What is Diverticulosis?
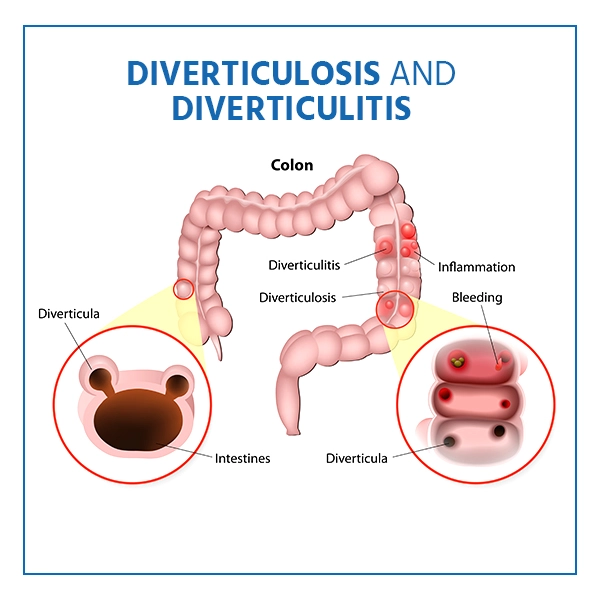
Diverticula is a condition when tiny, bulging pouches form in the lining of the digestive system. They are discovered in the lower area of the large intestine (colon). The chances of getting diverticula are frequent after the age of 40 but they rarely cause difficulties.
Diverticulosis is the presence of diverticula. It is a disorder that occurs when one or more of the pouches become inflamed and infected. It can result in severe stomach pain, a fever, nausea, and a significant change in bowel patterns. Let us discuss what are the symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment for Diverticulosis in detail.
Symptoms of Diverticulosis
The signs and symptoms of diverticulitis are as follows:
- Pain in the side and back, below the ribcage, is severe and intense
- Pain in the lower abdomen and groyne that radiates
- Urinating causes pain or a burning sensation.
Other signs and symptoms may include:
Causes of Diverticulosis
Diverticulitis is caused by a tear in the diverticula, which causes inflammation and, in some circumstances, infection. Diverticula form when naturally weak areas of the colon give way under strain. Marble-sized pockets develop through the colon wall due to this.
Risk Factors of Diverticulosis
The following factors may increase the risk of developing diverticulitis:
- The risk of this increases with age, it can occur after 40 mostly.
- Being overweight increases the chances of getting diverticulitis.
- People who smoke cigarettes very often are more likely to get diverticulitis.
- Lack of physical activity and inactiveness will increase the risk.
- A diet that has low fibre and a high intake of animal fat might increase the risk.
- Some medications such as steroids, opioids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs might cause this.
How is Diverticulosis diagnosed?
Acute diverticulitis is frequently detected during a flare-up. Abdominal discomfort can be a sign of a variety of issues, your doctor will need to rule out other possibilities.
Your doctor will begin by performing a physical examination, which will include a check for soreness in your abdomen. A pelvic examination is usually performed on women to rule out pelvic illness.
Following are some tests the doctor will prescribe:
- Tests of the blood and urine to look for evidence of infection.
- A pregnancy test is used to rule out pregnancy as a cause of abdominal pain in women of childbearing age.
- To rule out liver-related causes of stomach pain, a liver enzyme test is performed.
- In those who experience diarrhea, a stool test is used to rule out infection.
Treatment for Diverticulosis
Treatment is determined by the severity of your symptoms and signals.
Diverticulitis with no complications
If your symptoms are minor, you may be able to receive treatment at home. The following are likely to be suggested by your doctor:
- Antibiotics are used to treat infections, while updated guidelines say that they may not be necessary in very mild instances.
- For a few days, stick to a watery diet while your bowels heal. You can gradually add solid meals to your diet as your symptoms improve.
Most persons with simple diverticulitis respond well to this medication.
Diverticulitis with complications
If you have a serious attack or other health concerns, you will almost certainly need to be admitted to the hospital. In general, treatment entails
- Antibiotics given intravenously
- If an abdominal abscess has formed, a tube is inserted to drain it.
Surgery
If you have diverticulitis, you'll probably require surgery in case
The two most common types of surgery are:
- Resection of the primary bowel: The surgeon disconnects the healthy parts of your intestine after removing the diseased segments. You will be able to have regular bowel motions and may need open surgery or a minimally invasive technique, depending on the severity of the inflammation.
- Resection of the bowel with colostomy: The surgeon will perform a colostomy if the inflammation is so severe that rejoining your colon and rectum is impossible. The healthy part of your colon is connected to an opening in your abdominal wall. Waste is deposited in a bag through the aperture. The colostomy may be reversed and the colon rejoined once the irritation has subsided.