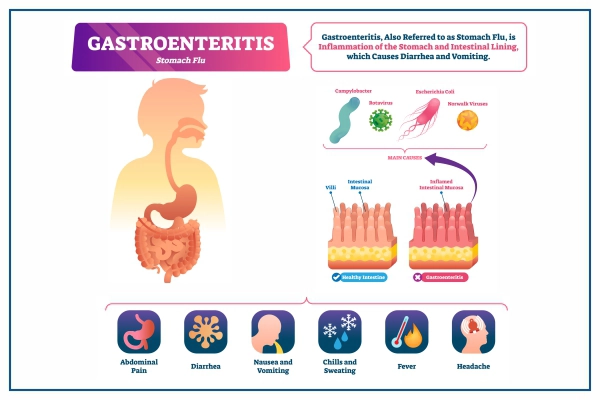
What is Gastroenteritis?
Gastroenteritis, also called gastro or infectious diarrhea, is due to inflammation or infection of the gastrointestinal tract, which comprises the stomach and intestine. Many people also refer to it as a "stomach bug," "stomach virus," or "stomach flu," but it is not influenza. Although most individuals complain of a painful stomach, it can also involve the small intestine and colon.
Symptoms of Gastroenteritis:
The symptoms of gastroenteritis can include:
Causes And Risks Factors of Gastroenteritis:
There are various gastroenteritis causes based on etiology, including
- Bacteria : Campylobacter bacterium
- Viruses : Norovirus, rotavirus, calicivirus, adenovirus and astrovirus.
- Parasites : Entamoeba histolytica, Cryptosporidium and Giardia lamblia
- Bacterial toxins : Bacterial micro-organisms themselves are not responsible for causing diseases, but the bacterial poisonous by-products can result in contaminated food. Specific staphylococcal bacterial strains generate toxins that can give rise to gastroenteritis.
- Chemicals : Lead poisoning can induce gastroenteritis
- Medications : Few medications, for example - antibiotics can trigger gastroenteritis.
Diagnosis of Gastroenteritis
Your doctor will record your medical history and ask for symptoms and past travelling history. He may further recommend some tests to find out the underlying cause. The gastroenteritis diagnosis is done as follows.
Diagnosis of Viral Gastroenteritis
- Stool electron microscopy
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR test)
- Enzyme-linked immunoassay (Elisa test)
- Latex agglutination test
Diagnosis of Bacterial gastroenteritis
- Microscopy
- Stool culture
- Biochemical reactions
- Serological typing
- Sigmoidoscopy
Treatment of Gastroenteritis:
Gastroenteritis treatment depends on the cause of the infection. The therapy usually followed is
- Drink plenty of fluids and oral rehydration drinks
- Hospital admission and intravenous fluid replacement, are required in critical cases.
- Antibiotics for bacterial gastroenteritis
- Antiparasitic drugs for infections by parasites
- Refrain from taking anti-vomiting or anti-diarrhoea drugs because these medicines will keep the infection inside the body. These drugs should be taken as per the doctor's prescription only.
Prevention of Gastroenteritis
- Proper handwashing with soap and water is recommended after using the toilet or changing a baby's nappies, after smoking tobacco, and after handling animals.
- Only use raw and cooked foods with the kitchen appliances if they have been adequately washed after each use.
- Breastfeeding babies instead of using substitute milk formula
- Keep all kitchen surfaces, utensils and appliances clean.
- Store cold food below 5 °C to keep it cool and keep hot food hot above 60 °C to prevent bacterial growth.
- Take care that the food is entirely cooked.
- Keep the toilet and bathroom clean.
- When travelling to other countries where sanitation is a problem, only drink purified bottled water.