What is Epididymitis?
- Epididymitis refers to the swelling of the epididymis, a spiral tube positioned at the rear of the testicle. It can affect men of any age.
- Often, the inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection, particularly sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia.
- In certain instances, the inflammation might extend to the testicle itself, a state known as epididymal orchitis.
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhat are the Epididymitis symptoms?
Epididymitis symptoms and signs include:
- A bulging, heated, or red scrotum.
- Testicular soreness and tenderness often affect one side and develop over time.
- Urination that hurts or that is required urgently or frequently.
- Discharge from the penis.
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain or discomfort.
- A blemish on the sperm.
- Fever (less common).
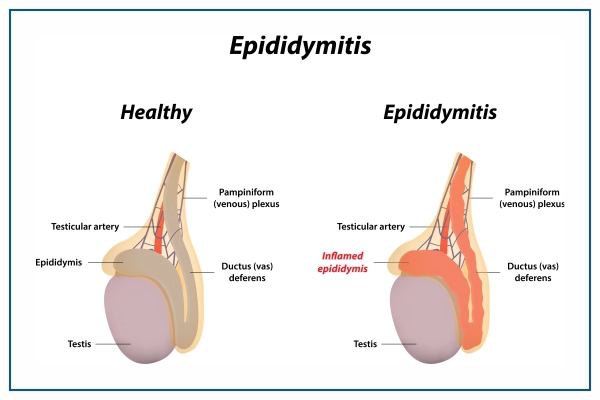
What are the Epididymitis causes?
There are several causes of epididymitis, such as
- STIs : In young, sexually active men, chlamydia and gonorrhoea are the leading causes of epididymitis.
- STDs : Sexually transmitted infections are also responsible for causing Epididymitis.
- Other infections : The epididymis can become infected with bacteria from prostate or urinary tract infections. Furthermore, epididymitis can be triggered by viral infections such as mumps.
- Chemical epididymitis : This condition emerges when urine flows backwards into the epididymis, often due to heavy lifting or straining.
- Physical injury : Damage to the groin area can lead to epididymitis as well.
What are the Complications of Epididymitis?
Complications include:
- An abscess or infection in the scrotum filled with pus can occur.
- Occasionally, this may lead to reduced fertility.
- When the infection spreads from the epididymis to the testicles, the condition is referred to as epididymal orchitis.
How to Diagnose of Epididymitis?
To diagnose Epididymitis, your physician will examine you for signs of swelling in the testicles on the side that is affected and swelling in the lymph nodes in the groin area. Additionally, a rectal examination might be conducted by your physician to check for any enlargement of the prostate or discomfort.
Your doctor might recommend several tests, including:
- STI Test : A small swab will be inserted into the tip of your penis to collect discharge, which will then be analyzed in a lab for signs of chlamydia and gonorrhoea.
- Blood and Urine Analysis : Tests will be carried out on your blood and urine to identify any irregularities.
- Ultrasound : Your doctor may advise you to have an ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion. If the blood flow to your testicles is higher or lower than normal, it would indicate torsion. Ultrasound with colour Doppler can assist in diagnosing this.
What is the Prevention of Epididymitis?
Practice safer intercourse to help prevent STIs that can lead to epididymitis.
If you have recurrent urinary tract infections or other risk factors for epididymitis, your doctor may go over additional methods of preventing a recurrence with you.
What is the Epididymitis treatment?
Treating epididymitis and epididymal-orchitis necessitates antibiotics. When a sexually transmitted infection is identified as the cause, your partner must undergo treatment as well. It's essential to finish the full course of antibiotics prescribed by your physician, even if you begin feeling better ahead of schedule.
You're likely to notice an improvement in your condition within 48 to 72 hours of starting antibiotic treatment. To alleviate discomfort, consider lying down, using a jockstrap for scrotal support, applying cold packs, or consuming analgesics. Your healthcare provider will likely schedule a follow-up visit to verify the infection has been fully cleared. Surgical intervention might be needed to drain an abscess if one forms. Additionally, if physical abnormalities are the root of the epididymitis, partially or fully removing the epididymis through surgery (epididymectomy) might become necessary.
