Dengue Fever: Symptoms, Causes & Treatments
Dengue fever is considered one of the most common tropical viral infections seen in India. Dengue (DENG-gey) is a mosquito-borne illness that mostly affects tropical and subtropical countries. A high temperature and flu-like symptoms are common signs of dengue. A severe form of dengue, dengue hemorrhagic fever, can cause substantial bleeding, a drop in blood pressure (shock), and fatality.
It commonly occurs in the post-monsoon period. Dengue is caused by 4 closely related serotypes of the dengue (Flaviviridae family) virus. It is transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which typically bite during day times. The incubation period ranges from 2-7 days. Let us discuss what are the different types of dengue, their symptoms, causes, risk factors, preventions, diagnosis and treatments in detail.
Types Of Dengue Fever
Dengue affects around 40% of the population in the 100 countries where it is endemic. It is divided into three categories based on the intensity and symptoms experienced by the host.
- Mild Dengue Fever
- Dengue Haemorrhagic fever
- Dengue Shock Syndrome
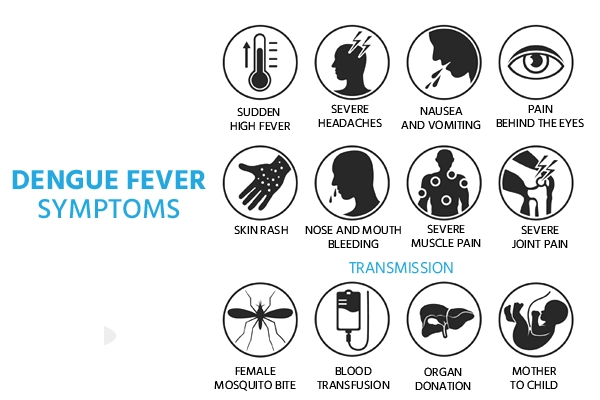
Symptoms Of Dengue Fever
Symptoms of dengue generally appear four to ten days after the initial infection. They are similar to flu or other illness symptoms. Young children and persons who have never been infected may endure a less severe sickness than older children and adults.
High-grade fever with chills, retro orbital pain, joint pains, body aches, headache, severe generalized weakness, diffuse flushing red color rash initially after 1-2 days of fever, later petechial rash seen over trunk, legs, and arms, conjunctival redness, etc.
Severe symptoms include severe breathlessness, low heart rate, recurrent vomiting, cold clammy extremities, jaundice, decreased urine output, severe headache and abdominal pain, spontaneous or uncontrolled bleeding episodes, heavy sweating, altered sensorium, neck stiffness, etc.
Symptoms of severe dengue can include :
- Belly pain and tenderness
- Vomiting blood or blood in stool
- Mild bleeding from the nose or gums
- Mild to severe vomiting (three times in 24 hours)
- Fatigue, restlessness, or irritability
Causes of Dengue Fever
One of four dengue viruses causes dengue disease. When you are bitten by a mosquito carrying the dengue virus, the virus can enter your bloodstream and replicate itself. You may become ill due to the infection and your immune system's response. The virus can harm sections of your blood that form clots and give your blood vessels shape. This, along with specific chemicals produced by your immune system, can cause blood to flow out of your vessels, resulting in internal bleeding. This causes severe dengue fever, which can be fatal.
Risk Factors of Dengue Fever
If you have dengue or a more severe version of the disease, you're more likely to get it.
- Living in or traveling to a tropical location: Being in tropical and subtropical climates increases your chances of contracting the dengue virus. Southeast Asia, the western Pacific islands, Latin America, and Africa are high-risk zones.
- You've previously got dengue fever: If you've had dengue earlier, you're more likely to have severe symptoms, if you get it again.
Complications of Dengue Fever
The complications of Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever include:
- Bleeding under the skin
- Cough and sore throat
- Bloody Spit
- Bleeding on the skin
- Patchy skin
- Bloody Stool
- Weariness
- Excessive sweating
- High fever
- Sudden chills
- Bloody vomit
- Irregular urine discharge
- Dry eyes
Diagnosis for Dengue Fever
A blood test detects dengue infection by looking for the virus or antibodies against it. Inform your doctor if you fall ill after visiting a tropical place. This will help your doctor determine whether your symptoms result from dengue infection. Doctors use blood tests to look for antibodies to the dengue and phlegm viruses.
Various diagnostic tests are available and includes a rapid immunochromatographic test (Dengue Rapicheck). ELISA for Dengue is the commonly used confirmatory test.
Investigations include Hemogram, RFTs, LFTs, CUE, Chest X-ray, USG scan whole abdomen, etc.
A few tests done to diagnose dengue are listed below:
- Virological test: This test looks for viral components directly. Because this testing frequently necessitates specialized equipment and a technically skilled team, it may not be offered in all medical institutions.
- Serological test: Antibodies in the blood are detected to confirm a current or recent infection. If you get dengue symptoms after traveling outside the nation, you should consult a doctor to ensure you don't have the virus.
Treatment for Dengue Fever
Secondary infections are known to be more severe in nature, with more chances of development of DHF/DSS. If treatment is delayed, patients can land into DSS, which can lead to life threatening consequences.
Platelet level and Hematocrit should be regularly monitored. A fall in Hematocrit level is suggestive of impending shock syndrome.
Management is mainly symptomatic and supportive. Maintaining hydration (with isotonic NS) is very important to maintain blood pressure. Platelet transfusion is indicated only if there is severe thrombocytopenia (<20,000/mm3) / overt bleeding.
Treatment options for milder forms include:
- Preventing dehydration: Dehydration can be avoided by avoiding a high temperature and vomiting. Clean water, preferably bottled rather than tap water, should be consumed. Minerals and fluids can also be replaced using rehydration salts.
- Pain medications like Tylenol or paracetamol can help reduce heat and pain: Aspirin and ibuprofen are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), which might increase the risk of internal bleeding.
