What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a common non-destructive gingival disease. It causes inflammation of the gums and is considered a mild form of gum disease (periodontal disease). It's important to take gingivitis seriously or else it can cause serious dental problems like periodontitis and loss of all the teeth. It is possible to cure or reverse it with timely dental treatment.
Types
Gum diseases are divided into two different types
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
Gingivitis Symptoms
The symptoms of gingivitis are
- Swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
- Sore gums
- Red gums
- Halitosis or Bad Breath
- Gum recession
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods
- Pain while chewing foods.
When to see a doctor?
Follow your regular dental checkups. If you detect any gingivitis symptoms, make a dental appointment with a dentist as soon as possible. As this gum disease can be cured or reversed, it is crucial that its symptoms are not ignored and its progression to periodontitis is stopped with timely dental treatment.
Get the best treatment for gingivitis from our dentists at Medicover Hospitals.
Causes of Gingivitis
The causes of gingivitis include
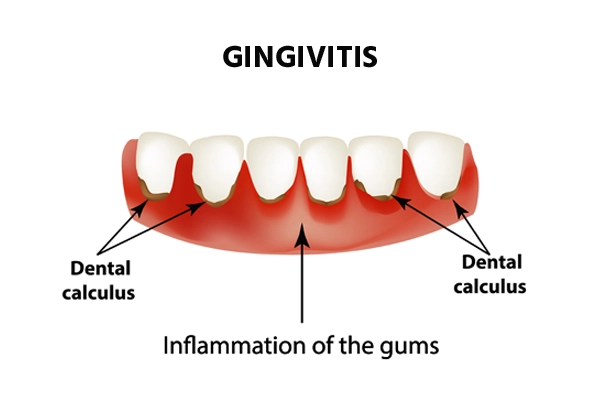
The most common cause of gingivitis (gum inflammation) is poor oral health. It facilitates the build-up of plaque on the various surfaces of teeth, resulting in inflammation of the surrounding gum tissues. The development of gingivitis includes the following steps
- Dental plaque on the teeth's surfaces : Dental plaque is an invisible, sticky substance consisting of bacteria that forms on the surfaces of the teeth. The main cause of gum disease is the development of plaque around the gum line. Bacterial plaque, if left uncleaned, can turn into a hard, mineralised substance called dental calculus (or tartar).
- Hardening of plaque to form tartar : Dental plaque, if not cleaned, hardens into tartar, also called dental calculus. The calculus, containing a lot of bacteria, is difficult to remove and needs to be cleaned by a dental hygienist or a periodontist. If left unchecked, it can cause gingival problems and tooth loss.
- Inflammation of gingiva (gingivitis) : The prolonged presence of plaque and tartar on the tooth surfaces triggers continuous gingival tissue irritation, which in turn leads to gum inflammation (gingivitis). During this process, the gums become swollen, tender, and bleed easily. If not treated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis and also cause tooth decay.
Gingivitis Risk factors
The risk factors for gingivitis are
- Poor oral hygiene
- Chewing tobacco
- Smoking
- Few medications and conditions that dry the mouth
- Mouth breathing during sleep
- Orthodontic braces
- Old age
- Genetic factors
- Stress
- Vitamin C deficiency
- Improper dental restorations cause gum irritation.
- Certain conditions can cause low immunity, such as leukaemia, HIV/AIDS and cancer treatment.
- Hormonal changes related to pregnancy, menstrual cycle or use of contraceptive pills
- Certain viral and fungal infections
- Mental health issues like depression
Prevention of Gingivitis
It is possible to prevent gingivitis by practicing good oral health care habits and getting regular dental check-ups. Follow the below-given oral hygiene tips to stay away from dental problems.
- Brush teeth for at least two minutes twice a day - morning and before bedtime.
- Use mouthwash
- Drink more water
- Use no tobacco products.
- Quite smoking
- Limit intake of alcoholic beverages
- Thoroughly clean the tongue.
- Do flossing once a day
- Replace the toothbrush every three to four months.
- Eat a healthy, fibre-rich diet and reduce intake of sugary foods and drinks.
- Go for regular dental check-ups
- Follow the correct brushing techniques.
Diagnosis of Gingivitis
Make a dental appointment if gingivitis symptoms are present. Before proceeding with the dental treatment, the dentist will take a medical history of the patient and ask about the eating habits and general health.
During the dental examination, the dental doctor will examine the mouth (oral cavity) of the patient for any dental caries, plaque accumulation, and gum problems.
The doctor will use a periodontal probe to check for deep gum pockets below the gum line. In the case of good gum health, the pocket depth is nearly 1 to 3 millimetres (mm). Gum pockets deeper than 4 mm may point to gum disease.
Dental X-rays test help to detect tooth decay and changes in bone structure due to gum problems. With dental X-rays, the dentist can decide the most appropriate dental treatment for the patient.
The dentist may also recommend some blood tests to determine the general health of the patient. For example, more precaution is needed for diabetic patients as they have a slow wound healing process.
Treatment of Gingivitis
Early dental treatment reverses symptoms of gingival disease and prevents its progression to dental periodontitis. It includes
- Dental cleaning : A dental hygienist or a dentist will perform a dental procedure known as scaling and root planning to remove dental plaque, tartar, stains, and other stuck food particles that trigger dental caries.
- Dental restoration : It is done to correct misaligned teeth or poorly fitting crowns, bridges, or other dental restorations that are causing irritation to the gingival tissues and causing plaque buildup. Adopt healthy eating habits such as avoiding eating sticky and sugary foods and practising home dental hygiene to keep dental problems at bay.
Gingivitis Dos and Don’ts
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums. Its symptoms include gum swelling and pain, and easy bruising during tooth brushing. Ignoring its symptoms can lead to periodontitis and also affect the overall health of the person. Its treatment includes dental cleaning involving scaling and root planning and maintaining good oral hygiene.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Maintain good oral health | Smoke and chew tobacco products. |
| Stick to proper tooth brushing techniques. | Compromise with brushing your teeth regularly |
| Use fluoride toothpaste | Take much sugary foods and soda beverages. |
| Regular dental check-ups | Ignore the treatment if you are diabetic |
| Replace your toothbrush every 2-3 months. | Eat too hot or too cold food items. |
Follow the do’s and dont’s for gingivitis to prevent gingival diseases and other serious dental issues. Gingivitis is a reversible condition, so treating it on time can prevent serious dental problems.
Gingivitis Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover hospitals, we have the most reliable dental team, comprising of different dental specialists, who design a personalized treatment pathway for each patient. We adopt a multi-dimensional approach to treating gingival diseases with the active participation of dental doctors of different specializations to address dental diseases for holistic recovery and wellness. We aim to provide the best treatment outcomes and a satisfactory patient experience at a highly affordable cost.
Citations
GingivitisGingivitis and periodontitis: Overview
Gingivitis
Gingivitis
