Crohn's Disease: What It Is, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Written by Medicover Team and Medically Reviewed by Dr Arun Arora Pagadapelli , Gastroenterologists Medical
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disorder (IBD). It inflames the digestive tract, resulting in stomachaches, severe diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, and malnutrition. Crohn's disease-related inflammation can affect different areas of the digestive tract in various individuals.
Crohn's disease is a chronic disease that most usually manifests itself in the small intestine and the first part of the large intestine. This disease can affect any part of the GI system, from the mouth to the anus.
It may involve some portions of the GI tract while ignoring others. The severity of Crohn's disease can vary from moderate to fatal. Symptoms differ and can shift over time.
This condition can be life-threatening in critical patients. A healthy diet and an improvement in lifestyle can help to control Crohn's disease. Your doctor may suggest a specific diet based on your symptoms or medications, such as a high-calorie, lactose-free, or low-fat diet.
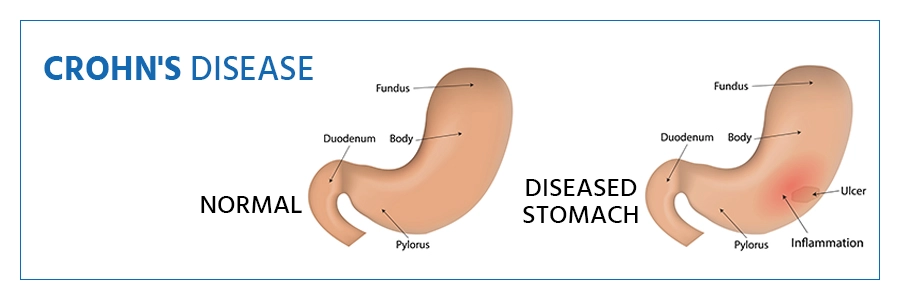
What are the Different Types of Crohn's disease?
Crohn's disease is classified into five categories, each with a set of symptoms.
Ileocolitis
It is an inflammatory disease that affects the end of the small intestine (ileum) and a section of the large intestine (colon). Ileocolitis patients may have symptoms such as:
- Diarrhea
- Substantial weight loss
- Abdominal ache or cramps in the lower and middle quadrants.
Ileitis
It is inflammation of the small intestine's final portion (ileum). Ileitis symptoms are similar to those of ileocolitis. Ileitis patients may sometimes suffer from fistulas (inflammatory abscesses) inside the lower-right belly. Symptoms include:
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Cramping
- Abdominal pain
Gastroduodenal Crohn's disease
It damages the stomach and the first few inches of the small intestinal tract (duodenum). Patients may vomit if small sections of their intestine get clogged with gastroduodenal Crohn's disease. This is due to inflammation in the intestine. Its symptoms include -
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Loss of weight
- Vomiting
Jejunoileitis
It involves inflammation of the middle section of the small intestine (jejunum). Patients with jejunoileitis may have the following symptoms:
- Cramping after eating
- Fistulas
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain that might be intense at times
Granulomatous Colitis
It involves inflammation of only the colon. It can result in the formation of fistulas, ulcers, and abscesses around the anus. It also includes the following symptoms:
- Skin lesions
- Joint discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Rectal hemorrhage
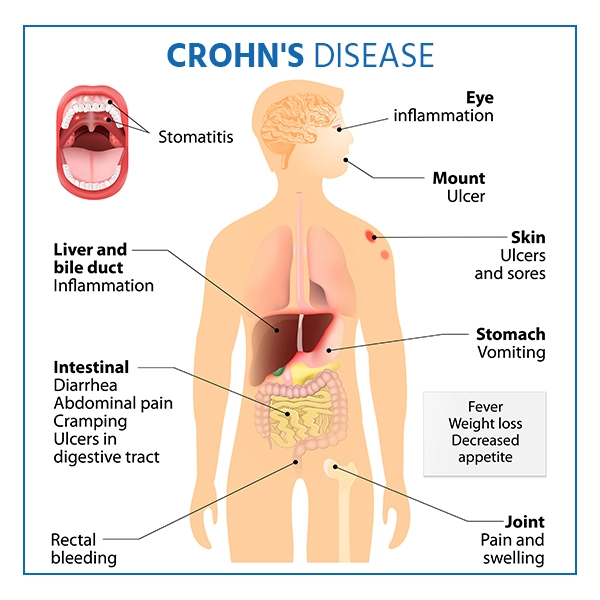
What are the Causes and Risk Factors of Crohn's Disease?
The precise cause of Crohn's disease is unknown. Previously, diet and stress were suspected to cause this disease. But doctors now know that these factors may only worsen the disease and not cause it.
Its development is most likely influenced by a number of variables, including inheritance and a dysfunctional immune system.
- The immune system : A virus or bacterium could cause Crohn's disease, but scientists have yet to uncover such a trigger. When your immune system attempts to fight off the invading microbe, an aberrant immunological reaction causes the immune system to attack digestive tract cells as well.
- Heredity : Crohn's disease is much more common in people who have a family member with this condition. Therefore, genes may have a role in predisposing people to this disease. However, most Crohn's disease patients do not have a family history of the condition.
Risk factors
Crohn's disease risk factors may include:
- Age: Crohn's disease can strike at any age, but it is most likely to strike at a young age.
- Ethnicity: Although Crohn's disease can affect people of any ethnicity, whites are at the highest risk, particularly those of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jewish origin.
- Family background: If you have a first-degree relative suffering with Crohn's disease, including a parent, brother, or child, you are at a higher risk.
- Smoking cigarettes: Smoking cigarettes is the most significant modifiable risk factor for Crohn's disease.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Naproxen sodium (Aleve),Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, and others), diclofenac sodium, and other drugs can increase the risk of Crohn's disease.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionWhat are the Symptoms of Crohn's Disease?
Crohn's disease symptoms are frequent and they appear gradually. Certain symptoms could also worsen with time. Rarely, the Crohn's disease symptoms appear suddenly and rapidly.
Some of the initial symptoms of Crohn's disease include:
- Diarrhea
- The cramping in the abdomen
- There is bleeding in your stool
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Appetite suppression
- Loss of weight
- After a bowel movement, you have the feeling that your bowels are not empty.
- Feeling to urinate frequently
It's possible to confuse these symptoms with those of other ailments, like food poisoning, stomach distress, or an allergy. If either of these symptoms persists, you should consult a doctor.
How is Crohn's Disease Diagnosed?
Typically, doctors do not use a single test to diagnose Crohn's disease. Various tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis. In addition, your doctor will ask you about your health and family history, as well as do a physical examination.
The following test methods may be used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Blood and stool tests
- Biopsy
- Sigmoidoscopy, which includes inspecting the lower colon using a short, elastic tube-like instrument called a sigmoidoscope.
- Colonoscopy which involves inspecting the colon with a flexible, tube-like instrument called a colonoscope.
- Endoscopy is a procedure that involves sending a long, thin, flexible probe known as an endoscope down the esophagus to the stomach to examine the top portion of the gut.
- A CT scan or barium enema X-ray may be used to detect abnormalities in the bowel.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is done to observe a fistula near the anal area or the small intestine.
What are the Treatment Options for Crohn's Disease?
There is no cure for Crohn's disease. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation in the intestines, avoid symptom flare-ups, and maintain remission.
Crohn's disease is treated by a gastroenterologist using medications, bowel rest, and surgery.
Medicines
Various drugs are used to treat Crohn's disease by reducing the inflammation. They include anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, biologics for Crohn's disease, and antibiotics.
Some other remedies include anti-diarrheals, pain relievers, vitamins and supplements, and nutritional therapy.
Bowel rest
It includes consuming only certain liquids and not drinking or eating anything. This method allows the intestine to rest. It is done if the disease symptoms are severe.
Surgery
The doctor may suggest surgery if medications and other therapies do not relieve the Crohn's disease symptoms. Surgery provides only temporary relief because the disease can reappear again.
The best treatment plan includes surgery with the intake of medicines to reduce the risk of recurrence.
The treatment plan will be determined by:
- Where is the inflammation?
- The gravity of the problem
- Any complexities
- A person's reaction to prior treatments
Some people can live for many years without having any symptoms. Remission of Crohn's disease varies so significantly that it can be difficult to predict how effective treatment will be and how long remission will persist.
When to see a doctor?
Consult your doctor if you have prolonged changes in the bowel movements or any of the Crohn's disease signs and symptoms, such as:
- Pain in the abdomen
- Bleeding in the stool
- Vomiting and nausea
- Chronic diarrhea that does not get better with over-the-counter (OTC) treatments.
- Unknown cause of fever extending more than a day or two.
- Unknown cause of weight reduction.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
What Is the Recovery Process After Crohn's Disease Treatment?
Recovery from Crohn's disease focuses on controlling symptoms, reducing flare-ups, and maintaining long-term remission.
Follow-Up Care
- Regular check-ups with a gastroenterologist
- Periodic blood tests or colonoscopy to monitor inflammation
- Extra care for patients on immunosuppressants or biologics
Lifestyle & Diet Tips
- Eat small, soft meals during flare-ups
- Avoid spicy, oily, and high-fibre foods
- Stay hydrated and take prescribed medicines without skipping
- Quit smoking and manage stress through yoga or meditation
- Track food triggers with a symptom diary
Long-Term Outlook
With the right treatment, many live in remission for long periods. Early care helps avoid complications like fistulas, malnutrition, or bowel blockage.
What Precautions Can Help Prevent Crohn's Disease?
Prevention
- Don't smoke, it worsens symptoms
- Eat a balanced diet; avoid known triggers
- Stay active and manage stress
- Get early screening if you have digestive issues or family history
Complications if Untreated
- Intestinal blockage
- Nutrient deficiencies
- Fistulas and chronic diarrhoea
- Increased risk of colon cancer
Dos and Don'ts
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that includes symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, and fever. No exact cure is known and it can be diagnosed through blood and stool tests, colonoscopy, endoscopy, and medical imaging techniques.
| Do's | Don'ts |
|---|---|
|
Try meditation, yoga, |
Smoking and having tobacco products |
|
Be alert for the symptoms. |
Stay away from multivitamins. |
|
Take dietician advice |
Eat processed foods, refined sugar, dairy products, coffee and alcohol. |
|
Be hydrated |
Drink less water. |
|
Keep an emergency kit ready. |
Eat large meals. |
The disease could be taken care of with the help of medications and surgery. Follow the do's and don'ts for Crohn's disease because it can help to prevent the severity of the symptoms and keep the disease under control.
Crohn's Disease Care at Medicover
At Medicover hospitals, we have the most reliable healthcare team like Crohn's disease specialists and gastroenterologists, who design an individual treatment pathway for each patient.
We adopt a multi-faceted approach to managing Crohn's disease with the active participation of healthcare specialists from different departments to treat the disease for holistic recovery and wellness.
We aim to provide the best treatment outcomes and satisfactory patient experiences at a highly affordable cost.
Citations
Diarrhea Dos and Don'ts: 10 Tips for Crohn's
