Scabies: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Written by Medicover Team and Medically Reviewed by Dr Koppisetti Satya Naga Ravi Teja , Dermatologist
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin, triggering intense itching and rashes. It commonly affects areas like the wrists, elbows, waist, and between fingers.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help ease discomfort, stop the spread, and protect both personal health and the well-being of close contacts.
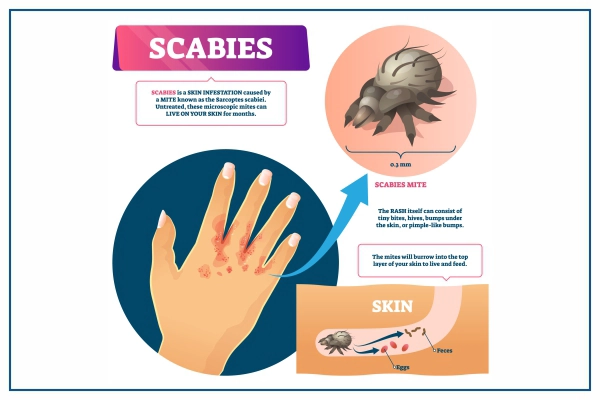
What are the Scabies Symptoms and Warning Signs?
Scabies signs and symptoms include:
- Itching, often severe and usually worse at night
- Thin, wiggly lines with tiny blisters or bumps on the skin.
The tracks usually show up in skin folds. Scabies infections are mostly found in adults and older kids, but it can be found anywhere on the body.
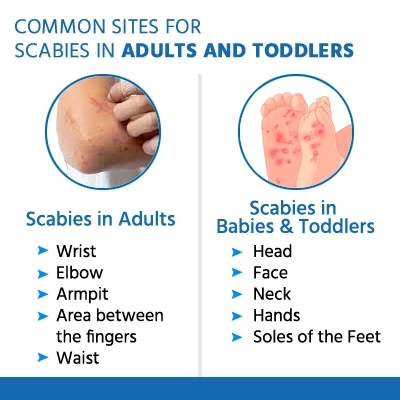
In grown-ups and older kids, scabies usually appears
- Between the fingers
- In the armpits
- Around the waist
- Along the insides of the wrists
- On the inner elbows
- On the soles of the feet
- Around the breasts
- Around the male genital area
- On the buttocks
- On the knees
What Are the Different Types of Scabies?
Most cases of scabies fall under a single medical condition caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. However, in some cases, scabies may appear in different forms based on severity and the individual's immune response:
Classic Scabies
This is the most common type, causing intense itching and a rash, usually between fingers, wrists, elbows, and other warm skin folds.
Crusted Scabies (Norwegian Scabies)
A severe form seen in people with weakened immunity. It features thick crusts of skin filled with mites and is highly contagious.
Nodular Scabies
Some individuals develop firm, itchy nodules, especially in the groin or underarms, even after treatment, due to a strong immune reaction.
What are the Common Causes and Risk Factors of Scabies?
Scabies infections are typically transmitted through prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
It can also spread through sharing infested bedding, towels, or clothing.
Common causes of scabies include
- Close contact with an infected person
- Sharing infested items
- Crowded living conditions
- Compromised immune system
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionHow Scabies is Diagnosed?
Diagnosing scabies begins with understanding your symptoms and checking for tell-tale signs like persistent itching and skin rashes. Since scabies can resemble other skin issues, a proper medical evaluation is crucial for accurate identification and effective treatment. Early diagnosis not only eases discomfort but also prevents it from spreading to others.
At Medicover, our dermatology team follows a patient-friendly, thorough diagnostic process that includes:
- Visual Examination: A dermatologist carefully examines affected areas for burrows, rashes, or skin lesions typically seen in scabies.
- Ink or Burrow Test: A special ink or dye may be applied to the skin to highlight mite tracks under magnification.
- Skin Scraping: A painless scraping of the skin is done to check for mites, eggs, or waste under a microscope.
- Dermatoscopy: This non-invasive imaging tool magnifies the skin, helping specialists identify mites and burrows without scraping.
- Rule-Out Testing: In cases where symptoms are unclear, tests may be done to rule out eczema, dermatitis, or fungal infections.
What are the Treatment Options for Scabies?
Scabies is a skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin, triggering intense itching and discomfort. Fortunately, it's fully treatable with proper care. Early and complete treatment helps you recover faster and prevents the mites from spreading to family members.
At Medicover, our dermatology specialists tailor your treatment based on the severity and spread of the infection. Here's what we typically offer:
- Topical Medications:
- Permethrin cream: Applied from neck to toe and left overnight to kill mites.
- Sulphur ointment or benzyl benzoate: Used when permethrin is unsuitable, especially for infants or pregnant women.
- Oral Medications:
- Ivermectin: A single-dose pill used in moderate to severe cases or when topical treatments don't work.
- Antihistamines:
- Help control the intense itching, especially during nighttime.
- Antibiotics (if needed):
- Prescribed in case of secondary infections due to excessive scratching.
Recovery Timeline
- Itching may persist for 2-4 weeks even after mites are killed this is normal and manageable.
- Most patients feel better within 1 to 2 weeks of starting treatment.
Ensuring everyone in close contact is protected. With hygienic environments, expert follow-up, and compassionate care, we focus on complete skin health and long-term comfort.
When to See a Doctor?
If you've been experiencing persistent itching especially at night along with red bumps, rashes, or burrow marks, it's time to consult a doctor. These symptoms could indicate scabies or another skin condition that needs timely care.
You should see a specialist immediately if:
- Itching has lasted more than a week and is worsening.
- You've developed open sores or notice signs of infection like swelling or pus.
- Someone in close contact with you has been diagnosed with scabies.
- You belong to a high-risk group such as infants, elderly, or immunocompromised individuals.
At Medicover Hospitals, our dermatologists ensure quick diagnosis and personalised treatment plans for scabies.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
What Is the Recovery Process After Scabies Treatment?
Recovering from scabies involves more than just applying medication and it's about caring for your skin, maintaining hygiene, and avoiding reinfestation. After treatment begins, itching and irritation may continue for up to 2-4 weeks
Follow-up schedule
- A review is usually recommended within 1-2 weeks after starting treatment.
- In cases with persistent symptoms or infections, further evaluation may be needed.
Skincare after treatment
- Use gentle moisturisers to reduce dryness and soothe irritated skin.
- Avoid scratching to prevent secondary bacterial infections.
Lifestyle tips
- Wash all clothes, bed linens, and towels in hot water and dry on high heat.
- Items that can't be washed should be sealed in a plastic bag for at least 3 days.
- Clean household surfaces and vacuum thoroughly to eliminate mites from the environment.
Dietary guidance
- While there's no specific scabies diet, staying hydrated and maintaining good nutrition supports faster skin healing.
Long-term outlook
- With timely treatment and proper hygiene, full recovery is expected. Reinfestation can occur if close contacts are not treated simultaneously.
What Precautions Can Help Prevent Scabies?
Scabies is highly contagious and spreads through direct skin contact or shared personal items. Preventive measures are key, especially in households, schools, or healthcare settings. At Medicover, we promote proactive prevention to safeguard families and communities.
Prevention Tips
- Avoid close physical contact with someone showing symptoms of scabies.
- Do not share towels, bedding, or clothing, especially during outbreaks.
- Maintain regular personal hygiene and frequent washing of clothes and linens.
- After confirmed exposure, consider preventive treatment for all household members.
- Schedule regular skin check-ups, especially in crowded living environments or high-risk settings.
Potential Complications If Untreated
- Secondary infections such as impetigo or cellulitis from excessive scratching.
- Crusted (Norwegian) scabies in people with weakened immunity, this severe form is highly contagious and hard to treat.
- Prolonged discomfort due to itching and skin inflammation.
- Psychological effects like sleep disturbance or anxiety from persistent irritation.
Our Experience Treating Scabies
At Medicover, we care deeply about the comfort and well-being of every patient who walks through our doors.
Our dermatology specialists understand the discomfort and distress scabies can cause, and we work with compassion to offer quick relief and long-lasting solutions.
