Indications of Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is recommended for various medical reasons when more information about the heart's anatomy, function, and blood flow is needed. Common indications include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): To assess the severity of blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries and determine the need for intervention.
- Angina or Chest Pain: To identify the cause of angina or chest pain, and evaluate blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): In emergency cases, to quickly diagnose the location and severity of blockages causing a heart attack.
- Valvular Heart Disease: To assess the function of heart valves, determine the degree of stenosis or regurgitation, and guide valve repair or replacement.
- Heart Failure: To evaluate heart function and identify any contributing factors such as blocked arteries or valve issues.
- Congenital Heart Defects: To diagnose and assess the severity of structural heart abnormalities present since birth.
- Arrhythmias: To locate abnormal electrical pathways causing arrhythmias and guide procedures such as catheter ablation.
- Unexplained Symptoms: To investigate unexplained symptoms such as shortness of breath or palpitations.
- Monitoring Progress: To monitor the progress of a previously placed stent or other cardiac interventions.
- Guidance for Surgery: To provide information before heart surgery or other interventions.
Steps involved in Cardiac catheterization:
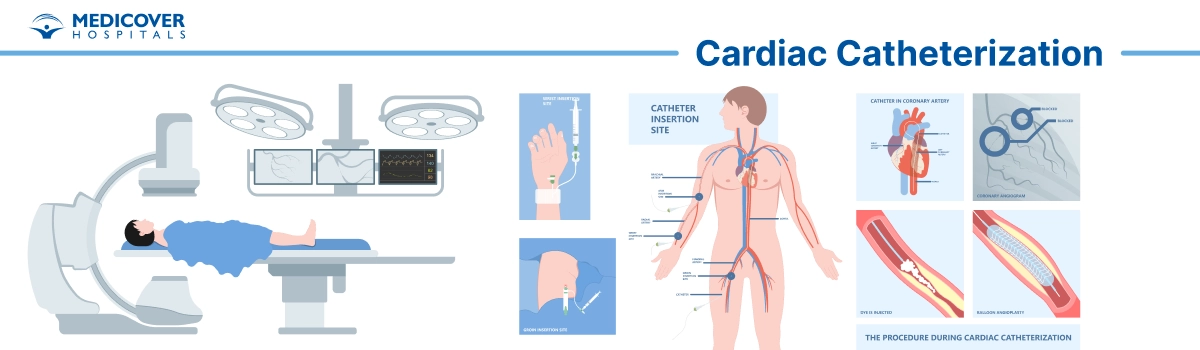
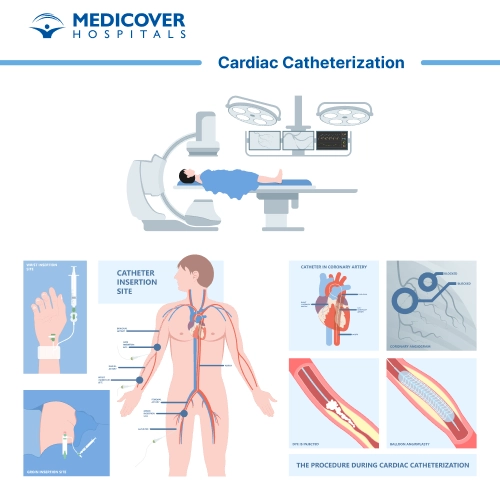
Cardiac catheterization, also known as coronary angiography or heart catheterization, is a diagnostic procedure used to visualize and assess the heart's blood vessels and chambers. It involves the insertion of a catheter into the blood vessels and heart to obtain detailed information about blood flow, pressure, and anatomy. Here are the general steps involved in a cardiac catheterization procedure:
- Preparation:
- The patient undergoes a thorough medical evaluation, including reviewing medical history, medications, and allergies.
- Fasting may be required before the procedure, usually starting at midnight the night before.
- Consent and Anesthesia:
- The patient meets with the healthcare provider to discuss the procedure, its risks, benefits, and alternatives. Informed consent is obtained.
- Local anesthesia is administered at the insertion site to numb the area. In some cases, sedation or general anesthesia may be used to keep the patient relaxed and pain-free.
- Insertion Site Preparation: The insertion site (usually the groin, wrist, or arm) is cleansed and sterilized to prevent infection.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter (a thin, flexible tube) is inserted through a small incision in the skin and advanced into the blood vessels. The catheter is guided using real-time X-ray imaging known as fluoroscopy.
- Guidewire Placement: A guidewire is threaded through the catheter and navigated to the desired location within the blood vessels or heart.
- Catheter Advancement: Over the guidewire, the diagnostic catheter is advanced to the target location, such as the coronary arteries or heart chambers.
- Contrast Injection and Imaging: A contrast dye is injected through the catheter into the blood vessels or heart chambers. This dye makes the blood vessels visible on X-ray images, allowing the healthcare team to visualize blood flow, blockages, and abnormalities.
- X-ray Imaging (Angiography):
X-ray
images (angiograms) are taken as the contrast dye flows through the blood vessels. The images provide detailed information about the blood vessels' condition, any narrowing (stenosis), and potential blockages.
- Pressure Measurements: Pressure measurements are taken using the catheter to assess blood pressure within different areas of the heart and blood vessels.
- Additional Procedures: Depending on the findings, additional procedures might be performed during the same catheterization, such as angioplasty and stent placement to treat blockages or valve assessments.
- Catheter Removal: Once the necessary information is obtained and any additional procedures are completed, the catheter is gently removed.
- Closure of the Insertion Site: The insertion site is typically closed using a closure device, sutures, or manual pressure to ensure proper healing.
- Recovery and Observation: The patient is taken to a recovery area and monitored as they wake up from anesthesia. Vital signs are checked, and any potential complications are addressed.
- Hospital Stay: Most cardiac catheterizations are performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home on the same day. In some cases, an overnight stay may be required for observation.
- Postoperative Care and Follow-Up:
- Patients receive instructions for recovery, including wound care, activity restrictions, and medication management.
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled to review the results, discuss treatment options, and plan for any necessary interventions.
Who will Treat the Cardiac Catheterization procedure
Cardiac catheterization procedures are typically performed by a specialized team of medical professionals in a specialized cardiac catheterization lab. Here are the key members of the team involved in performing cardiac catheterization:
- Interventional Cardiologist: An interventional cardiologist is a medical doctor with specialized training in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular
conditions using minimally invasive techniques. They are skilled in performing procedures such as cardiac catheterization, angioplasty, and stent placement.
- Cardiac Electrophysiologist (if needed): If the catheterization is performed to address arrhythmias, a cardiac electrophysiologist or a cardiologist with expertise in heart rhythm disorders may be part of the team.
- Cardiac Catheterization Lab Team: This team includes nurses, technologists, and other healthcare professionals who assist in preparing the patient, operating the equipment, and monitoring the patient during the procedure.
- Anesthesiologist or Nurse Anesthetist: If required, an anesthesiologist
or nurse anesthetist administers anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort during the procedure.
- Radiology Technologist: Radiology technologists operate the imaging equipment, such as fluoroscopy or X-ray machines, to guide the catheter to the correct position within the heart and blood vessels.
Preparing for Cardiac Catheterization procedure
Preparing for a cardiac catheterization procedure involves several steps to ensure a safe & successful experience. Here's a guide on how to prepare:
- Consultation and Education: Schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider to discuss the procedure, its purpose, and what to expect. Ask any questions you have and ensure you fully understand the process.
- Medication Review: Provide a list of all medications, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies. Your healthcare provider will advise you on which medications to continue or adjust before the procedure.
- Fasting Instructions: You'll likely need to fast (avoid eating and drinking) for a specified period before the procedure. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions carefully.
- Medical History and Allergies: Provide your complete medical history, including any allergies, to the healthcare team. This information is crucial for your safety during the procedure.
- Blood Tests: Your healthcare provider may order blood tests before the procedure to assess your kidney function and other health markers.
- Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, consider reducing or quitting before the procedure. Avoid alcohol for at least 24 hours before the procedure.
- Medication Adjustments: Your healthcare provider will guide you on any adjustments to your medications, especially if you take blood thinners or other medications that could affect the procedure.
- Arrange Transportation: Arrange for someone to drive you to and from the hospital or clinic on the day of the procedure, as you may be under the influence of anesthesia.
- Comfortable Clothing: Wear comfortable clothing that is easy to change out of for the procedure. You'll likely need to change into a hospital gown.
- Valuables and Jewelry: Leave valuables and jewelry at home to ensure they don't get lost or damaged during the procedure.
- Consent Forms: Review and sign any required consent forms after discussing the procedure with your healthcare provider.
- Follow Fasting Instructions: Adhere to the fasting instructions provided by your healthcare provider. This is essential to ensure accurate test results and safe anesthesia administration.
- Shower : Shower or bathe before the procedure to reduce the risk of infection.
- Mental and Emotional Preparation: Mentally prepare for the procedure by understanding its purpose and benefits. Manage any anxiety by discussing your concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Ask Questions: If you have any remaining questions or concerns, address them with your healthcare provider before the procedure.
Recovery after Cardiac Catheterization
Recovery after a cardiac catheterization procedure is generally smooth and relatively quick, especially for diagnostic procedures. However, there are some important considerations and steps to follow to ensure a successful recovery. Here's what you can expect after a cardiac catheterization:
- Immediate Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, you'll be moved to a recovery area where medical staff will monitor your vital signs and the insertion site for any signs of bleeding or complications.
- Bed Rest and Monitoring: You'll likely be instructed to lie flat and keep the leg or arm with the catheter insertion site straight for a certain period (usually a few hours) to prevent bleeding.
- Monitoring for Complications: Medical staff will closely monitor your heart rate, blood pressure, and the insertion site to ensure there are no complications.
- Hydration: Drinking fluids is important to stay hydrated and help flush out the contrast dye used during the procedure.
- Gradual Activity Resumption: Once your medical team gives the green light, you can gradually begin to move and sit up.
- Discharge Planning: If your procedure was diagnostic and went well, you may be discharged on the same day. Your doctor will provide instructions for post-procedure care and follow-up appointments.
- Wound Care: If the catheter was inserted through the groin, you'll receive specific instructions for caring for the insertion site to prevent infection and bleeding.
- Rest and Recovery: Listen to your body and take it easy for a day or two after the procedure. Avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting.
- Avoid Certain Activities: You might need to avoid activities that could strain the catheter insertion site, such as driving or intense physical activity, for a specified period.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Your medical team will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery, assess the results of the procedure, and discuss any further steps or interventions if needed.
- Report Any Concerns: If you experience persistent pain, bleeding, swelling, or any other concerning symptoms, contact your medical team promptly.
- Medication Management: Follow your doctor's instructions regarding medications. If you were prescribed any new medications, take them as directed.
- Return to Work: You can usually return to work within a day or two, depending on your job and how you're feeling.
- Gradual Resumption of Normal Activities: Over the next few days, you can gradually resume your usual activities as you continue to recover.
Lifestyle changes after Cardiac Catheterization
After undergoing a cardiac catheterization procedure, adopting certain lifestyle changes can contribute to your overall heart health and help maintain the benefits of the procedure. Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider:
- Heart-Healthy Diet: Focus on a Proper balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise as recommended by your healthcare provider. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the strain on your heart and improve cardiovascular health.
- Stop Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is one of the most beneficial steps you can take for your heart health.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limiting alcohol consumption supports heart health.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or mindfulness to promote heart health.
- Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications as directed by your doctor to manage conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or arrhythmias.
- Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Observe and manage your blood pressure and cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Diabetes Management: If you have diabetes, manage your blood sugar levels through a combination of diet, exercise, and medications as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, which supports overall cardiovascular health.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your heart health and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Limit Caffeine and Energy Drinks: Excessive caffeine consumption can contribute to heart palpitations and irregular heart rhythms. Limit intake if advised by your doctor.
- Read Labels: Pay attention to food labels for hidden sodium, sugar, and unhealthy fats that can impact heart health.
- Choose Heart-Healthy Cooking Methods: Opt for cooking methods like baking, grilling, steaming, or sautéing instead of frying.
- Social Support: Surround yourself with supportive friends, family, or support groups to help you stick to your heart-healthy lifestyle changes.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about heart health, the benefits of your procedure, and how to maintain a healthy lifestyle.