What is Leukemia?
When the DNA of a single cell in the bone marrow changes (mutates), the cell can no longer grow or function normally; it is known as leukemia. It is a kind of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. The soft, spongy substance in the center cavity of all bones is called bone marrow. It's a small area where all the blood cells are produced, and nutrients are provided to help the healthy blood cells. But when these cells grow abnormally, it's known as Cancer.
It may spread throughout the body. This fast, out-of-control development of abnormal cells happens in the bone marrow of patients with leukemia. These cancerous cells subsequently spread throughout the body. Unlike other cancers, leukemia seldom forms a tumor (tumor) that may be detected on imaging tests like X-rays. It comes in a variety of forms. Some are more prevalent among youngsters, while others are more prevalent among adults. The type of leukemia patients have, and other factors influence the treatment.
Types of Leukemia
It is classified by how rapidly it progresses and the type of blood cell involved.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): AML is a fast-growing blood cancer where immature white blood cells multiply rapidly, crowding out healthy blood cells. Treatment includes aggressive chemotherapy and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation.
- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML): CML is a slow-progressing leukemia characterized by the overgrowth of myeloid white blood cells. It is often linked to the Philadelphia chromosome. Targeted therapies have revolutionized CML treatment.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): CLL is a slow-growing cancer that affects mature lymphocytes in the blood and bone marrow. It may not require immediate treatment but can be managed with therapies like chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted treatments when necessary.
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): ALL is a fast-progressing leukemia, especially common in children. It involves immature lymphocytes and requires immediate, aggressive treatment with chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and stem cell transplantation in some cases.
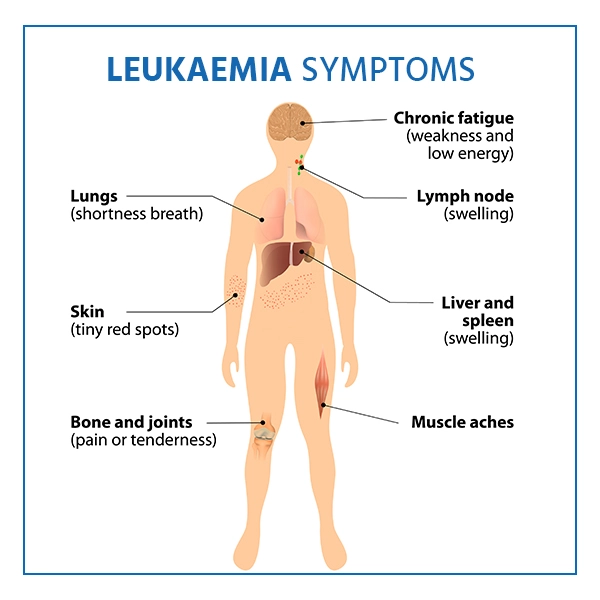
Leukemia Symptoms
Causes
While the exact cause of leukemia is unclear, certain risk factors have been identified, including radiation exposure, past cancer therapy, and being over the age of 65. Researchers are analyzing various combinations of genetic and environmental factors which are considered to be associated with leukemia and bone marrow cell mutation. Some of the factors are as follows:
Risk Factors
- A history of leukemia in the family
- Tobacco smoking which increases the risk of developing acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- A hereditary issue such as Down syndrome
- Myelodysplastic syndrome, sometimes called "preleukemia", which is a kind of blood disorder
- Past treatment of cancer with chemotherapy or radiation
Prevention
Making healthy choices can lower the risk of acquiring cancer in various ways. Some cancers can be discovered early when treatment is most successful. Vaccines (shots) can also help prevent a wide range of malignancies. The preventions are as follows:
- Breast, cervical, and colorectal cancers can all be detected early when therapy is most effective.
- Vaccines (shots) can also assist in lowering cancer risk. The HPV vaccine protects against the majority of cervical cancers and several other cancers.
- Making healthy choices, such as keeping a healthy weight, avoiding cigarettes, limiting alcohol use, and protecting your skin, can help reduce your risk of developing cancer.
How is Leukemia diagnosed
A doctor will begin by reviewing the patient's medical history and performing a physical examination. Physical examination is, however, not a trusted way to diagnose leukemia. Instead, the doctor will do diagnoses based on the following criteria:
- Blood tests: A complete blood count (CBC) looks at the number and maturity of different types of blood cells. A blood smear is used to look for abnormal or immature cells.
- Bone marrow biopsy: During a bone marrow biopsy, a long needle is used to collect marrow from the pelvic bone. It can tell a doctor what sort of leukemia someone has and how severe it is.
- Spinal tap: The removal of fluid from the spinal cord is known as a spinal tap. It can tell a doctor whether or not the leukemia has spread
- Imaging tests: CT, MRI, and PET scans can all be used to identify leukemia.
Leukemia Treatment
The form of leukemia, the amount to which it has spread, and the general health of the patient affect the leukemia treatment to be provided. The following are the most important treatment options:
- Chemotherapy: It is a leukemia treatment that uses medicines to eliminate cancer cells in the blood and bone marrow. The medication is easily accessible.
- Radiation: It employs high-energy X-rays to destroy or prevent the development of leukemia cells. It can be acquired all over the body or only in one place with many cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy or biological therapy: It is a biological treatment which assists the immune system in finding and fighting cancer cells. Drugs like interleukins and interferon can help the body's natural defenses against leukemia.
- Targeted treatment: It involves using drugs to stop cancer cells from growing by inhibiting specific genes or proteins. This treatment can halt the growth and multiplication of leukemia cells, cut off their blood supply, or kill them immediately.
- A stem cell transplant: In the bone marrow, a stem cell transplant replaces leukemia cells with new blood-producing cells. The new stem cells may originate from your own body or a donor. Chemotherapy in high dosages will kill the cancer cells in your bone marrow. The new stem cells will then be injected into one of the veins. They will mature into new, healthy blood cells.
- Surgery: The doctor may remove the spleen if it is loaded with cancer cells and pressing on other organs. The medical word for this leukemia treatment procedure is splenectomy.