Knee Arthroscopy Treatment
Knee arthroscopy has become a commonly performed procedure in orthopedic surgery due to its advantages over traditional open surgery. It allows for smaller incisions, reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, faster recovery times, and potentially less postoperative pain.
Indications for Knee Arthroscopy:
Indications:
It is used to diagnose and treat a range of knee joint conditions, including:
- Meniscus Tears: Tears in the meniscus, the cartilage that cushions the knee joint, often causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears: A common knee injury involving a tear in the ACL, a ligament that stabilizes the knee joint.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tears: Tears in the PCL, another ligament that helps stabilize the knee.
- Cartilage Injuries: Damage or defects in the articular cartilage that covers the ends of bones in the knee joint, causing pain and joint dysfunction.
- Synovitis: Inflammation of the synovial membrane lining the knee joint, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Loose Bodies: Small fragments of bone or cartilage that become dislodged within the joint, causing pain and limited movement.
- Patellar (Kneecap) Disorders: Conditions like patellar chondromalacia (softening of cartilage), which leads to pain behind the kneecap.
- Tendon Injuries: Torn or damaged tendons, such as the patellar tendon or quadriceps tendon.
- Ligament Sprains: Mild to moderate sprains of various knee ligaments.
- Removal of Scar Tissue: After previous knee surgeries or injuries, scar tissue (adhesions) can develop and limit joint movement.
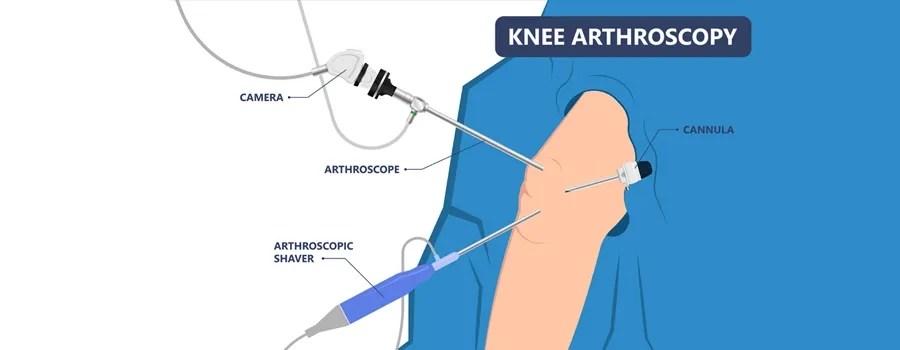
Steps involved in knee arthroscopy procedure
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows orthopedic surgeons to diagnose and treat various knee-related conditions. It involves using a small camera, called an arthroscope, along with specialized surgical instruments to visualize and address issues within the knee joint. Here are the general steps involved in a knee arthroscopy procedure
- Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is typically given anesthesia. Depending on the case, this could be local anesthesia (numbing only the knee area) or general anesthesia (making the patient unconscious).
- Incisions: The surgeon makes small incisions around the knee to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments. These incisions are usually less than half an inch in size.
- Arthroscope Insertion: The Arthroscope, a thin and flexible fiber-optic camera, is inserted through one of the incisions. This allows the surgeon to view the inside of the knee joint on a monitor.
- Inspection: Saline solution is pumped into the knee joint to expand it, creating more space for the surgeon to work. The arthroscope provides a clear view of the various structures within the knee, including the cartilage, ligaments, menisci, and synovial lining
- Diagnosis: The surgeon examines the knee joint to identify any issues, such as torn ligaments, damaged cartilage, inflamed synovium, or loose fragments.
- Treatment: Depending on the findings, the surgeon may perform various procedures to address the issues. Some common procedures include:
- Ligament Repair or Reconstruction: If a ligament (such as the anterior cruciate ligament, ACL) is torn, it may be repaired or reconstructed using sutures or grafts.
- Meniscus Repair or Trimming: Torn sections of the meniscus (c-shaped cartilage) may be repaired using sutures or removed through a procedure called meniscectomy.
- Cartilage Repair: Techniques such as microfracture, drilling, or cartilage transplantation might be used to stimulate the growth of new cartilage in damaged areas.
- Synovial Tissue Removal: If the synovium is inflamed (synovitis), it may be removed to alleviate symptoms.
- Loose Body Removal: Any loose bone fragments or cartilage that could cause pain or interfere with joint movement are removed.
- Closure: After completing the necessary procedures, the surgeon removes the arthroscope and other instruments. The saline solution is drained from the knee joint, and the incisions are typically closed with stitches or surgical tape.
- Recovery: The patient is taken to a recovery area, where they are monitored as they wake up from anesthesia. Depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient's condition, they might be allowed to go home the same day or need to stay in the hospital overnight.
- Postoperative Care: Patients are provided with instructions on how to care for their knee after the procedure. This often includes guidelines on rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as specific exercises and rehabilitation to aid in recovery and regain strength and mobility.
Who will Treat the knee arthroscopy procedure
Orthopedic surgeon:
A knee arthroscopy procedure is typically performed by an Orthopedic Surgeon who specializes in the treatment of musculoskeletal conditions and injuries, particularly those related to the bones, joints, ligaments, and tendons of the knee. Orthopedic surgeons are medical doctors who have received specialized training in orthopedic surgery and have expertise in performing a variety of surgical procedures, including arthroscopic surgeries.Within the field of orthopedic surgery, there are subspecialists who focus specifically on knee-related issues. These specialists are often referred to as knee surgeons or knee orthopedic surgeons. They have extensive experience in diagnosing and treating a wide range of knee conditions and injuries, and they are well-equipped to perform knee arthroscopy procedures.
Preparing for a knee arthroscopy procedure
- Consultation and Information Gathering: Attend a preoperative consultation with your orthopedic surgeon. During this visit, you'll discuss the procedure, its benefits, potential risks, and what to expect during the recovery period. Ask any questions you may have and ensure you fully understand the procedure.
- Medical Evaluation: Your surgeon will likely order various medical tests, such as blood work and possibly imaging tests (X-rays or MRI), to assess your overall health and the condition of your knee joint.
- Medication Review: Discuss your current medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, with your surgeon. They will advise you on which medications to continue taking before the procedure and which ones you might need to temporarily stop.
- Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke or consume alcohol, consider quitting or reducing these habits before the surgery. Smoking can affect your healing process, and alcohol can interact with anesthesia and medications.
- Fasting: Follow your surgeon's instructions regarding fasting before the procedure. Typically, you'll need to avoid eating or drinking anything for a certain period before the surgery to ensure a safe anesthesia experience.
- Preoperative Exercises: Engage in any preoperative exercises recommended by your surgeon or physical therapist. Strengthening the muscles around your knee can aid in your postoperative recovery.
- Arrangements for After Surgery: Arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure, as the effects of anesthesia might temporarily impair your ability to drive. Additionally, having someone to assist you at home during the initial recovery period is helpful.
- Comfortable Clothing: Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing on the day of the procedure. This will make it easier to change into a hospital gown and will be more comfortable afterward.
- Personal Items: Bring any necessary personal items, such as your identification, insurance information, and a list of your current medications.
- Notify Your Surgeon: Inform your surgeon of any changes in your health, including illnesses, infections, or fever, leading up to the surgery.
- Hygiene: Follow any instructions regarding preoperative cleansing of the surgical area, which might involve using an antiseptic solution or soap.
- Follow Fasting Guidelines: Abide by the fasting guidelines provided by your surgeon or anesthesiologist. Typically, you'll need to stop eating and drinking for a specific period before the surgery.
- Anesthesia Discussion: If you have concerns or questions about Anesthesia, discuss them with the anesthesia team during the preoperative visit.
- Follow Instructions: Your surgeon may provide specific instructions regarding medications, dietary restrictions, and other guidelines. Make sure to follow these instructions diligently.
- Mental Preparation: Take time to mentally prepare for the procedure. Stay positive and focus on the benefits of the surgery for your long-term knee health.
Recovery after knee arthroscopy procedure
Recovery after a knee arthroscopy procedure is a crucial phase that involves taking proper care of your knee, following your surgeon's instructions, and engaging in rehabilitation to ensure a successful outcome. While recovery experiences can vary based on the specific procedure performed and individual factors, here are general guidelines for what to expect during the recovery period:
- Immediate Post-Operative Period:
- You will spend some time in the recovery area as you wake up from anesthesia.
- Your knee might be wrapped in a bandage or brace to provide support and minimize swelling.
- Pain Management: You may experience some pain, swelling, and discomfort in the initial days after the surgery. Pain medications prescribed by your surgeon will help manage this.
- Weight-Bearing and Mobility: You'll be instructed on whether you can put weight on your operated leg and how to use crutches or a brace, if needed.
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
- Your surgeon will likely prescribe a physical therapy plan to help you regain strength, range of motion, and functionality in your knee.
- Rehabilitation exercises are crucial to prevent stiffness and promote proper healing.
- Dressings and Incision Care: Follow the dressing and wound care instructions provided by your surgeon. Keep the incisions clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress, remove stitches or staples, and adjust your treatment plan as necessary.
- Gradual Resumption of Activities:
- As your knee heals, you'll gradually increase your activity level under the guidance of your surgeon and physical therapist.
- Return to work and regular activities will depend on the nature of your job and your recovery progress.
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling and bruising are common after knee arthroscopy. Elevating your leg, applying ice, and wearing compression garments as advised can help reduce these symptoms.
- Rest and Patience: Adequate rest is essential for healing. Allow your body the time it needs to recover fully.
- Driving: You may need to avoid driving for a period of time, especially if your right knee (the leg used for driving) was operated on. Follow your surgeon's guidelines.
- Gradual Return to Sports and Activities: Your surgeon will guide you on when it's safe to resume sports and other strenuous activities. Return to these activities should be gradual and controlled.
Lifestyle changes after knee arthroscopy procedure
After undergoing a knee arthroscopy procedure, adopting certain lifestyle changes can aid in your recovery and contribute to the long-term health of your knee. Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider:
- Follow Rehabilitation Recommendations: Adhere to the rehabilitation plan prescribed by your surgeon and physical therapist. Engaging in recommended exercises and stretches will help regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in your knee.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients can support the healing process. Adequate protein intake is particularly important for tissue repair and recovery.
- Manage Your Weight: >Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on your knee joint. Excess weight can increase the risk of knee issues and hinder recovery.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports overall health and helps with tissue healing. Consult your healthcare provider regarding fluid intake guidelines.
- Protect Your Knee:
- Use supportive devices (crutches, braces) as instructed by your surgeon during the early stages of recovery.
- Avoid activities that could put unnecessary stress on your knee.
- Gradual Return to Physical Activities: Once cleared by your surgeon, gradually reintroduce physical activities and exercises. Always prioritize proper form and technique to prevent injuries.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: High-impact sports and activities can strain the knee joint. Consult your surgeon about what activities are safe and appropriate for your specific case.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any discomfort, pain, or signs of overexertion. Rest when needed and consult your healthcare provider if you experience persistent issues.
- Footwear and Orthotics: Wear supportive footwear that provides cushioning and stability for your feet and knees. Orthotic inserts might be recommended to help align your feet and knees.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Engage in regular exercise to promote overall health, but choose activities that are gentle on your knee joint.
- Refrain from smoking, as it can impede the healing process and elevate the likelihood of complications.
- Avoid Sitting or Standing for Prolonged Periods: Changing positions regularly can prevent stiffness and discomfort in your knee. Gentle movement is beneficial for recovery.
- Posture Awareness:
- Maintain good posture to avoid putting unnecessary strain on your knee joint.
- Maintain good posture to avoid putting unnecessary strain on your knee joint.
- Stay Informed: Learn about your specific condition and the limitations or precautions you should be aware of. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions.
- Follow Up with Your Surgeon: Attend all follow-up appointments and communicate any concerns or changes in your knee's condition.

