Periodontitis Treatment: Symptoms & Causes, Its Stages
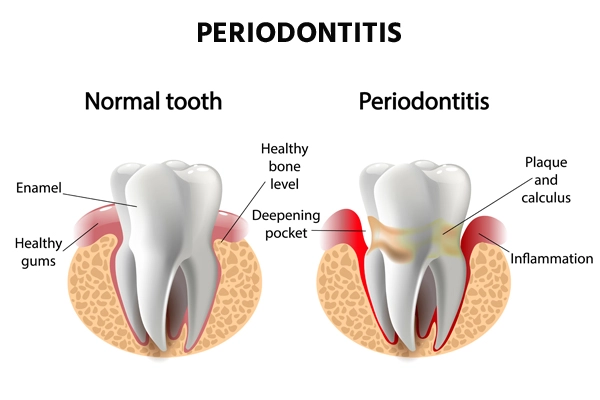
Periodontitis, also called dental pyorrhea, is a gum disease. It is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the oral mucosa around the teeth and is caused by bacterial microorganisms. It is a gum infection where the gums pull away from the teeth, resulting in bone loss, loosening of teeth, or complete loss of teeth.
The early stage of periodontal disease is known as gingivitis, in which the gums can get swollen, red, and sensitive with gum bleeding. Gingivitis further develops into periodontitis (pyorrhea disease). This dental problem is mostly seen in adults.
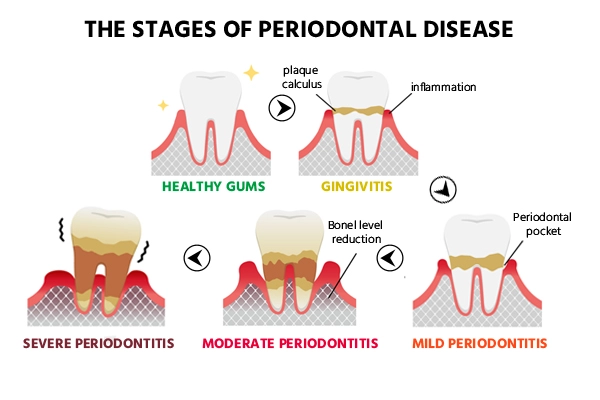
Periodontal disease can be divided into four stages -
- Periodontitis stage 1 - Initial stage with gum swelling
- Periodontitis stage 2 - Moderate with swelling and gum bleeding
- Periodontitis stage 3 - Severe with chances of tooth loss
- Periodontitis stage 4 - Severe with loss of all the teeth
Symptoms of periodontal disease
Periodontitis symptoms include -
- Bad breath or halitosis
- Gingival recession
- Swollen gums
- Bleeding gums
- Discolouration of gums: - Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums
- Tender gums
- Lose teeth
- Tooth sensitivity
- Deep pockets, known as periodontal pockets, are formed between the gums and the teeth.
- Pus around the teeth and gums
- Difficulty to chew food
- Spitting out blood when brushing or flossing the teeth
When to see a dentist?
Follow your regular dental checkups. If you detect any periodontal disease symptoms, make a dental appointment with a periodontist as soon as possible. Early periodontitis treatment improves your chances of reversing the damage from this gum disease.
Get the best treatment for periodontitis from our Dentists at Medicover Hospitals.
Causes and Risks
The causes of periodontal disease include:
- An accumulation of bacterial micro-organisms in the mouth can give rise to periodontitis. The oral cavity consists of many healthy bacteria. But certain bacteria get mixed with mucus and other food substances to form a sticky film on the teeth's surfaces called dental plaque.
- Plaque can be easily removed by maintaining proper dental hygiene. But if teeth are not thoroughly cleaned, the dental plaque hardens and forms tartar (calculus). Only a dental doctor or dental hygienist can clean this tartar from the teeth.
- The buildup of plaque and tartar results in gingivitis (gum disease). It involves swelling and bleeding of the gums. It can be treated and reversed with dental treatment and by following good dental hygiene practices at home. If this gum disease is left untreated, it will eventually progress to periodontitis.
Risk factors -
Factors that can affect gum health and increase the risk of periodontitis include-
- Gingivitis
- Bad oral care habits
- Smoking
- Chewing tobacco
- Hormonal changes in women (related to pregnancy or menopause)
- Obesity
- Vitamin C deficiency
- Genetics
- Certain drugs can give rise to dry mouth or gum problems.
- Certain conditions can cause low immunity, such as leukaemia, HIV/AIDS and cancer treatment.
- Some illnesses, such as, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, alzheimer's disease, osteoporosis, and Crohn's disease.
Prevention
It is possible to prevent periodontitis by practising good oral hygiene and getting regular dental check-ups.
Good oral hygiene - It includes -
- Brushing the teeth for at least two minutes twice daily (in the morning and before bedtime)
- Do flossing once a day
- Drink more water
- Use mouthwash to remove stuck food particles from the teeth and prevent bad breath.
- Eat a healthy diet and reduce intake of sugary food and drink
- Replace the toothbrush every three to four months.
Regular dental health check-up -
Visit your dentist or dental hygienist regularly every six to 12 months. A dental examination is important as it prevents future dental problems, treats tooth cavities thus saving the tooth and instructs about dental cleaning habits.
Diagnosis and Treatment
To determine whether you have periodontitis and how severe it is, your dentist may do the below things or advise a certain tests.
- The dentist will enquire about the medical history (any previous dental treatment), eating habits, and medications to identify any contributing factors causing teeth diseases
- The dentist will perform a thorough examination of the mouth teeth, and gums to look for plaque and tartar buildup and gum problems.
- The dental doctor will measure the periodontal pocket depth around each tooth with a periodontal probe to determine the presence of periodontal disease and how far it has progressed. Gum pockets deeper than 4 mm may point to periodontitis. Pockets with a depth of more than 5 mm are difficult to clean.
- Dental X-rays can help a dentist identify bone loss at an early stage, gum disease, and damage to the tooth structure.
Treatment
Periodontitis treatment may involve less invasive procedures if the gum infection is in its initial stage. It involves -
- Scaling: It is a common dental procedure to remove plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and below the gum line. It may be performed using handheld instruments such as a dental scaler and curette or, a laser or an ultrasonic device.
- Root planing: It involves a deeper cleaning with scaling of the root surface to smooth out the root surfaces.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics can help control gum infections. Topical antibiotics for periodontitis are applied in the space between the teeth and gums or into gum pockets after deep cleaning. They are available in gel, chip, and strip form. Oral antibiotics are used to prevent bacterial infections.
Surgical treatments -
In the case of advanced periodontitis, dental surgery may have to be done. It includes -
- Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery) - It is also known as gingivectomy or osseous surgery. It is a dental surgery to clean bacteria present in the space between the gums and teeth in the case of the advanced stage of periodontitis.
- Soft tissue grafts - It is done to halt gum recession and to correct the appearance of the gum line.
- Bone grafting - This procedure helps to repair, or rebuild, bones and prevent tooth loss. It also facilitates the regrowth of natural bone.
- Guided tissue regeneration - It promotes bone regeneration, prevents tooth loss, and helps to maintain the natural aesthetics of the gums and the teeth.
- Tissue-stimulating proteins - It involves applying a special type of gel to an infected tooth root. This gel stimulates the growth of healthy bone and gum tissue.
Dos and Don’ts
Periodontitis is a gum infection that causes inflammation of the soft gum tissue and results in damage to the tooth structure. It starts with the development of bacterial dental plaque found on the tooth surfaces. If it is left untreated in later stages, it can give rise to gingivitis, which will eventually progress into periodontal disease.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Maintain dental hygiene | Smoke or chew tobacco |
| Limit sugary and junk foods | Ignore brushing your teeth twice a day |
| Avoid smoking and chewing tobacco products. | Eat more sweet foods. |
| Frequent dental check-ups | Eat hot and cold food items together |
| Change your toothbrush every 2-3 months. | Ignore any underlying symptoms that needs a check-up |
Periodontitis Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover hospitals, we have the most reliable dental team, comprising of dental specialists and surgeons who design a personalized treatment pathway for each patient. We adopt a multi-faceted approach in managing periodontal problems with the active participation of dentists from different specializations to address teeth problems with a holistic approach for complete recovery and wellness. We aim to provide the best treatment outcomes and a satisfactory patient experience at a highly affordable cost.
Citations
Periodontal DiseasePeriodontal (Gum) Disease
Periodontal Diseases
Stages of gum disease
