What is Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D3, commonly known as the "sunshine vitamin," has numerous health benefits. It aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus as it circulates through your bloodstream, which helps keep your bones strong. It aids in having a healthy innate immunity, as well as improving mood, heart health, and even weight loss. Vitamin D3 is cholecalciferol. It is the supplement that is taken by people who do not obtain enough vitamin D in their meals to stay healthy. If you constantly wear sunscreen, don't get much sun exposure, and/or have darker skin pigmentation, you may not obtain enough vitamin D.
Supplements may be a useful alternative for some people because few foods naturally contain the vitamin. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that aids calcium and phosphorus absorption in the body. It's critical to get enough vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus to build and maintain strong bones. Vitamin D is a nutrient that is used to cure and prevent bone problems (such as rickets, osteomalacia). When the skin is exposed to sunlight, the body produces vitamin D.
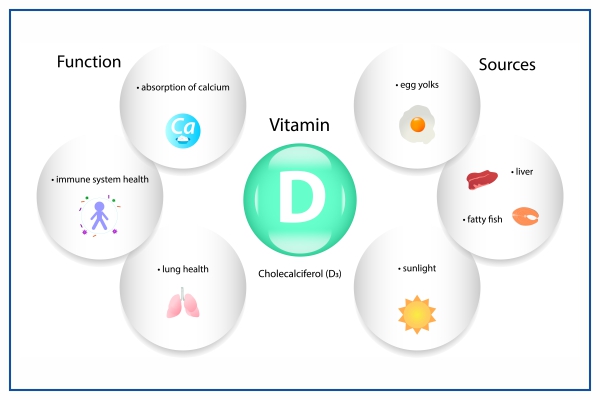
Vitamin D3 has multiple roles in the body:
- Maintain the health of bones and teeth
- Support the immune system, brain, and nervous system
- Regulate insulin levels and diabetes management
- Helpful in lung functioning and cardiovascular health
- Influence the growth of genes involved in cancer development
Health Benefits of Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 has multiple roles in the body:
- Vitamin D has been shown to benefit both muscles and bones. It improves calcium absorption in the small intestine. If you don't get enough vitamin D, your body will extract calcium from your bones to absorb it. This weakens the bones and increases the risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
- Vitamin D has been demonstrated to protect against acute respiratory infections and pneumonia in studies. During the COVID-19 pandemic, preliminary research suggested that vitamin D deficiency may increase the likelihood of infection as well as severe disease.
- Obesity and high blood pressure have been linked to reduced vitamin D levels, according to research. According to some studies, vitamins can help decrease blood pressure. Although some researchers have found that those with higher vitamin D levels have a higher risk of stroke and heart attack, clinical trials have not proved that supplementing with vitamin D reduces the risk.
- Women with adequate vitamin D3 levels reduced more body fat, had a smaller waist circumference, and dropped more weight.
- It is helpful to Reduce Risks of Flu
- Vitamin D3 deficiency in children can cause rickets. In adults, vitamin D deficiency manifests as osteomalacia or osteoporosis.
- Studies have shown a reverse relationship between blood concentrations of vitamin D3 in the body and the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Vitamin D3 is helpful for infants to become healthy. The deficiency has been associated with a higher risk and severity of childhood diseases and allergic diseases, asthma, atopic dermatitis.
- Pregnant women with the deficiency seem to be at greater risk of developing preeclampsia and needing a cesarean section. Also, this deficiency is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus and bacterial vaginosis in pregnant women.
- It is beneficial for Cancer Prevention. Vitamin D3 is extremely important for regulating cell growth and for cell-to-cell communication. Vitamin D3 helps reduce cancer progression by slowing the growth and development of new blood vessels in cancerous tissue, increasing cancer cell death, and by reducing cell proliferation and metastases.
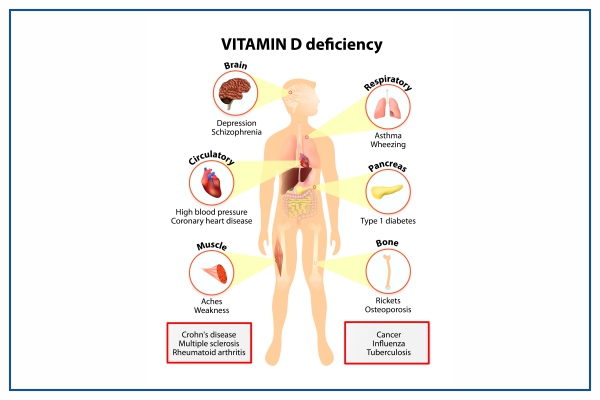
Deficiency of Vitamin D3
There are billions of people who go through Vitamin D deficiency. Symptoms that are associated with it are:
- Muscle weakness and aches
- Weak bones
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Depression
- Hypertension
- Inflammation
- Arthritis
- Eczema
How To Take Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D3 is a fat-soluble vitamin, it must be taken with fat for maximum absorption. It doesn't matter if you take it in the morning, afternoon, or evening, as long as you eat something with fat. Many organs in the body rely on it for development and appropriate functioning. You should aim to meet your daily vitamin requirements. If you don't receive enough vitamin D from your diet, take supplements.
When To Visit a Doctor?
If you're not sure if your vitamin D levels are enough, consult your doctor about getting a blood test and perhaps supplementing. It's probably preferable to receive your daily requirements from dietary sources, as it is with most other vitamins and nutrients.

