What is Folic Acid Deficiency?
Folic Acid Deficiency is a condition that occurs when there is a lack of sufficient folate in the body. Folate is a type of B vitamin (B9) that is essential for the formation of red blood cells and DNA synthesis. It is found naturally in various foods, such as leafy green vegetables, fruits, beans, and fortified cereals.
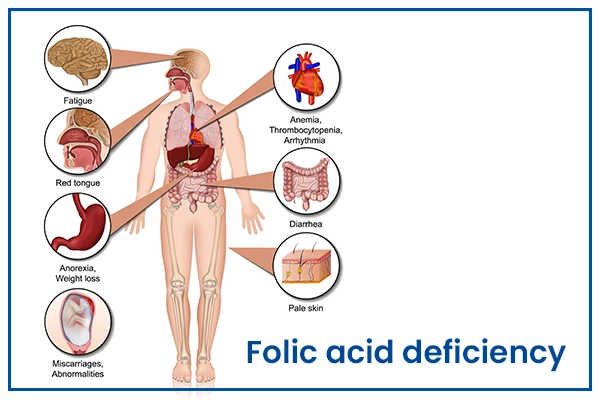
A deficiency in folic acid can lead to a range of health problems. Some common symptoms of folic acid deficiency include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin and a swollen tongue. It can also lead to anemia.
In pregnant women, folic acid deficiency can increase the risk of neural tube defects (spina bifida) in the developing fetus. This is why it is recommended for women planning a baby or in the early stages of pregnancy to take folic acid supplements.
Folic Acid Deficiency can be diagnosed through blood tests, and treatment typically involves taking folic acid supplements. It is also essential to increase the intake of foods rich in folate. In some cases, underlying medical conditions or medications may be contributing to the deficiency and may need to be addressed as well.
Causes of folic acid deficiency
There are several types of folic acid deficiency, which can be categorized based on the cause of the deficiency:
Dietary deficiency
This is the most common type of folic acid deficiency and occurs when a person does not consume enough folate-rich foods.
Malabsorption
Folic acid is absorbed in the small intestine, so conditions affecting nutrient absorption in this area can lead to folic acid deficiency. Such conditions include celiac disease,inflammatory bowel disease, and other malabsorption syndromes.
Increased demand
Some medical conditions, such as pregnancy, lactation, and certain types of cancer, can increase the demand for folic acid, leading to a deficiency.
Medications
Certain medications can interfere with the absorption and utilization of folic acid in the body, leading to a deficiency.
Alcoholism
Heavy drinking decreases folic acid from the body in a no. of ways, like damaging the gut lining, it increases urinary excretion of folic acid, liver and good bacteria in the gut are damaged, alcoholics are addicted to alcohol and avoiding eating folate-rich foods.
Genetic defects
Some genetic conditions, such as folate malabsorption syndrome and hereditary folate malabsorption, can impair the body's ability to absorb and use folic acid, leading to folic acid deficiency.
It's important to determine the underlying cause of folic acid deficiency to provide appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
Symptoms
The symptoms of folic acid deficiency can vary depending on the duration of the deficiency and its severity. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- Irritability
- Poor concentration
- Headaches
- Heart palpitations
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Diarrhoea
- Tongue swelling and tenderness
- Tingling sensation and numbness in the hands and feet
- Depression and anxiety
In pregnant women, folic acid deficiency can lead to complications such as neural tube defects in the developing fetus. Therefore, it's crucial to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, especially if you are pregnant or planning for pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Folic Acid Deficiency can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, laboratory tests and physical examination. The diagnosis of folic acid deficiency typically involves the following steps:
Medical history
The doctor will ask questions about your symptoms, medical history, and diet.
Physical examination
The doctor will do a physical examination to check for signs of anaemia or other health issues that may be causing your symptoms.
Blood tests
A simple blood test can determine the level of folic acid in your blood. The test may include a complete blood count (CBC) to check for anaemia and other blood disorders.
Other tests
If the doctor suspects an underlying medical condition or malabsorption syndrome is causing the deficiency, additional tests may be ordered, such as a small bowel biopsy,endoscopy, or colonoscopy.
It's important to discuss with your doctor any medications you are taking, as some medications can alter the absorption of folic acid in the body. In some cases, when a malabsorption issue causes the deficiency, additional medical treatment may be necessary.
Treatment for folic acid deficiency
The treatment for folic acid deficiency involves increasing your intake of folate, which is the natural form of vitamin B9. You can do this by eating foods that are high in folate, such as:
- Green leafy vegetables like kale and spinach.
- Beans and legumes, such as lentils and black beans
- Citrus fruits, such as oranges and grapefruits
- Fortified cereals and bread
- Liver and other organ meats (if you are not a vegetarian)
In addition to increasing your intake of folate-rich foods, your doctor may also recommend taking a folic acid supplement. The body more easily absorbs this synthetic form of vitamin B9. The recommended daily dose of folic acid for adults is 400 micrograms (mcg) per day. However, your doctor may recommend a higher dose if your deficiency is severe.
Points to remember to prevent folic acid deficiency
To prevent folic acid deficiency, you can take several precautions, including:
- Eating a healthy diet with balanced nutrition that includes plenty of folate-rich foods, such as leafy green vegetables, beans, legumes, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals.
- Taking a folic acid supplement if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. This is important because a deficiency in folic acid during pregnancy can lead to serious birth defects in the baby's brain and spine.
- Limiting your alcohol intake, as excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with folate absorption.
- Quit smoking, as smoking can also interfere with the absorption of folate.
- Treating any underlying medical conditions that may interfere with folate absorption, such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Avoiding medications that can interfere with folate absorption, such as certain anticonvulsant medications, methotrexate (used to treat cancer and autoimmune diseases), and sulfasalazine (used to treat inflammatory bowel disease).
It's important to discuss with your doctor to determine the underlying cause of your folic acid deficiency and address any other underlying health issues that may be contributing to the deficiency.