What is Parkinson's Disease?
Written by Medicover Team and Medically Reviewed by Dr Priyanka D , Neurologist
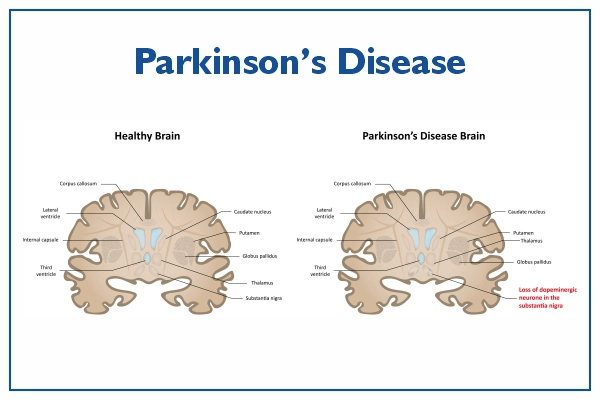
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative brain disorder caused by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in a region called the substantia nigra.
Parkinson's disease is a neurological disorder that mainly affects the nervous system of the body. This system is very important for movement. The nervous system is spread through nerve cells in the body to control the many parts of the body.
Parkinson's disease slowly starts with passing signs like tremor in body parts such as hands, jaw and foot etc. Tremor is the primary symptom of Parkinson's disease. It results from the degeneration of nerve cells in the brain, particularly in areas that control motor function.
Parkinson's disease is a chronic neurological condition that primarily affects older adults. It primarily affects people over 50. It's slightly more common in men than women. While rare, it can occur in younger adults (as early as 20) with a family history of the condition.
Ignoring Parkinson's disease leads to movement-related problems such as tremors at rest, stiffness (rigidity), slowness of movement (bradykinesia), and postural instability, along with non-motor symptoms like sleep trouble, mood changes, cognitive decline, and constipation.
Parkinson's Disease in India
Globally, over 8.5 million people had Parkinson's in 2019, with the disease responsible for approximately 329,000 deaths and 5.8 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs). In India, studies show rates range from about 33 to 192 per 100,000 population, depending on region and community, with particularly high rates observed in the Parsi community of Mumbai (approximately 192 per 100,000).
A recent survey from rural Gujarat reported a crude prevalence of 42.3 per 100,000, rising to 308.9 per 100,000 among those over 60. According to the Global Burden of Disease data, India had around 771,000 people living with Parkinson's in 2019.
What Are the Types of Parkinson's Disease?
Parkinson's disease is a chronic and progressive neurological condition that affects a small group of nerve cells (neurons) in a part of the brain. The classification of Parkinson's Disease is classified into two main groups. One is Primary Parkinsonism, and the second one is Secondary Parkinsonism.
Primary Parkinsonism
- Idiopathic Parkinson's disease: Idiopathic Parkinson's disease or simple Parkinson's disease is common in 85–90% of cases. Its cause is unknown. It leads to motor symptoms such as tremor, stiffness, slowness, and balance problems, along with non‑motor symptoms like sleep issues and mood changes.
- Early‑Onset (Youth‑Onset) Parkinson's Disease: It occurs before age 50. It progresses more slowly but often involves genetic factors. Individuals commonly experience side effects like dyskinesia earlier and face a greater psychological impact.
- Familial (Genetic) Parkinson's Disease: It accounts for about 5–15% of cases and is associated with specific gene mutations (e.g. Parkin, PINK1, DJ‑1). This form can appear earlier and may cluster in families.
Secondary Parkinsonism
The Secondary Parkinsonism occurs from external causes such as medications (especially antipsychotics), certain toxins, stroke, or head injury. Same as the primary Parkinsonism, it has similar symptoms. Depending on the disorder and treatment, the symptoms go away.
- Drug-induced Parkinsonism: Drug-induced Parkinsonism is one of the most common causes of Parkinsonism. The drugs that impacted the dopamine levels lead to Parkinsonism. Neuroleptic drugs are the main cause of drug-induced Parkinsonism.
- Vascular parkinsonism: Vascular parkinsonism mostly affects your lower body. This happens due to multiple small strokes in the part of your brain that controls movement. This is also known as lower-body Parkinsonism.
Atypical Parkinson's Conditions
Atypical Parkinsonism (Parkinson‑Plus Syndromes) includes conditions that mimic Parkinson's but progress faster, respond poorly to levodopa, and involve other neurologic features:
- Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB):Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) is a condition characterised by an abnormal buildup of Lewy bodies, or alpha-synuclein proteins.
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP): Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) causes early balance problems, frequent falls, difficulty with vertical eye movements, speech/swallowing issues, and cognitive decline.
- Multiple System Atrophy (MSA): Multiple System Atrophy is also known as Shy-Drager syndrome. This severely affects the nervous system in the body.
- Corticobasal Degeneration (CBD): Corticobasal degeneration is last common type of Atypical Parkinsonism. It causes asymmetrical motor symptoms like rigidity, dystonia, and myoclonus, often with apraxia and language problems.
Parkinson's Disease Stages
There are a total of five stages that describe parkinsons disease. Hoehn & Yahr defined the stages of PD in 1961. Stages 1 to 2 are considered early stages, Stage 2 to 3 are mild stages, and Stages 4 to 5 are advanced stages of Parkinson's Disease.
Here are the detailed stages of Parkinson's disease according to the Hoehn and Yahr scale:
- Stage 1: During this initial stage, Symptoms are very mild and appear only on one side of the body, such as a tremor in one hand. There's minimal or no disruption to daily activities.
- Stage 2: Symptoms become more noticeable and involve both sides of the body (bilateral involvement), but balance remains intact. Daily activities may take longer, but the person remains independent.
- Stage 3: This leads to an increased risk of falls. However, the person is still physically independent and can manage daily tasks with more effort.
- Stage 4: Symptoms are severe and disabling. Standing or walking unassisted becomes difficult. The person usually requires help with most daily activities but may still be able to stand or walk with support.
- Stage 5: This is the most advanced stage. The person is often bedbound or in a wheelchair, requiring constant care. There may also be cognitive symptoms like hallucinations or dementia.
There is also a modified scale that includes stages 1.5 and 2.5 to capture earlier or intermediate symptom progression: stage 1.5 involves both unilateral and axial signs, while stage 2.5 includes mild balance impairment (tested via the “pull test”) despite still being able to recover.
What are the Parkinson's Disease Symptoms?
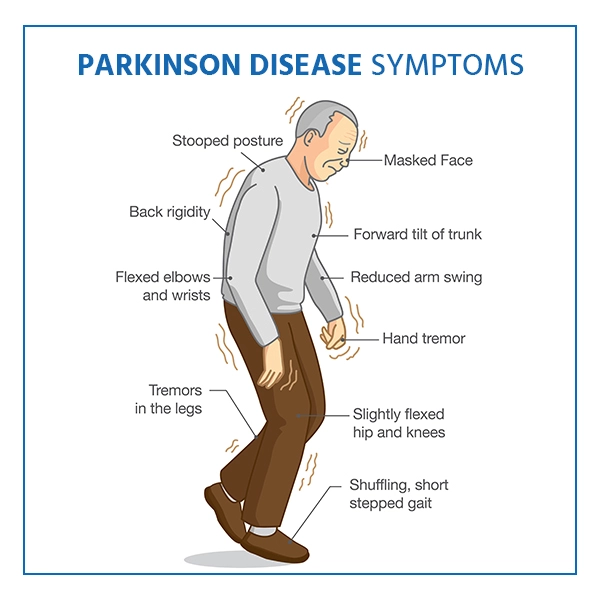
Parkinson's disease symptoms appear slowly. They are different from person to person. The tremor in one hand and a sensation of rigidity throughout the body are the primary symptoms of Parkinson's Disease. There is a risk of misdiagnosis for this condition due to its symptoms being similar to those of other neurological conditions.
Motor Symptoms
Parkinson's motor symptoms may include:
- Tremor: Parkinson's disease typically begins with a resting tremor in about 70–75% of people at some point. It starts in one hand with a slow “pill‑rolling” movement (4–6 Hz) that appears when the limb is at rest and often disappears with movement or sleep.
- Bradykinesia (slowness of movement) is the most characteristic symptom. People who have this face difficulty starting movements, slower walking (shuffling gait), reduced arm swing, micrographia (tiny handwriting), and less facial expression (masked face).
- Rigidity: Rigidity refers to stiffness and resistance in muscles. It often shows as cogwheel or lead‑pipe resistance, and may cause joint pain or a stooped posture with reduced mobility.
- Poor posture and balance
- Loss of automatic movements
- Speech changes
Among non‑motor symptoms, up to 90% of people experience early symptoms of parkinson's disease , such as olfactory loss (smell problems), often years before motor signs. Sleep disturbances like REM sleep behavior disorder, constipation, and urinary issues are common early signs. Mood disorders such as depression, anxiety, and apathy) also occur frequently.
What Are the Parkinson's Disease Causes?
Parkinson's occurs primarily when neurons in the substantia nigra part of the brain weaken or die. These neurons produce the chemical messenger dopamine to regulate movement properly.
The exact reason for Parkinson's Disease is unknown. But the researchers strongly support a mix of genetic and environmental factors, along with aging, that lead to Parkinson's Disease.
- Genetics: Approximately 10–15% of Parkinson's cases are associated with known inherited gene mutations (e.g., LRRK2, Parkin, PINK1, DJ-1, SNCA). In India, Parkin gene mutations account for 6–14% of familial or early-onset cases, often seen before age 40.
- Environmental exposures: Pesticide and herbicide exposure, especially agents like paraquat, rotenone, and DDT-related chemicals, can double the risk of developing Parkinson's in certain populations. Other contributors include solvents, heavy metals, chronic air pollution, and repeated mild traumatic brain injury.
- Biological mechanisms: Major theories involve mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, protein misfolding (especially alpha-synuclein accumulation), inflammation and impaired cell-degradation pathways, which collectively damage neurons over time.
Risk Factors
The Parkinson's Disease risk factors are as follows:
- Age: Parkinson's Disease mainly affects individuals aged 60 and over; the risk increases with age.
- Family history: Having a family member with PD increases the chances of developing it if their parent, brother, or sister has it.
- Serious head injury: Severe brain trauma can lead to Parkinson's disease if they hit their head hard enough to lose consciousness or forget things.
- Gender Men: Men get it more than women. Doctors aren't sure why.
- Some drugs and medications: Some chemicals and medications can cause Parkinsonism, which is characterised by tremors and other symptoms but is not the same as Parkinson's disease.
- Toxin exposure: Pesticides, solvents, metals, and other pollutants.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionHow is Parkinson's Disease Diagnosed?
The diagnostic process of Parkinson's Disease is done by a neurologist who has experience in nervous system conditions. The diagnosis process is mostly a clinical process, which means reviewing your medical history and symptoms.
- Clinical Diagnosis (Primary Method): The diagnosis process is primarily a clinical process. It means the observation of motor symptoms such as tremors at rest, slowed movement (bradykinesia), stiffness, and balance issues. Tools like the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) evaluate severity, with motor exam scores helping monitor disease progression.
- Levodopa or Apomorphine Challenge: Doctors may give a single dose of levodopa to see if symptoms improve by 30% on UPDRS. This has about 70% sensitivity and 80% specificity for confirming PD, though not all countries use apomorphine due to side effects.
- Dopamine Transporter SPECT Imaging (DaTscan): A DaTscan is a type of imaging that allows a doctor to examine how much dopamine is present in the brain. This imaging test visualises dopamine transporter loss in the striatum. In one audit of 731 patients, DaTscan accuracy was 99.1% with very few false positives or negatives.
- Skin Biopsy for Alpha‑Synuclein: A newer method detects abnormal a-synuclein protein in skin nerves. A recent study showed ~93% diagnostic accuracy and offers a less invasive biological confirmation of PD, especially when clinical signs are unclear.
Other Tests Will Be Done to Diagnose This Condition
Doctors use clinical factors to diagnose the condition.
- Blood tests
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Genetic testing
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
How is Parkinson's Disease Treated?
Parkinson's Disease is not cured permanently. The doctors suggest treatment to reduce its symptoms. These include medications, surgery, therapy, and exercises. The following are the treatment options for Parkinson's disease:
Pharmacological Treatments
- Levodopa (with Carbidopa or Benserazide): Levodopa converts into dopamine in the brain, helping reduce motor symptoms like rigidity and slowness, while co-administered carbidopa prevents side effects from peripheral dopamine. It remains the most effective medication for bradykinesia and rigidity, though tremor and gait issues may respond less well.
- Selegiline: This MAO‑B inhibitor is often added to levodopa to delay the need for higher levodopa doses by about 7 months (from 11 to 18 months after diagnosis). It may also have mild neuroprotective effects and can help with depressive symptoms.
- Emerging Medications (e.g., Tavapadon): Under clinical trials such as TEMPO 3, tavapadon targets dopamine D1/D5 receptors and has shown promise by reducing motor fluctuations and providing on time with fewer side effects, potentially useful both in early and advanced stages.
- Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion (foscarbidopa/foslevodopa, brand Vyalev/Produodopa): This pump delivers steady levodopa levels, dramatically reducing off‑episodes and smoothing symptom control in advanced PD. It's approved in Canada, Australia, the UK NHS in early 2024, and the U.S. in late 2024.
Surgical Intervention
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): DBS surgery is typically offered after about 5+ years of PD, primarily for individuals with disabling motor fluctuations, tremor, or dyskinesia not well controlled with medication. Electrodes are implanted into brain targets (such as the subthalamic nucleus or globus pallidus interna) and connected to a pulse generator.
Rehabilitation and Support Therapies
- Speech and movement therapies like LSVT LOUD/BIG help with voice loudness and large movements; these structured programs lead to measurable improvements in communication and mobility.
- Exercise-based programs such as Rock Steady Boxing have shown significant benefits in reducing depressive symptoms and improving motor function and quality of life in Parkinson's patients.
When to See a Doctor for Parkinson's Disease?
You should consult a neurologist, preferably a movement disorder specialist, if you begin to notice:
- slowness (bradykinesia)
- resting tremors
- stiffness (rigidity)
- balance issues (postural instability)
If two or more of these motor signs appear, a specialist can evaluate you accurately. Your GP will take your history, assess symptoms, and refer you when Parkinson's is suspected.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Recovery Process After Parkinson's Disease Treatment
Recovery depends on treatment type. Recovery from Parkinson's treatment is a long-term, adaptive process.
- Follow-Up Schedule
- Neurology consults every 3-6 months
- Regular therapy assessments
- Lifestyle and Diet
- A high-fiber diet to manage constipation
- Regular physical activity to improve mobility and mood
Most patients can lead fulfilling lives with proper care and support.
Parkinson's Disease Complications
Leaving Parkinson's Disease untreated leads to severe complications. Some of the complications are the following.
- Freezing of gait
- Aspiration Pneumonia
- Dyskinesias
- Dystonia
- Trouble with swallowing and chewing
- Speech changes
- Autonomic Dysfunction
- Urinary problems
- Constipation
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Loss of smell
- Balance and coordination problems
- Tremors
- Insomnia
- REM sleep behaviour disorder
- Nightmares
- Restless legs syndrome
- Sleep apnea
- Micrographia
- Reduced facial expressions
- Dementia
- Depression and anxiety
- Psychosis
- Impulse Control Disorders
- Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome
Our Experience Treating Parkinson's Disease
As health care providers, we know how challenging it can be to live with Parkinson's Disease for both patients and their families.
At Medicover, we have the best team of Neurologists and Neurosurgeons who work together to provide Parkinson's disease treatment. Our highly skilled team utilizes the latest medical equipment, diagnostic procedures and technologies to treat various types of neurological diseases and ailments.
We've treated thousands of Parkinson's patients over the years, offering care that combines medical expertise. Our team includes neurologists, therapists, and support staff who understand the condition deeply and work closely with you to improve your quality of life.
