Skin Cancer: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Skin cancer, or skin neoplasm, is the uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis. The harmful UV radiation from the sun causes mutations in the DNA of skin cells, leading to genetic changes that result in faster cell division than normal, which then forms malignant tumors. Skin malignancy usually starts in the epidermis, which is made up of three main types of cells: squamous cells, basal cells, and melanocytes. Skin melanoma, a type of skin cancer, can develop from melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin.
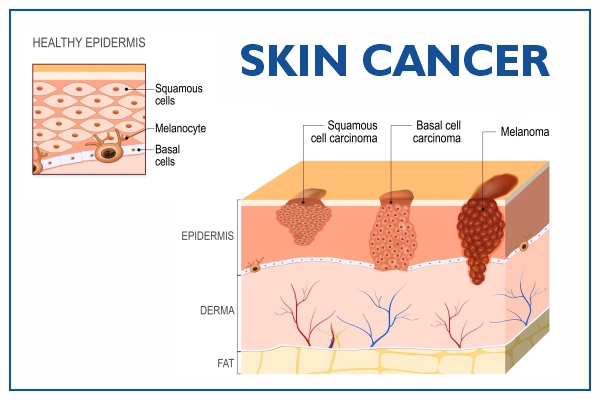
Skin cancer types
The most common skin cancer types are:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
This is a common type of skin cancer.
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is an abnormal, uncontrolled cell growth that originates from the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin (epidermis). It is commonly seen in fair skin people.
- These cancers primarily develop on skin parts exposed to the sun, such as the face, shoulders, ears, neck, hands, scalp, and back.
- However, BCC can appear anywhere in the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
- The cancer is usually caused by excessive, continuous exposure to the sun’s UV radiation.
- Early diagnosis and treatment for basal cell carcinoma are important as it can grow and penetrate the nerves and bones, resulting in serious health problems.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
The second most prevalent type of skin cancer is SCC.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is a multiplication of abnormal cells originating from the squamous cells in the epidermis.
- This cancer is common on sun-exposed skin areas such as the face, hands, neck and shoulders where the sun damage is visible, including wrinkles and age spots.
- Excessive, long-term exposure to the sun’s UV radiation and tanning beds are the main risk factors for most SCCs.
- If not detected and treated early, SCCs can expand rapidly and metastasize to other body parts.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a severe skin cancer because it can easily spread.
- Melanoma is a severe skin cancer because it can easily spread.
- Melanoma skin cancer grows from melanocytes, the skin cells that make melanin pigment. This pigment also gives skin its colour.
- Melanomas usually resemble moles and rarely may start from them. This cancer can occur on any body part in areas not exposed to the sun.
- Melanoma is often set off by intense and prolonged sun exposure resulting in sunburn. The use of a tanning bed also increases the risk for melanoma.
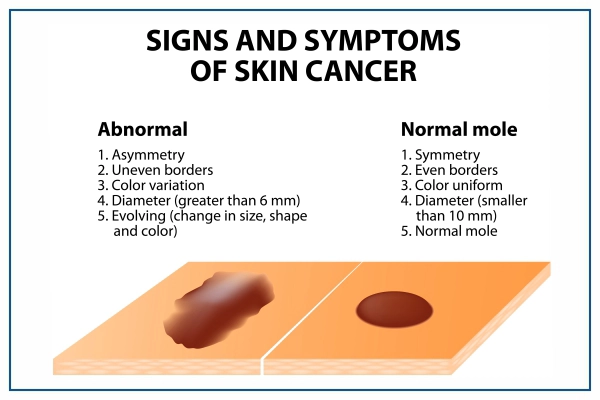
- The first sign of melanoma is changing the mole's appearance, which can be a mole cancer.
Other skin cancer types are:
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)
- Merkel cell carcinoma
- Sebaceous carcinoma
- Kaposi sarcoma
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionSkin Cancer Signs and Symptoms:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) symptoms:
- A smooth, small, pearl-type or waxy bump on the face, neck and ears.
- A flat, flesh-type brown-coloured sore on the trunk or arms and legs.
- Scars like appearance on the body.
- Lesions that are deep crusty and often bleed.
Squamous cell cancer (SCC) symptoms:
- A hard pink or red nodule.
- A bumpy, scaly lesion may cause itching, bleeding and a crusty surface.
Melanoma symptoms:
- The earliest indication of melanoma is a new mole or a change in an existing mole indicating a mole cancer.
- A mole that changes its appearance or that bleeds.
- A brown-pigmented skin patch or bump.
Causes of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer happens when skin cells grow abnormally, often due to damage in their DNA. The main skin cancer causes include:
- Too Much Sun Exposure: Strong UV rays from the sun can damage skin cells, increasing the risk of cancer.
- Tanning Beds: Artificial UV rays from tanning machines can also harm the skin and cause cancer.
- Fair Skin Tone: People with lighter skin have less melanin, making them more prone to sun damage.
- Family History: If someone in the family has had skin cancer, the chances of getting it are higher.
- Weak Immune System: Conditions like HIV or certain medicines that suppress immunity can increase the risk.
- Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: Regular contact with chemicals like arsenic, coal tar, or industrial substances can lead to skin cancer.
- Frequent Sunburns: Getting sunburnt often, especially in childhood, can make a person more likely to develop skin cancer later in life.
When to see a doctor?
Take a doctor's appointment if you are suspicious about certain skin changes. All skin changes are not due to skin cancer and your skin doctor will inspect the skin alterations to find the exact cause.
- The area where the skin cancer begins helps decide its type and treatment options.
- The chief cause of skin cancer is the extreme exposure to sunlight, mainly when it can cause sunburn and blistering of the skin. The sun’s UV rays are damaging as it affects the DNA in the skin cells, resulting in abnormal cells forming. The mutated DNA results in unusual cell division, forming a malignant tumour.
- The other cause of skin cancer is regular skin contact with few chemicals, such as tar and coal.
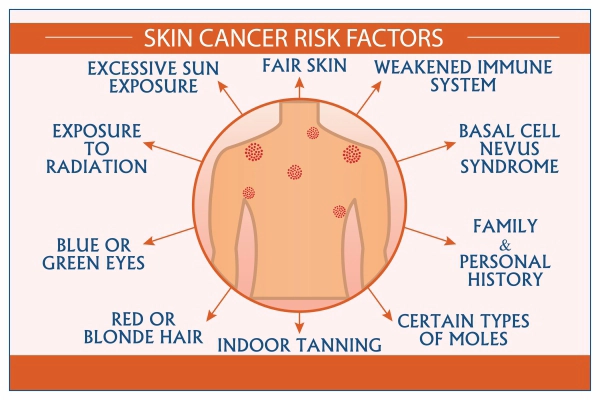
Skin Cancer Risk Factors
The risk factors of skin cancer include:
- Fair skin
- Moles
- History of sunburns
- Sunny or high-altitude climates
- Extreme sun exposure
- Hereditary
- Personal history of skin cancer
- Precancerous skin lesions
- Weak immune system
- Radiation exposure
- Exposure to arsenic substances
- Old age
Preventions of Skin Cancer
- Avoid sunburns, as it greatly increases the risk of having skin cancer, mainly for children.
- Spend less time in the midday sun because the sun's rays are quite high during the midday time.
- Get a shade to protect yourself from UV rays. But remember that trees, canopies and umbrellas do not provide complete sun protection.
- Wearing protective clothing, sunglasses, and wide hats protect from strong UV light.
- Don’t forget to use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on the exposed skin and use it again every two hours.
How is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
To diagnose skin cancer, the dermatologist may ask about any changes in existing moles or other skin spots, and also check for any new abnormal skin growths. They will look for symptoms related to skin cancer as part of the skin cancer diagnosis. If any skin lesion seems suspicious, a biopsy test may be suggested. The doctor might also recommend a blood test to check the person's overall health.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Skin Cancer Treatment
The treatment options for cancer of the skin and the precancerous skin lesions called “actinic keratoses” are different, and it may also depend on the type, size, depth and location of the lesions.
Other treatment methods for skin cancer may include::
- Freezing: The doctor may kill actinic keratoses and a few small, early stage skin cancer cells with liquid nitrogen (cryosurgery).
- Excisional surgery: The skin doctor cuts out the malignant tissue and a small nearby portion of healthy skin.
- Mohs surgery: It is performed for major, recurring or severe skin cancers. This surgery allows removal of cancerous cells without taking out most of the nearby healthy skin.
- Curettage, electrodesiccation or cryotherapy: When most abnormal growth has been removed, the doctor will scrape away cancerous cell layers with a circular blade (curet). The other device, an electric needle, eliminates the remaining tumour cells.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy or radiotherapy makes use of high doses of ionising radiation to destroy cancerous cells and shrink tumours. This therapy is preferred when surgery cannot completely eliminate cancer.
- Chemotherapy: It is preferred for treating cancers present at the outermost skin layer. Creams or lotions consisting of anti-cancer agents are applied directly to the affected skin. Anti-cancer drugs (systemic chemotherapy) can be used to treat skin cancers that have metastasized throughout the body.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT): This therapy destroys malignant cells by using a collaboration of a light sensitising drug and a very bright light.
- Biological therapy: Biological therapy for skin cancer consists of substances from living organisms that stimulate the body's immune system to fight cancer cells. This therapy includes immunotherapy and other targeted therapies and is far easier to tolerate than chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Care at Medicover Hospitals
At Medicover hospitals, we have the most reliable medical team of oncologists and dermatologists who design a personalised treatment pathway for each patient. We adopt a holistic approach in managing skin cancer with the active participation of healthcare specialists from different departments with their unique expertise to address the disease for complete treatment, recovery and wellness. To cure skin cancer, we explore all the avenues as per unique patient requirements and design a customised treatment pathway keeping the patient and the family informed at every stage of the treatment. Utilising the latest diagnostic tools and techniques and the most advanced cancer care methodology, we ensure to offer the best possible treatment outcomes.
Still have questions? Speak with our experts now!
040-68334455Frequently Asked Questions
What is early-stage skin cancer?
Early-stage skin cancer refers to abnormal skin cell growth that is confined to the outer layers of the skin. It is often treatable with minimal procedures if detected early.
Is skin cancer treatable?
Yes, skin cancer is treatable, especially when diagnosed early. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted medications, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Are skin cancers painful?
In the early stages, skin cancer is usually painless. However, as it progresses, it may cause itching, tenderness, bleeding, or discomfort, especially if it spreads deeper into the skin.
Can skin cancer cause death?
Yes, if left untreated, skin cancer can spread to other organs and become life-threatening. However, early detection and treatment significantly improve survival rates.
What is the final stage of skin cancer?
The final stage, known as Stage 4 skin cancer, occurs when cancer has spread to distant organs such as the lungs, liver, or brain. At this stage, treatment focuses on slowing progression and managing symptoms.
