Atherosclerosis
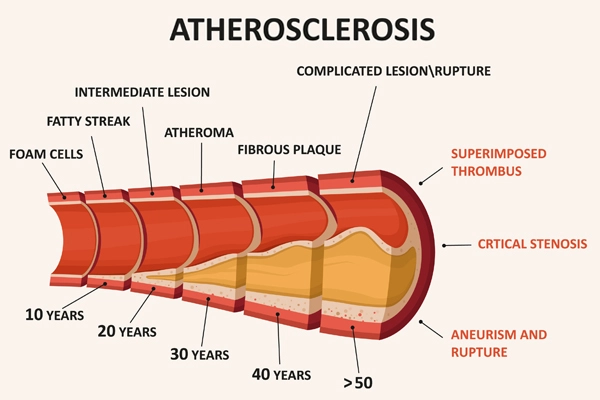
Atherosclerosis is a condition when fats, cholesterol, and other chemicals build up on the walls of the arteries. This accumulation is called plaque. The arteries may narrow as a result of the plaque, obstructing the blood flow. A blood clot can result if the plaque bursts.
Although Atherosclerosis is commonly associated with the heart, it can affect arteries throughout the body. It can be treated, managed and prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis:
- Mild Atherosclerosis does not have more symptoms and they usually don't appear until an artery has constricted or clogged to the point where it can't allow enough blood flow to your organs and tissues. A blood clot can sometimes totally block the blood flow or even break apart, resulting in a heart attack or stroke.
- Depending on which arteries are compromised, the symptoms of moderate to severe Atherosclerosis vary.
- If you have atherosclerosis in your heart arteries (angina), you may have symptoms such as chest pain or pressure.
- If plaque formation is in the arteries leading to the brain, one may experience sudden numbness or weakness in arms or legs, difficulty speaking or slurred speech, temporary loss of vision in one eye, and other signs and symptoms of Atherosclerosis. These symptoms indicate a transient ischemic attack (TIA), which can lead to a stroke if left untreated.
- If one has atherosclerosis in the arteries of arms and legs, one may experience indications or symptoms of peripheral artery disease, such as leg pain when walking (claudication) or low blood pressure in an affected limb.
- High blood pressure or renal failure can result from Atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to the kidneys.
When to see a doctor?
Consult your doctor if you suspect you have Atherosclerosis. Keep an eye out for early signs of poor blood flow, such as chest pain (angina), limb pain, and numbness.
Atherosclerosis can be stopped from worsening, and a heart attack, stroke, or another medical emergency can be avoided with early detection and treatment. Get the best treatment for Atherosclerosis from the best Cardiology doctors at Medicover Hospitals.
Causes of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic, slow-moving illness that can start early in your childhood or adulthood. Although the specific cause of Atherosclerosis is uncertain, it is thought to begin with damage or injury to the inner layer of an artery. The following factors may contribute to the damage:
- Blood pressure that is too high
- High Cholesterol levels
- High blood triglycerides, a form of fat (lipid).
- Tobacco use (smoking and other forms)
- Obesity, diabetes, or insulin resistance
- An unknown cause or disorders, including arthritis, lupus, psoriasis, or inflammatory bowel disease cause inflammation.
Blood cells and other chemicals clump at the injury site and can build up in the inner lining of the artery if the inner wall is injured.
At the injury site, fatty deposits (plaque) formed from cholesterol and other cellular products solidify over time, restricting the arteries. Organs and tissues connected to clogged arteries receive insufficient blood to operate correctly.
Fragments of the fatty deposits may eventually break off and enter your bloodstream.
Furthermore, the plaque's smooth lining may tear, releasing cholesterol and other chemicals into your bloodstream. This can result in a blood clot, which can stop blood flow to a specific portion of your body, such as when blood flow to your heart is obstructed, resulting in a heart attack. A blood clot can also spread to other places in your body, obstructing blood flow to an organ.
Risk factors of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the hardening of the arteries over time. Aside from age, the following factors may raise your risk of Atherosclerosis:
- High Blood pressure
- High Cholesterol levels
- High C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Apnea (sleep deprivation)
- Tobacco usage, including smoking and chewing
- A family history of heart disease
- Lack of physical activity
- Unhealthy eating habits
Prevention of Atherosclerosis
The same healthy lifestyle adjustments that are advocated for treating Atherosclerosis are also beneficial in preventing it. These are some of them:
- Smoking should be avoided.
- Consumption of nutritious foods should be encouraged
- Regular exercise is essential.
- Keeping a healthy weight is important.
- Blood pressure should be checked and maintained at a healthy level.
- Keeping healthy cholesterol and blood sugar levels is important.
Just remember to take things one step at a time and consider what lifestyle adjustments you can handle in the long run.
Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis
Your doctor will do a physical examination and inquire about your personal and family medical history. When your doctor listens to your arteries with a stethoscope, they may detect a whooshing sound (bruit). Your doctor may recommend one or more tests such as -
- Blood tests: The doctor will order blood sugar and cholesterol tests to assess blood sugar and cholesterol levels. High blood sugar and cholesterol levels cause atherosclerosis. A C-reactive protein (CRP) test may also be performed to look for a protein linked to artery inflammation.
- ECG or EKG: An EKG (electrocardiogram) might be recommended in which electrical signals in the heart are recorded.
- Stress test with exercise: This test may be recommended if signs and symptoms occur most frequently during activity. While attached to an ECG, you'll walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary cycle. This exercise stress test can uncover heart abnormalities that might otherwise go undetected. If you are unable to exercise, a medicine that replicates the effects of exercise on your heart may be prescribed.
- Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to show how well blood flows through the arteries as your heart beats. Exercise stress testing is sometimes used in conjunction with it.
- Ultrasound with Doppler: A sophisticated ultrasound instrument (Doppler ultrasound) may be used by the doctor to monitor blood pressure at numerous places along your arm or leg. These readings can help to evaluate the severity of any blockages in arteries, as well as the rate at which blood flows through them.
- Ankle-brachial index (ABI): The ankle-brachial index is a measurement of the distance between the ankle and the wrist. This test can determine if the arteries in the legs and feet have Atherosclerosis. Your doctor compares the blood pressure in your ankle to the blood pressure in your arm during an ABI test. Peripheral vascular disease, which Atherosclerosis mainly causes, can be identified by an abnormal difference.
- Catheterization and angiography of the heart: This test can reveal if your coronary arteries are restricted or clogged. During this treatment, a doctor inserts a tiny catheter into a blood vessel and into the heart. The catheter is dipped in dye. The arteries become visible on X-ray when the dye fills them, revealing areas of obstruction.
- Calcium scan of the coronary arteries: This standard test, often known as a heart scan, uses computed tomography imaging to obtain detailed images of the heart. Calcium deposits in the arterial walls might be seen. The test results are reported as a score. The higher the score when calcium is present, the greater your risk of atherosclerotic heart disease
- Other types of imaging examination: Your doctor may also study your arteries using MRA or PET. These tests can detect large artery hardness and narrowing, as well as aneurysms.
Treatment of Atherosclerosis :
Lifestyle modifications, including eating a balanced diet and exercising, are the first line of defence against Atherosclerosis. However, medicines or surgical procedures may be required in some cases.
Medications of Atherosclerosis
There are a variety of medications available to help delay or even reverse the consequences of Atherosclerosis. The following are some of the drugs that are used to treat Atherosclerosis:
- Statins and other cholesterol medications
- Blood thinners
- Blood pressure medications
Surgical or non-surgical techniques
A more aggressive approach to treating Atherosclerosis is sometimes required. The doctor may consider one of the following surgical procedures if you have significant symptoms or a blockage:
- Stent implantation and angioplasty: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a treatment that helps unblock a clogged or blocked artery. A catheter is inserted into the affected artery by your doctor. A second catheter is passed through the first catheter to the blockage, with a deflated balloon on its tip. The balloon is inflated by your doctor, which widens the artery. To aid in the opening of the artery, a mesh tube (stent) is frequently left in place.
- Endarterectomy: Plaque buildup on the walls of a restricted artery may require surgical removal. When the treatment is performed on the neck arteries
- Fibrinolytic therapy: If a blood clot is blocking an artery, your doctor may use a clot-dissolving medicine to break it apart.
- Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to show how well blood flows through the arteries as your heart beats. Exercise stress testing is sometimes used in conjunction with it.
- Bypass surgery for the coronary arteries: Your doctor uses a healthy blood vessel from another region of the body to create a bypass around the blocked artery, diverting blood flow. A graft consisting of synthetic material is sometimes used as a bypass.
Lifestyle changes and self-care
- Quit smoking: Smoking causes artery damage. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to keep your arteries healthy and avoid the consequences of Atherosclerosis.
- Exercise: Regular exercise improves blood flow, decreases blood pressure, and lowers your risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease-related diseases. Exercise for at least 30 minutes.
- Lose weight and stay healthy: Losing even a few pounds if you're overweight can lower your chances of high blood pressure and high cholesterol, two important risk factors for Atherosclerosis.
- Consume nutritious foods: A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as refined carbs, sweets, saturated fat, and sodium, will help you manage your weight, blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. Instead of white bread, try using whole-grain bread. Snack on an apple, a banana, or carrot sticks. Use nutrition labels as a guide to keep your salt and fat intake in check. Reduce or eliminate sugar and sugar substitutes and replace them with monounsaturated fats like olive oil.
- Do not take tension: As much as possible, reduce your tension. Use healthy stress-management practices like muscular relaxation and deep breathing.If you have high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, or any chronic disease, work with your doctor to control it and improve your general health.
Dos and Don’ts
A person with Atherosclerosis has to follow sets of do’s and don’ts to manage it and the related symptoms. Lifestyle changes matter a lot in this condition and one should be strict about adhering to healthy habits.
Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover Hospitals, we have the most trusted team of doctors and medical experts who are experienced in providing excellent healthcare services to the patients with compassion and care. Our diagnostic department is equipped with modern technology and equipment to conduct the tests required for the diagnosis of Atherosclerosis, based on which a dedicated treatment plan is designed. We have an excellent team of Cardiologists and cardiac surgeons who diagnose and treat this condition with utmost precision that brings successful treatment outcomes.
Citations
https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJM198602203140806
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1471491402023857
https://www.jstor.org/stable/26059682
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/hc0902.104353
https://www.nature.com/articles/ni.2001
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.179705
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4258672/