Breast augmentation, also known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure performed to enhance the size and shape of the breasts using implants or fat transfer. Here are the general steps involved in a breast augmentation procedure:
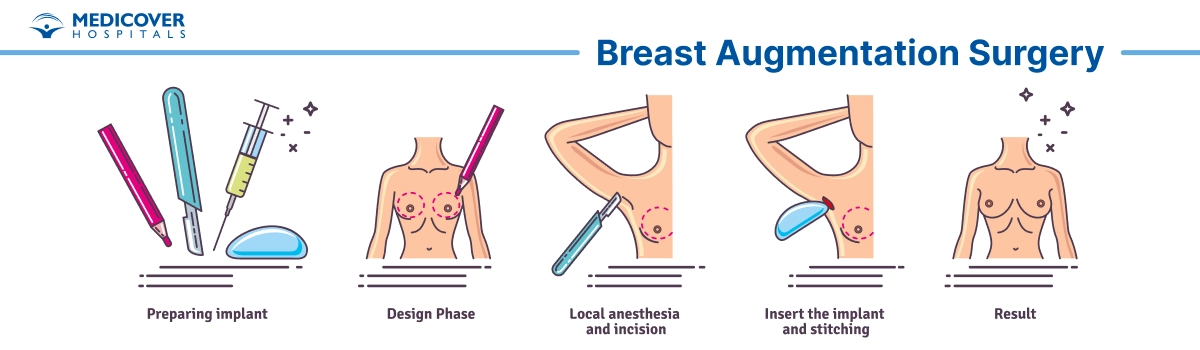
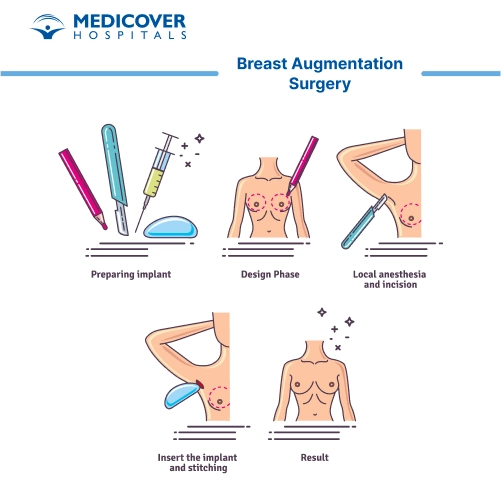
Steps involved in Breast augmentation
To prepare for your breast augmentation procedure, your surgeon may provide specific instructions tailored to your individual needs. Some general preparation guidelines include:
-
Preoperative Evaluation: The patient undergoes a medical evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and discussions about goals and expectations for the procedure.
-
Implant Selection and Planning: The patient and surgeon discuss the desired breast size, implant type (saline, silicone gel), implant shape (round or anatomical), and placement (submuscular or subglandular). The surgeon provides recommendations based on the patient's anatomy and preferences.
-
Consent and Anesthesia: The patient meets with the surgeon to discuss the procedure, its risks, benefits, and potential alternatives. Informed consent is obtained.
Anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the surgery. General anesthesia is typically used.
-
Positioning: The patient is positioned on the operating table, usually lying on their back.
-
Preparation of the Surgical Site: The chest area is cleansed and sterilized to reduce the risk of infection.
-
Incision: Incisions are made in specific locations, such as the crease under the breast (inframammary fold), around the areola (periareolar), or in the armpit (transaxillary). The choice of incision depends on factors like implant type and surgeon's preference.
-
Implant Placement: The surgeon creates a pocket for the implant, either behind the breast tissue (subglandular) or behind the chest muscle (submuscular). The implant is placed in the pocket, and its position is adjusted for symmetry.
-
Suture or Closure: The incisions are closed using sutures or stitches. In some cases, surgical glue or adhesive strips may be used.
-
Dressing and Bandages: The breasts are dressed with bandages, and a surgical bra or compression garment may be applied to provide support and reduce swelling.
-
Recovery and Observation: The patient is taken to a recovery area as they wake up from anesthesia. Vital signs are monitored, and pain management measures are implemented.
-
Hospital Stay: Breast augmentation is typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Postoperative Care and Follow-Up
Breast augmentation is typically performed under general anesthesia, ensuring your comfort throughout the procedure. The surgical technique and incision location will depend on the discussed plan and your surgeon's recommendations. The steps involved in the procedure may include:
- Patients receive instructions for wound care, pain management, and activities to avoid during the recovery period.
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the healing process, assess implant position, and address any concerns.
Who will Treat for Breast augmentation
Plastic surgeons: Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure performed by qualified and experienced plastic surgeons. When considering breast augmentation, it's essential to choose a board-certified plastic surgeon with expertise in performing this specific type of surgery. Plastic surgeons are trained to assess individual needs, discuss surgical options, and provide personalized recommendations based on the patient's anatomy and goals.
Preparing for Breast augmentation
Preparing for breast augmentation surgery involves a combination of physical, emotional, and logistical preparations to ensure a smooth and successful procedure and recovery. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to prepare for breast augmentation:
- Consultation with a Plastic Surgeon: Schedule a consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon who specializes in breast augmentation. During this appointment, discuss your goals, expectations, medical history, and any concerns you may have.
- Communicate Your Goals: Clearly communicate your desired breast size, shape, and aesthetic goals with your surgeon. This helps the surgeon understand your expectations and plan the procedure accordingly.
- Medical Evaluation: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation make sure you are in good overall health for surgery. Your surgeon may request medical tests, blood work, and a physical examination.
- Stop Smoking: If you smoke, it's recommended to quit or at least reduce smoking before the surgery. Smoking can affect healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Medication Review: Provide a list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before the surgery.
- Avoid Certain Medications: Your surgeon may recommend avoiding medications and supplements that can increase the risk of bleeding, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and certain herbal supplements.
- Arrange for Support: Arrange for someone to accompany you to the surgical facility and assist you during the initial recovery period at home.
- Plan Transportation: Arrange transportation to and from the surgical facility on the day of the procedure, as you may not be able to drive yourself.
- Fasting Instructions: Follow the fasting instructions provided by your surgical team. Typically, you will need to avoid eating or drinking anything for a specific period before the surgery.
- Plan for Recovery: Prepare your home for a comfortable recovery by setting up a designated recovery area with pillows, blankets, and entertainment.
- Prescription Medications: Fill any prescribed medications before the surgery, so they are readily available for postoperative pain management.
- Comfortable Clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing to the surgical facility. Avoid tight-fitting tops that may rub against the incision sites.
- Recovery Garments: Your surgeon may provide instructions on wearing compression garments or surgical bras postoperatively. Have these garments ready for use.
- Clear Information: Fully understand the surgical plan, expected outcomes, recovery process, and potential risks before the procedure.
- Emotional Readiness: Be emotionally prepared for the changes in your body and the recovery process. Discuss any concerns with your surgeon during the consultation.
- Final Questions: Use your consultation to ask any remaining questions about the procedure, recovery, and postoperative care.
Recovery after Breast Augmentation Surgery?
Recovery after breast augmentation surgery is a gradual process that requires patience, adherence to postoperative instructions, and self-care to ensure a smooth healing journey. The duration and specifics of the recovery period can vary based on various factors such as the surgical technique used, implant placement, individual healing capacity, and lifestyle. Here's what to expect during the recovery after breast augmentation surgery:
- Immediate Postoperative Period:After the surgery, you will be monitored in the recovery area as you wake up from anesthesia.
Dressings, bandages, and a surgical bra or compression garment will be applied to support the healing process and minimize swelling.
- Pain Management:You may experience discomfort, tightness, and soreness in the chest area. Prescription or over-the-counter pain medications will be prescribed to manage postoperative pain.
- Swelling and Bruising:Swelling and bruising around the surgical site are common and will gradually subside over the next several weeks.
- Restricted Activities:You will be advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and vigorous upper body movements during the initial recovery period.
- Returning Home:Most breast augmentation procedures are performed on an outpatient basis, allowing you to return home the same day as the surgery.
- Follow-Up Appointments:Your surgeon will arrange follow-up appointments to track your recovery process and, if applicable, to remove any sutures or drains.
- Resuming Normal Activities:Most individuals can return to light activities within a week or two after surgery. However, it may take several weeks before you can fully engage in strenuous exercises or heavy lifting.
- Driving:You may need to avoid driving for a few days or until you are off prescription pain medication and can safely control a vehicle.
- Returning to Work:The timing of your return to work will depend on your job requirements and the nature of the surgery. Some individuals can return within a week, while others may need more time.
- Supportive Bras:Your surgeon may recommend wearing a supportive surgical bra or compression garment to provide proper support to the healing breasts.
- Physical Sensations:Changes in sensation, such as numbness or hypersensitivity, around the surgical area are common and usually temporary.
- Exercise and Physical Activity:Gradually reintroduce exercise and physical activities as guided by your surgeon. Avoid activities that strain the chest muscles during the initial recovery phase.
- Final Results:While you will notice initial changes, it takes several weeks to months for the breasts to settle into their final shape and position.
Lifestyle changes after Breast augmentation Surgery
After breast augmentation surgery, certain lifestyle changes and considerations are important to support your recovery, promote healing, and maintain the long-term results of the procedure. Here are some lifestyle changes to keep in mind:
- Rest and Recovery: Allow yourself sufficient time to rest & recover after surgery. Avoid strenuous activities and heavy weight lifting during the initial healing period.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support the healing process and overall well-being.
- Hydration: Drink a sufficient amount of water to stay hydrated, which supports the healing process and general health.
- Avoid Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking. It can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
- Avoid Alcohol: Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol intake can interfere with medications and healing.
- Medication Management: Take prescribed medications as directed, including pain relievers and any antibiotics, to prevent infection.
- Wound Care: Follow proper wound care instructions provided by your surgeon. Keep the surgical site dry & clean to minimize the risk of infection.
- Avoid Sun Exposure: Protect your surgical incisions from sun exposure to prevent hyperpigmentation or scarring. Use sunscreen and cover the area when outdoors.
- Avoid Tight Bras: Choose bras that provide gentle support without putting pressure on the healing breasts. Your surgeon may suggest a specific type of bra.
- Physical Activity: Gradually reintroduce physical activities as advised by your surgeon. Avoid activities that strain the chest muscles during the initial recovery phase.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. These appointments are crucial for monitoring your healing progress and addressing any concerns.
- Limit High-Impact Activities: Avoid high-impact activities that may strain the breasts or chest muscles for the first few months after surgery.
- Supportive Bras: Wear supportive bras as recommended by your surgeon during the recovery period and afterward to maintain breast shape and comfort.
- Be Patient: Be patient with the recovery process. Healing and results may take several weeks to months.
- Emotional Well-Being: Address any emotional concerns or adjustments related to body image changes with a supportive network or therapist if needed.
- Regular Checkups: Continue to attend regular breast health checkups and screenings as recommended by your healthcare provider.