
Treading the zone of caution and noticing red strains during pregnancy can be scary! However, not all forms of bleeding are a cause for concern. Let’s know in detail.
Pregnancy bleeding
Any bleeding, including a spot of blood from the vagina, that occurs during the pregnancy is called bleeding during pregnancy.
Does bleeding always mean miscarriage?
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy that causes vaginal bleeding. This usually happens within the first 12 weeks of pregnancy (the first trimester), and most miscarriages have no obvious cause.
However, light vaginal bleeding during the first trimester (first 3 months) of pregnancy does not necessarily mean you're having a miscarriage; in fact, it is quite common! 90% of women experiencing bleeding during the first trimester tend to have a healthy baby.
Now the question is: If not miscarriage, then what causes pregnancy bleeding?
Other causes of bleeding during pregnancy
The causes of bleeding during pregnancy do not vary much from one woman to another. Here are some of the causes of this bleeding:
- Ectopic pregnancy: Vaginal bleeding during the first trimester can indicate an ectopic pregnancy. This is the stage at which the foetus begins to develop outside of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms include cramps, vaginal bleeding, and abdominal pain. A ruptured fallopian tube may cause pain. This is a medical emergency, and immediate surgery is needed.
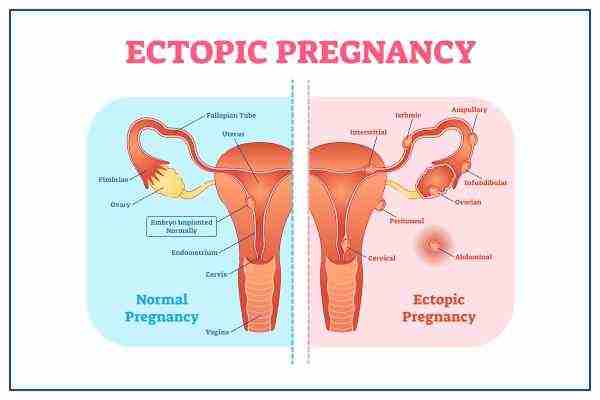
- Implantation bleeding: This is one cause of bleeding in early pregnancy which commonly manifests as light bleeding or spotting and occurs when the foetus implants (buries) itself into the lining of the womb.
- Placenta previa: This is a condition in which the placenta is implanted (wholly or partially) into the lower region of the uterus and covers the cervix. Bleeding after 28 weeks is one of the symptoms of placenta previa. Ultrasound is used to diagnose placenta previa.
- Placental abruption: This occurs when part or all of the placenta separates from the uterine wall prior to the delivery of the baby. In these cases, the treatment may include monitoring the mother and the baby, bed rest, or, in more serious cases, the early birth of the baby.
Are you sure it's bleeding or just spotting
Spotting during pregnancy (few droplets of blood), especially in the first trimester, is usually not a cause for concern, whereas bleeding is a continuous flow of blood that is more than a drop here and there.
If you notice spotting or bleeding, contact the doctor. To diagnose the cause, they may examine you or perform an ultrasound. It is important to be extra cautious to ensure the health of both you and your foetus (unborn baby).
How the bleeding during pregnancy is treated?
To diagnose the cause of the bleeding, the healthcare provider will perform an ultrasound and a physical exam. They may also ask for blood or urine tests, as well as additional imaging tests such as an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Some remedies for vaginal bleeding during pregnancy include:
- Relaxing and staying off your feet
- Avoiding sex
- Have bedrest
- Avoiding travel
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Get A Second OpinionWhen to see a doctor?
Normal pregnancy bleeding is usually not a cause of concern. However, if the bleeding is accompanied or followed by lightheadedness, contractions, fever, nausea, abdominal pain, or chills, and lasts for more than a few days, it is best to consult a doctor.
If you have already been told that your bleeding is normal, but if it becomes heavier, then it may not be normal. Seek medical help immediately!
Don't panic!
Let’s cherish every moment of pregnancy together :)
Secure your health with a second opinion. Make informed decisions and book your appointment today!
Book an AppointmentFrequently Asked Questions
PPH is heavy bleeding after birth. Normally about 200-500ml of bleeding is anticipated after delivery. If it exceeds 500ml it can affect the mother’s general health.
Certain women are at risk of developing PPH like:
- Placenta previa- where the placenta is located in the lower part of the uterus.
- Placenta abruption – when the placenta separates from the womb early.
- Twins or triplet pregnancy.
- Previous pregnancy with PPH.
- High BP in pregnancy.
- BMI>35.
- Prolonged labor, delay in delivery of the placenta, forceps, or vacuum application.
- Having large baby.
PPH is managed initially with medications to stop bleeding. A team of doctors will be involved in the case. Medications in the IV fluids are given, and blood transfusion and a second drip for extra IV fluids are started. If the bleeding continues, you will need to be taken into the theatre for procedures like balloon insertion in the womb to control bleeding, or laparotomy may be required as a lifesaving procedure.
There is an increased risk of PPH in future births and it is advised to have delivery in a tertiary care center to anticipate and manage PPH. You should take iron supplements to reduce the chance of becoming anemic.
You may become anemic, feel dizzy, and may still be tired, but you will recover with a good diet, iron supplements and rest.
