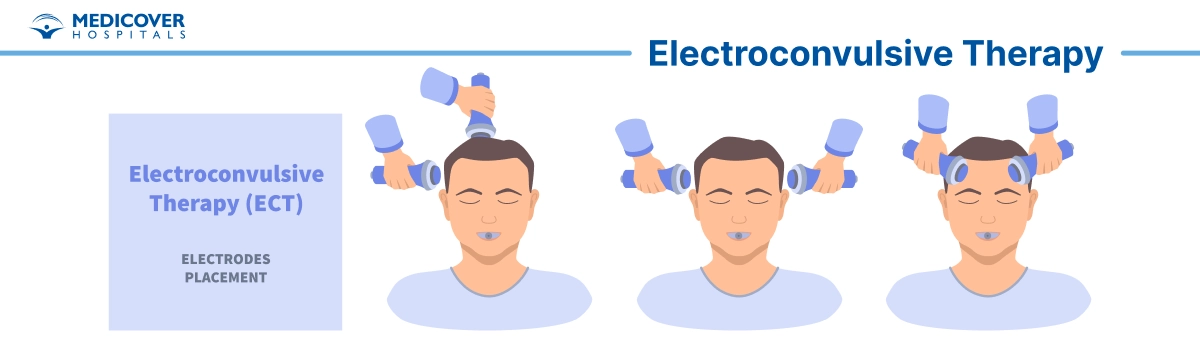
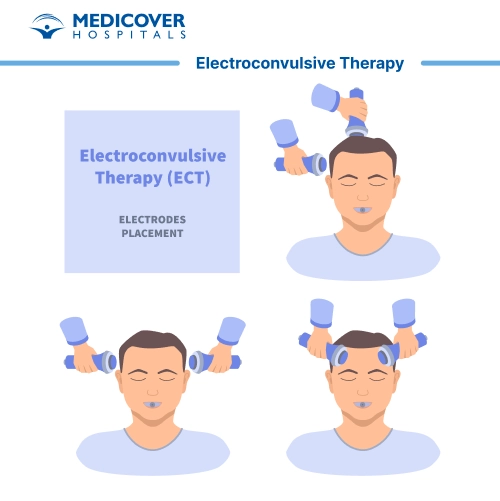
What is Electroconvulsive Therapy and its Purpose:
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical therapy that is used to treat serious mental illnesses, particularly when other interventions have proven ineffective. It involves inducing controlled seizures through the application of electric currents to the brain.
What They Do for Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive Therapy is administered under the guidance of a specialized medical team. This team typically includes a psychiatrist, an anesthesiologist, and a trained nurse. Their collaboration ensures the procedure's safety and effectiveness.
If you or a loved one is considering Electroconvulsive Therapy, it's imperative to initiate the process by consulting a psychiatrist or mental health professional. They will assess the severity of the condition, explore treatment options, and determine if ECT is a suitable course of action.
How to Prepare for Electroconvulsive Therapy
Effective preparation is essential for a smooth ECT experience. Here's how to prepare:
- Consultation: An initial consultation with a psychiatrist involves discussing your medical history, current mental health status, and potential risks and benefits of ECT.
- Medical Evaluation: A comprehensive medical evaluation, including blood tests and an electrocardiogram (ECG), might be conducted to ensure you're physically fit for the procedure.
- Medication Review: Your psychiatrist will review your medications and might make adjustments to optimize the ECT's effectiveness and safety.
- Anesthesia Discussion: An anesthesiologist will explain the anesthesia process, addressing any concerns you may have.
What Happens During Electroconvulsive Therapy
The ECT procedure is carried out with precision to ensure patient safety and efficacy:
- Anesthesia: A short-acting general anesthesia is administered to induce a temporary state of unconsciousness and muscle relaxation.
- Electrode Placement: Electrodes are strategically positioned on your scalp to deliver controlled electric currents to specific areas of your brain.
- Seizure Induction: The electric currents cause a carefully controlled seizure, which typically lasts for a brief period.
- Monitoring: Throughout the procedure, your heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels are closely monitored by medical professionals.
Recovery After Electroconvulsive Therapy:
The post-ECT recovery phase is crucial for optimal outcomes:
- Awakening: You will awaken in a recovery area under observation. As the anesthesia wears off, you might feel groggy.
- Memory: Some temporary memory loss or confusion is common immediately after ECT. This usually improves over time.
- Rest and Observation: You will remain in a recovery area for a brief period until you're alert and stable.
- Discharge: Once you're deemed fit for discharge, a responsible adult should accompany you home.
Lifestyle Changes After Electroconvulsive Therapy Procedure:
Post-ECT, certain lifestyle adjustments can contribute to your ongoing mental health:
- Support Network: Maintain a strong support system of friends, family, and mental health professionals to aid in your recovery.
- Medication Management: Continue following your psychiatrist's medication recommendations to manage your mental health.
- Therapy: Engage in therapy, such as individual or group counseling, to complement the effects of ECT.
- Healthy Habits: Prioritize sleep, exercise, and a balanced diet to support overall mental well-being.
- Open Communication: Stay in touch with your healthcare team, openly discussing any changes in symptoms or concerns.
Conclusion:
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) has emerged as a powerful treatment option for individuals confronting severe mental health conditions. By understanding the procedure, consulting a mental health professional, adhering to pre and post-procedure guidelines, and embracing positive lifestyle changes, you can embark on a path toward improved mental well-being. If you or someone you know is grappling with profound mental health challenges, exploring the potential benefits of ECT under the guidance of skilled professionals can offer renewed hope and a brighter future.
Citations
What is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) (Beyond the Basics)
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Electroconvulsive Therapy