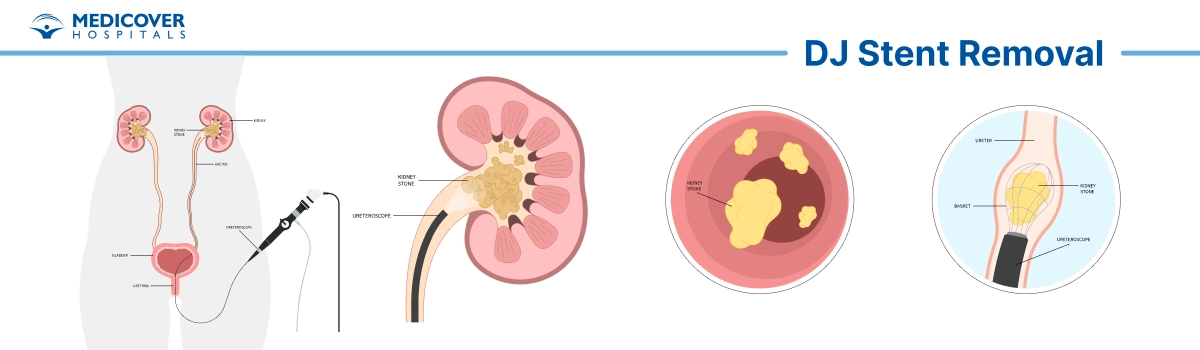
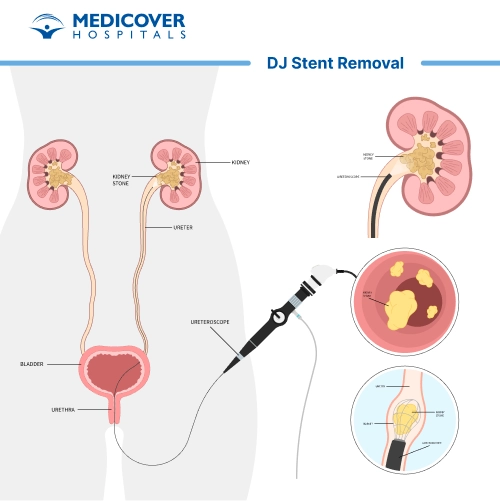
The Procedure
DJ stent removal is a relatively straightforward outpatient procedure, often performed in a urologist's office or a hospital setting. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient might be advised to drink fluids before the procedure to ensure the bladder is adequately filled. An empty bladder can make stent removal more uncomfortable.
- Anesthesia: Local or topical numbing agents may be applied to the urethra to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Cystoscopy: A thin tube with a camera and light on the end is inserted into the urethra and guided into the bladder. The cystoscope enables the urologist to visualize the stent and its positioning.
- Grasping and Removal: Using specialized instruments, the urologist gently gets the stent's retrieval string (a small tail attached to one end of the stent) and carefully pulls the stent out through the urethra.
- Confirmation: Once the stent is removed, the urologist may inspect the urinary tract to ensure that the stent was extracted fully and without complications.
Whom will treat for DJ Stent Removal
A DJ (double-J) stent is a medical device used to temporarily relieve obstruction in the urinary tract, often placed after procedures like kidney stone removal or surgery. The removal of a DJ stent is typically performed by a urologist, a medical doctor specializing in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the urinary system (including the kidneys, bladder, and urethra) and the male reproductive system.
If you have a DJ stent that needs to be removed, it's essential to contact your urologist or the medical professional who placed the stent. They will guide you on the appropriate timing for removal and the procedure itself. If you experience any discomfort, pain, or complications related to the stent, you should seek medical attention promptly.
How to prepare for DJ Stent Removal
I can provide you with general guidelines on preparing for DJ stent removal, but please note that you should always follow your doctor's specific instructions and advice. DJ stent removal is a medical procedure that involves the removal of a stent placed in the urinary tract to aid in the passage of urine. Here's what you can generally expect and how to prepare:
- Follow Doctor's Instructions: Your doctor will give specific instructions on when and how to prepare for the stent removal. Follow their advice closely to ensure a smooth procedure.
- Medications: If your doctor advises, you might be asked to take antibiotics before the procedure to prevent infection. Follow their medication instructions carefully.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids in the days leading up to the procedure can help keep your urinary tract well-lubricated and may make the removal process more comfortable.
- Pain Management: Discuss pain management options with your doctor. They might recommend taking over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribing medication to help manage discomfort after the procedure.
- Arrange Transportation: The procedure might involve mild sedation, which can impair your ability to drive afterwards. Arrange for someone to go you to and from the clinic or hospital.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable and loose-fitting clothing to the procedure, as this can help you feel more at ease.
- Empty Your Bladder: Before the procedure, empty your bladder. This can help your doctor during the removal process.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation to help calm any anxiety you may be feeling about the procedure.
- Ask Questions: Don't hesitate to ask your doctor if you have any concerns or questions about the procedure. Understanding what to expect can help ease your anxiety.
- Arrange for Rest: After the stent removal, you should take it easy for a day or two. Plan for some rest and light activity during your recovery.
Recovery and Aftercare
Following DJ stent removal, patients can expect discomfort and potential urinary symptoms, typically transient and should improve for a few days. Everyday experiences during recovery include:
- Urinary Symptoms: Patients might experience increased urgency, frequency, or mild burning sensations during urination. These symptoms should subside within a few days.
- Fluid Intake: Staying hydrated is crucial during recovery to flush out the urinary tract and prevent irritation.
- Activity: Patients are usually encouraged to avoid strenuous physical activities for a few days after the procedure to minimize the risk of irritation and discomfort.
- Follow-up: A follow-up appointment with the urologist may be scheduled to ensure proper healing and address any lingering concerns.
Considerations
Here are some important considerations related to DJ stent removal:
- Timing: DJ stents are typically removed a few weeks after the initial procedure. The exact duration may vary based on the patient's condition and the reason for stent placement.
- Medical Guidance: Patients should closely follow their urologist's stent removal and recovery recommendations. If any unusual symptoms arise, seeking medical attention promptly is advised.
- Expectations: While some discomfort is expected during stent removal and recovery, severe pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms should be reported to a healthcare professional.
- Individual Variability: Responses to DJ stent removal can vary widely among individuals. Some might experience minimal discomfort, while others might find the process more challenging.
Lifestyle changes after DJ Stent Removal
After removing a DJ (Double J) stent, a medical device often used to help treat kidney or urinary tract issues. There might be a few lifestyle changes or considerations to keep in mind as your body adjusts and heals. It's important to note that everyone's experience may be slightly different, and you should always follow your doctor's advice for a successful recovery. Here are some general guidelines:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help flush out your urinary system. Staying hydrated can also prevent the formation of kidney stones and aid in healing.
- Pain Management: Some discomfort or mild pain might persist after the stent removal. Your doctor might prescribe pain medications or recommend over-the-counter options to help manage this.
- Activity Level: While you may need to take it easy for a day or two after the stent removal, you can gradually return to your average activity level. Avoid strenuous exercises or heavy lifting for a week to give your body time to heal.
- Bathroom Habits: Pay attention to changes in your urinary habits, such as pain or discomfort while urinating, increased frequency, or urgency. These symptoms might indicate an infection or other issues and should be promptly addressed with your doctor.
- Diet: Maintain a balanced and healthy diet, including foods rich in fibre and nutrients. This can help prevent constipation, which might exacerbate any discomfort during recovery.
- Personal Hygiene: Practice good personal hygiene to prevent infections. Clean the genital area properly and avoid using harsh soaps or irritants.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Keep all follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider. They will monitor your recovery and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Painful Urination: It's normal to experience discomfort or a burning sensation while urinating after stent removal. This should improve over time, but consult your doctor if it persists or worsens.
- Monitoring: If you notice any unusual symptoms, such as fever, severe pain, excessive bleeding, or signs of infection (like cloudy or foul-smelling urine), contact your healthcare provider immediately.
- Medications: If you were prescribed antibiotics or other drugs, make sure to complete the entire course as directed by your doctor.