Muscular Dystrophy: Overview
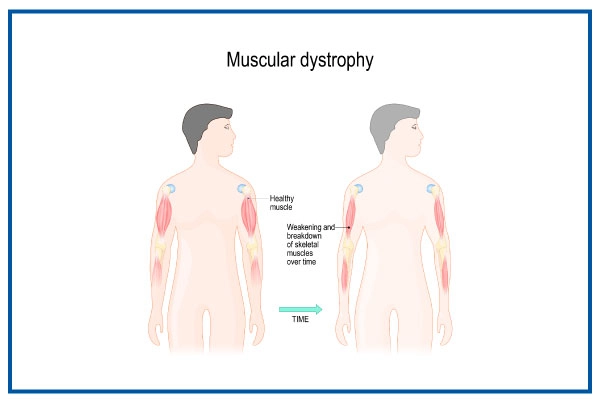
Muscular dystrophy is a group of muscular diseases caused by gene mutations. Muscle weakening reduces mobility over time, making daily tasks difficult. There are many types of muscular dystrophies, each affecting a different muscle group and causing signs and symptoms at different ages and severity levels. Muscular dystrophy can run in the family, or a person may be the first one in the family to be diagnosed with this disease. Although there is no known cure for any muscular dystrophy, treatments and therapies are available to manage this condition.
Types of Muscular Dystrophy
Listed below are nine major types of muscular dystrophy:
- Congenital
- Becker
- Distal
- Emery-Dreifuss
- Duchenne
- Facioscapulohumeral
- Myotonic
- Limb-Girdle
- Oculopharyngeal
Symptoms of Muscular Dystrophy
Symptoms of most types of muscular dystrophy develop in childhood. In general, kids suffering from the condition involve:
- Fall down often
- Muscle cramps
- Have trouble getting up, climbing stairs, running, jumping
- Walking on their toes or waddle
- Droopy eyelids
- Heart problems
- Trouble breathing or swallowing
- Vision problems
- Weakness in face muscles
When to see a doctor?
Consult the doctor if the condition worsens, and the symptoms of Muscular Dystrophy become more severe.
Get the best treatment for Muscular Dystrophy with our best orthopaedic surgeons at Medicover Hospitals.
Muscular Dystrophy Causes
Certain genes are involved in producing proteins that protect muscle fibres. Muscular dystrophy develops when one of these genes malfunctions. A single gene mutation can lead to dystrophin deficiency, an important protein. But muscular dystrophy can occur in more than one way. The genetic variations that cause muscular dystrophy are usually inherited, but they can sometimes occur due to a spontaneous mutation.
Muscular Dystrophy Risk Factors
Muscular dystrophy is a hereditary disease. A family history of muscular dystrophy puts you at risk of being a carrier or getting the disease.
Complications
The complications of progressive muscle weakness include
- Walking difficulties:Some patients with muscular dystrophy eventually require a wheelchair.
- Shortening of muscles or tendons:Contractures are shortenings of muscles or tendons around joints that can further limit movement.
- Difficulties using the arms: If the muscles in the arms and shoulders are compromised, daily tasks might become difficult.
- Breathing problems: Progressive weakness might compromise the muscles that control breathing. People with muscular dystrophy may need a breathing assistance device (ventilator) at some point, initially at night but maybe even during the day.
- Curved spine (Scoliosis): Weakened muscles cannot hold the spine straight
- Swallowing problems: Nutritional disorders and respiratory infections might arise if the muscles involved in swallowing are affected.
- Heart problems: Muscular dystrophy can reduce the efficiency of the heart muscle
Muscular Dystrophy Diagnosis
Techniques for diagnosing muscular dystrophies include assessing a patient's symptoms, medical history, and family history.
- Genetic testing: Mutation in some genes associated with specific forms of muscular dystrophy can be identified in blood samples.
- Enzyme tests: Damaged muscles release enzymes (such as creatine kinase) into the bloodstream. In the absence of a traumatic event, high CK levels in the blood indicate a muscle illness.
- Cardiovascular tests (electrocardiography and echocardiogram): These tests are used to test heart function, especially in people with myotonic muscular dystrophy.
- Muscle biopsy: A small portion of muscle can be extracted using an incision or a hollow needle. Muscular dystrophies can be distinguished from other muscle diseases based on tissue analysis.
- Lung-monitoring tests:These tests are conducted to measure lung function.
- Electromyography: An electrode needle is inserted to test the muscles. When muscle movements and changes in activity patterns indicate the presence of the disease, these impulses are monitored.
Muscular Dystrophy Treatment
There is no cure for this condition. However, several available therapies can reduce symptoms and make life easier for the patient. The doctor will prescribe a therapy based on the type of muscular dystrophy. These may include
- Physical therapy: It employs a wide range of exercises and stretches to keep your muscles strong and flexible.
- Occupational therapy:This teaches patients how to maximise the capabilities of their muscles. Therapists can also teach how to utilise wheelchairs, braces, and other assistive equipment.
- Speech therapy:If the child or the adult is experiencing breathing difficulties, respiratory treatment may be beneficial. They'll learn how to breathe more easily or employ equipment to assist them.
- Anti-seizure medications: This may relieve muscular spasms.
- Blood pressure medicines:These aid in the treatment of cardiac issues.
- Drugs that turn down the body’s immune system: Immunosuppressants are medications that suppress the body's immune system; they may slow muscle cell degeneration.
- Medicines: such as prednisone and deflazacort (Emflaza) can help the patient to breathe easily by slowing muscle deterioration. They can have major side effects, including weak bones and an increased risk of infection.
- Creatine: a naturally occurring substance in the body, can assist people to give energy to muscles and boost strength. Do consult your doctor to see whether these supplements are appropriate for children.
- Surgery: can assist with many consequences of muscular dystrophies, such as heart issues or swallowing difficulties.
Dos and Don’ts
Muscular Dystrophy refers to a group of over 30 hereditary diseases that affect the muscles. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common type, and it causes rapid muscle loss and progressive weakening beginning in childhood. Although there is no cure for MD, medications and other therapy can help slow the illness and enhance a patient’s quality of life. However, living with MD may be difficult for people and their loved ones, and the life expectancy of individuals with MD varies depending on the type and severity of the symptoms. Following these dos and don'ts will assist you in managing the condition.
Do’s |
Don’ts |
| Eat a well-balanced diet | Eat junk foods |
| Exercise regularly to improve muscle activity | Avoid taking medicines as prescribed by the doctor |
| Avoid dry foods with loose crumbs, like crackers or chips | Rush a meal, allowing time to eat |
| Avoid processed foods, such as white | Drink sugar-sweetened beverages, like |
| bread, sugar, and pasta | carbonated drinks, coffee, and alcohol, |
| Meditate and practise yoga to keep your mind healthy and positive | Stay sedentary with no physical activity |
Precautions and self-care will help you fight this condition positively and improve your quality of life.
Muscular Dystrophy Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover, we have the best team of Orthopaedic Surgeons and other doctors who work together to provide Muscular Dystrophy condition treatment with utmost precision. Our highly skilled team utilises the latest medical equipment, diagnostic procedures and technologies to treat various Muscular Dystrophy conditions and ailments. For treating Muscular Dystrophy, we adopt a multi-disciplinary approach, provide comprehensive care to the patients, and attend to all their medical needs for faster and sustained recovery.
