Hip Replacement Surgery: What You Need to Know
Hip replacement surgery, also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a transformative medical procedure that offers renewed mobility and relief to those suffering from hip joint pain and dysfunction. This surgical intervention involves the replacement of a damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial joint, typically made from metal, plastic, or ceramic components.
Steps involved in Hip Replacement Surgery Procedure
During a hip replacement surgery procedure, a damaged or diseased hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint, also known as a prosthesis. The main goal of the surgery is to relieve pain, improve joint function, and enhance the patient's quality of life. Here's an overview of what happens during a hip replacement surgery:
- Anesthesia: Prior to starting the surgery, the patient is given anesthesia to ensure their comfort and pain relief throughout the procedure.The type of anesthesia used can vary, including general anesthesia (you are asleep) or regional anesthesia (numbing the lower part of the body).
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision over the hip joint. The size and location of the incision may vary based on the surgical approach and the patient's specific needs.
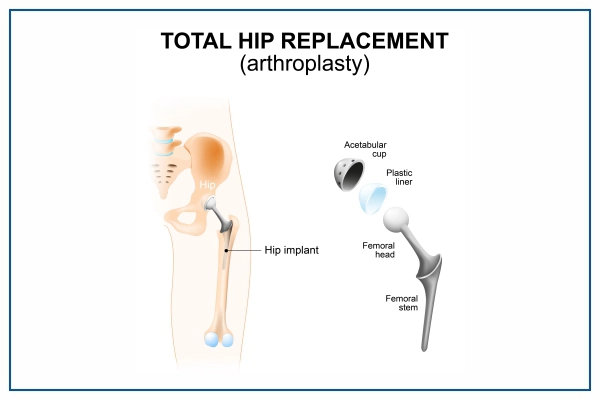
- Removal of Damaged Joint Components: The damaged or arthritic parts of the hip joint, including the ball (femoral head) and socket (acetabulum), are carefully removed.
- Preparation of the Bone: The remaining bone surfaces are prepared to accommodate the prosthetic components. This involves reshaping the femur (thighbone) to fit the femoral prosthesis and placing a socket implant in the acetabulum.
- Placing the Prosthetic Components: The prosthetic components are inserted into the prepared bone surfaces. The femoral component consists of a metal stem with a ball on top, while the acetabular component is a socket made of metal, plastic, or ceramic.
- Securing the Components: The prosthetic components are securely positioned within the bone using specialized surgical cement or through a technique called "press-fit," where the bone naturally grows into the prosthesis over time.
- Closing the Incision: After ensuring the proper placement of the components, the surgeon closes the incision using sutures or staples.
- Post-Operative Care: The patient is moved to a recovery area, where they are closely monitored as the effects of anesthesia wear off. Pain management and early mobilization are important aspects of the recovery process.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Following surgery, patients undergo a period of rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and function in the new hip joint.
Who will Treat for Hip Replacement Surgery Procedure
Hip replacement surgery is typically performed by an orthopedic surgeon who specializes in joint replacement surgeries. Orthopedic surgeons are medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis, treatment, and surgical management of musculoskeletal conditions, including issues related to joints, bones, muscles, and ligaments.
Here are the healthcare professionals involved in treating hip replacement surgery:
- Orthopedic Surgeon: An orthopedic surgeon is the primary specialist who performs hip replacement surgeries. They have the expertise to assess your hip condition, determine the need for surgery, and carry out the procedure.
- Surgical Team: A team of healthcare professionals, including surgical assistants, nurses, and anesthesiologists, supports the orthopedic surgeon during the surgery to ensure the procedure is safe and successful.
- Physical Therapist: After surgery, a physical therapist plays a crucial role in guiding your rehabilitation and helping you regain strength, mobility, and function in the newly replaced hip joint.
- Anesthesiologist: An anesthesiologist administers anesthesia to ensure your comfort and safety during the surgery.
- Medical Team: Your medical team may include your primary care physician or another specialist who diagnosed your hip condition and referred you to the orthopedic surgeon.
- Nurse Navigator: Some healthcare facilities provide nurse navigators who guide patients through the entire surgical process, offering information, support, and coordination of care.
Preparing for Hip Replacement Surgery
Preparing for hip replacement surgery involves several important steps to ensure that you are physically and mentally ready for the procedure. Proper preparation can contribute to a smoother surgery and a more successful recovery. Here's a guide on how to prepare:
-
Consultation with Your Surgeon: Schedule a consultation with the orthopedic surgeon who will be performing the hip replacement surgery. This is an opportunity to discuss your medical history, current health status, and any concerns you have.
-
Medical Evaluation: Undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation to assess your overall health. This may include blood tests, imaging scans, and other tests to ensure you are fit for surgery.
-
Medication Review: Inform your surgeon about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. Some medications may need to be adjusted before the surgery.
- Nutritional Preparation: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support your body's healing process.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated in the days leading up to the surgery.
- Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking before the surgery, as smoking can affect your healing and recovery.
- Weight Management: If you're overweight, losing some weight can help reduce stress on your new hip joint and enhance your surgical outcomes.
- Strengthen Muscles: Engage in gentle exercises recommended by your surgeon or physical therapist to strengthen the muscles around your hip joint. This can aid in your postoperative recovery.
- Preoperative Instructions: Follow any preoperative instructions provided by your surgeon. These may include guidelines for fasting before the surgery and medications to avoid.
- Arrange Transportation: Plan for transportation to and from the surgical facility, as you might not be able to drive immediately after the procedure due to anesthesia.
- Arrange Support: Enlist a family member or friend to provide support during your recovery period.
- Prepare Your Home: Make your home recovery-friendly by arranging a comfortable and easily accessible space with necessary items within reach.
- Discuss Anesthesia: Have a discussion with your anesthesiologist about the type of anesthesia to be used and any concerns you may have.
- Mental Preparation: Educate yourself about the procedure, potential outcomes, and the recovery process. Understanding what to expect can alleviate anxiety.
- Pack Essentials: Bring any required documents, identification, and essentials like comfortable clothing and personal items to the hospital.
Indications of Hip Replacement Surgery Procedure
Here are some common indications for hip replacement surgery:
- Osteoarthritis:Osteoarthritis is the most common reason for hip replacement surgery. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joint wears down over time, causing pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis:Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that can cause inflammation and damage to the hip joint, leading to pain and reduced function.
- Avascular Necrosis:Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to the hip joint is disrupted, causing bone tissue to die. This can lead to joint collapse and severe pain.
- Hip Fractures: Fractures of the hip joint, often due to trauma or falls, may require hip replacement surgery, especially if the fracture is severe and the joint cannot be effectively repaired.
- Hip Dysplasia: Hip dysplasia is a congenital condition where the hip joint doesn't develop properly. Over time, it can lead to pain and joint deterioration, necessitating surgery.
- Traumatic Arthritis: Traumatic arthritis can develop after a serious hip injury, causing ongoing joint pain and limited mobility.
- Other Arthritis Types: Other forms of inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis, can lead to hip joint damage and the need for a replacement.
- Bone Tumors: Tumors in the bone around the hip joint, whether benign or malignant, might require hip replacement surgery.
- Failed Previous Surgeries: If prior hip surgeries have not effectively addressed pain or mobility issues, a hip replacement may be considered as a last resort.
- Severe Pain and Loss of Function: When pain and limited mobility significantly affect the patient's quality of life and conservative treatments no longer provide relief, hip replacement might be recommended.
Recovery after Hip Replacement Surgery Procedure
Recovery after hip replacement surgery is a gradual process that involves both physical healing and rehabilitation to regain mobility and strength. Here's what you can generally expect during the recovery period after a hip replacement surgery:
- Hospital Stay: Most patients stay in the hospital for a few days after the surgery. During this time, you'll be monitored for any postoperative complications and receive pain management.
- Pain Management: Pain and discomfort are common after surgery. Your healthcare team will provide pain medication to keep you comfortable.
- Early Mobilization: On the day of or after surgery, you'll start with gentle movements and walking with the assistance of a walker or crutches. Gradually, you'll increase your mobility.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is a key aspect of recovery. A physical therapist will guide you through exercises to improve hip strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Rehabilitation Goals: The goals of rehabilitation include regaining your independence in daily activities, walking without assistance, and returning to a normal range of motion.
- Weight-Bearing: Depending on your surgeon's guidance, you'll begin to put weight on your new hip joint. The timeline for weight-bearing varies based on individual factors.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your healing progress, discuss any concerns, and adjust your recovery plan if needed.
- Precautions: You may need to follow specific precautions to avoid dislocation of the new hip joint, such as avoiding certain movements and positions.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Over the weeks and months following surgery, you'll gradually increase your physical activity level. Follow your surgeon's recommendations to avoid overexertion.
- Mobility Aids: You might use a walker, crutches, or a cane initially. As you regain strength and mobility, you'll be able to transition to walking without assistance.
- Pain Management at Home: Your surgeon will provide instructions for pain management at home, including medication and other techniques to alleviate discomfort.
- Driving: Consult your surgeon before resuming driving. It's typically safe to drive when you can control the vehicle comfortably and react quickly.
- Return to Work and Activities: Your ability to return to work and other activities will depend on your job and individual recovery progress. Discuss timelines with your surgeon.
- Swelling Management: Swelling around the surgical area is normal. Elevating your leg and using ice packs can help reduce swelling.
- Rest: Proper rest and sleep are important for healing. Listen to your body and avoid overexertion.
Lifestyle changes after Hip Replacement Surgery Procedure
After undergoing hip replacement surgery, making certain lifestyle changes can contribute to a successful recovery and improved long-term outcomes. These changes aim to protect the newly replaced hip joint, enhance your overall well-being, and promote a more active and comfortable life. Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support healing and overall health. Adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals are essential for tissue repair.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, which aids in healing and maintaining joint health.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: It is recommended that you participate in exercises and physical therapy sessions that will help to improve the strength of the muscles surrounding your hip joint.Follow your therapist's guidance to avoid strain.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the new hip joint and minimize the risk of complications.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: Refrain from activities that involve high impact or repetitive stress on the hip joint, such as running or jumping.
- Adapt Your Home Environment: Make your living space safer and more accommodating by removing tripping hazards and placing items within easy reach.
- Use Assistive Devices: If recommended, continue using assistive devices such as a cane or walker until you regain full strength and confidence.
- Avoid Cross-Legged Sitting: To prevent dislocation, avoid sitting cross-legged or bending the new hip joint beyond a certain angle.
- Be Mindful of Footwear: Wear comfortable and supportive shoes that promote good posture and balance.
- Gradual Return to Activities: Slowly reintroduce daily activities and hobbies as your hip heals. Consult your surgeon about specific activities.
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to your surgeon's recommendations for follow-up appointments, medications, and any restrictions.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain. Rest when needed and don't push yourself too hard.
- Posture Awareness: Maintain good posture to reduce strain on your hip joint and promote proper alignment.
- Incorporate Low-Impact Exercises: Swimming, cycling, and gentle yoga can help improve joint mobility and muscle strength without excessive stress.
- Continue Rehabilitation Exercises: Even after formal physical therapy ends, continue doing prescribed exercises to maintain hip strength and flexibility.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your orthopedic surgeon to monitor your hip's condition and address any concerns.
- Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking, as smoking can hinder healing and joint health.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques to manage stress, which can positively impact your overall health and healing process.
- Communication with Healthcare Team: Maintain open communication with your healthcare providers. Discuss any changes in your condition or concerns you may have.
- Enjoy an Active Lifestyle: With proper care, many individuals find that their hip replacement surgery allows them to lead a more active and fulfilling life.