyelitis Treatment
Osteomyelitis treatment options vary from person to person and the severity of the condition. The treatment of osteomyelitis aims to cure bone infection and reduce any long-term complications. Treatment may include:
- Medicines: A hospital stay may be required, and the patient will be given intravenous (IV) antibiotics. After that, oral antibiotic medications may be prescribed for several weeks. Chronic osteomyelitis may require long-term medications.
- Surgery: Osteomyelitis surgery is done when antibiotics cannot cure the bone infection. The surgery may be needed to drain the infected fluid, remove necrosed bone tissue, restore blood flow to the bone, take out any foreign objects or amputate the limb.
- Pain management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed to treat pain and inflammation.
- Bed rest:The patient may need to take bed rest to limit movements of the affected area and to avoid pain.
Dos and Don’ts
Follow the below-mentioned Do’s and Don’ts to prevent osteomyelitis and its complications. It is a bone infection, and the source of the blood infection is usually Staphylococcus aureus. It is mainly found in smokers, diabetes or kidney failure patients.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Take rest | Ignore osteomyelitis symptoms |
| Keep diabetes under control | Gain weight |
| Eat healthy food | Smoke and consume alcohol |
| Prevent falls | Do strenuous physical activities |
| Regular health check-up | Eat processed and junk foods |
Osteomyelitis symptoms include fever, fatigue, inflammation and redness in the affected bone area. Its treatment involves medications, pain relievers, bed rest and surgery.
Osteomyelitis Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover hospitals, we have the most experienced and trusted medical team consisting of general physicians and orthopaedic doctors who provide the best management for osteomyelitis. We are dedicated to providing excellent healthcare services to our patients holistically. Our team adopts a multidimensional approach to managing bone infection and related complications with utmost care and the active participation of medical experts from different specialities. We ensure world-class healthcare facilities in all our departments at affordable prices to ensure high-quality treatment outcomes.
