What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism, also known as an underactive thyroid gland, is a clinical disorder in which the thyroid gland does not generate sufficient thyroid hormones to meet the body's requirements. The thyroid gland releases hormones into the body that control how the body utilises energy. In the case of hypothyroidism, the body's functions slow down.
The normal thyroid levels are:
- T3: 100–200 nanograms per deciliter of blood (ng/dL)
- T4: 4.5 – 11.2 micrograms per deciliter of blood (mcg/dL)
- TSH: 0.4 – 5.0 milli-international units per litre (mIU/dL)
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionHypothyroidism symptoms
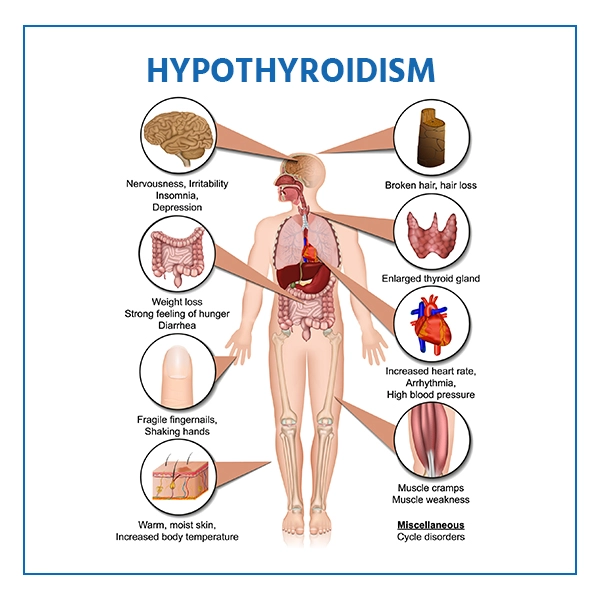
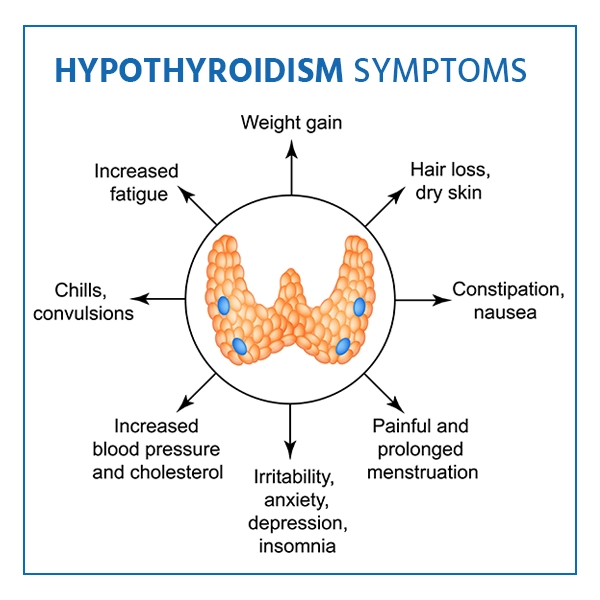
Hypothyroidism symptoms vary and may develop slowly, initially resembling depression. Common signs include fatigue, weight gain, cold sensitivity, dry skin, constipation, and muscle weakness.
- Weakness
- Irritability
- Depression
- Sensitivity to cold
- Dull facial expressions
- Hoarse voice
- Slow speech
- Droopy eyelids
- Puffy and swollen face
- Obesity
- Confusion
- Constipation
- Dry, coarse and sparse hair
- Coarse, dry, and thickened skin
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Slow pulse rate
- Muscle cramps
- Sides of eyebrows thin or fall out
Hypothyroidism symptoms in females
Women are more prone to having thyroid disease than men. Hypothyroidism symptoms in females are as follows:
Menstrual problems:
- It includes very light, heavy, or irregular periods Thyroid disorders can also stop your periods for many months or longer. This is a condition called amenorrhea.
- When thyroid problems affect the menstrual cycle in a woman, it also disturbs ovulation, thus making it difficult to get pregnant.
- Hypothyroidism during pregnancy can affect both the mother and the unborn baby.
- In a few cases, symptoms of thyroid disease are mistaken for menopause symptoms. Hypothyroidism is more likely to develop after menopause.
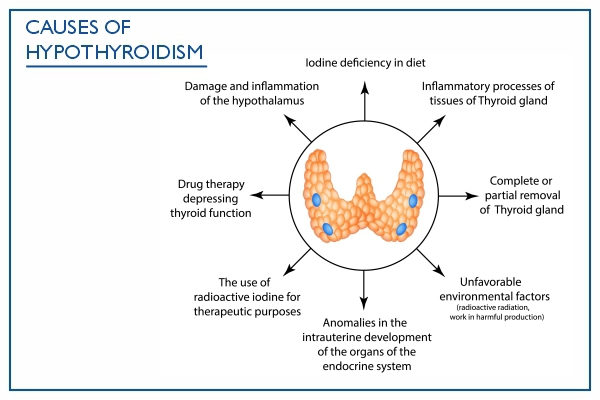
Hypothyroidism Causes
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce adequate hormones. The following conditions or problems can cause hypothyroidism:
- Autoimmune diseases: In rare cases, the immune system can mistake thyroid cells and enzymes as invaders, leading to a shortage of cells to produce enough thyroid hormones. This condition is more common in females. The main forms of autoimmune thyroiditis are Hashimoto's and atrophic thyroiditis.
- Thyroidectomy: For conditions like goiter, thyroid cancer, nodules, or Graves' disease, thyroidectomy may be necessary. Complete removal leads to hypothyroidism, while partial removal allows the gland to maintain hormone levels.
- Radiotherapy: Some cancer patients need to undergo radiotherapy involving the head and neck. This cancer treatment can affect the functioning of the thyroid gland, causing hypothyroidism.
- Congenital hypothyroidism (CHT): Hypothyroidism arises from ineffective thyroid gland development or function. Some newborns are born without a thyroid gland or have an incomplete one, including cases of ectopic thyroid. Thyroiditis, inflammation of the gland, results from autoimmune attacks or viral infections.
Risk factors of hypothyroidism
The risk factors involved are -
- Being a woman
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Thyroid surgery (thyroidectomy)
- Intake of certain medications
- Autoimmune disease
- Hereditary
- Old age
Hypothyroidism Diagnosis
The correct hypothyroidism test involves the following conditions.
- Medical history: If you have had any thyroid surgery or thyroid treatment, this may have an impact on the functional ability of your thyroid gland
- Physical examination: The thyroid specialists will examine your thyroid gland and look for symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as dry skin and hair, hoarse voice, droopy eyelids, swollen face, or a slower heart rate.
- Blood tests (thyroid function test, TFTs), including:
- TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) test
- T4 tests
- Imaging tests: Thyroid scan, radioactive iodine uptake test, or ultrasound scan.
Hypothyroidism Treatment
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: The primary treatment for hypothyroidism involves synthetic thyroid hormone like levothyroxine, effectively managing symptoms and restoring thyroid function.
- Individualized Dosage Adjustment: Treatment begins with an initial dose based on factors like severity, age, and weight, with adjustments made through regular monitoring to ensure effectiveness and minimise side effects.
- Consistent Medication Adherence: Consistency in medication intake is crucial, as missed doses or inconsistent usage can worsen symptoms due to fluctuating thyroid hormone levels.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Healthy habits like a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep can complement medical treatment for hypothyroidism, promoting overall well-being.
- Avoiding Interference with Medications: Consult a healthcare professional before altering medications or supplements to prevent potential interactions and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Prevention of Hypothyroidism
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc like seafood, dairy products, nuts, seeds, and whole grains to support thyroid function and reduce hypothyroidism risk.
- Manage Stress: Practise stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies to support thyroid health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity to support metabolism and overall well-being with a mix of cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises.
- Limit Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Minimise exposure to pollutants, pesticides, and heavy metals that can interfere with thyroid function by using natural cleaning products and filtering drinking water.
- Check Thyroid Function Regularly: Periodic blood tests can detect thyroid dysfunction early, especially with a family history or risk factors.
- Avoid Smoking: Quit smoking or avoid secondhand smoke to reduce the risk of autoimmune thyroid disorders.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Adopt a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet to achieve and maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of thyroid dysfunction.
