What Is Anemia?
Anemia is a blood disorder in which there are fewer red blood cells than the normal level or has less amount of hemoglobin than normal in each red blood cell. In any case, less amount of oxygen is carried in the bloodstream around the body. Red blood cells (RBCs)carry oxygen to the body tissues using a particular protein called hemoglobin. Anemia is not a disease, but it is a malfunction in the body. Anemia is a common blood condition, particularly in females. It is observed that around one in five menstruating women and half of all pregnant women are anemic.
Anemic individuals may have RBCs that consist of an abnormal shape or that appear normal, larger than normal, or smaller than normal. Here you can find all the types of Anemia, symptoms, causes, complications, diagnosis and different types of treatments for Anemia.
Types of anaemia
- Iron-deficiency Anemia: Common type caused by insufficient iron, often due to blood loss or pregnancy. Treatable with iron tablets and a diet rich in iron.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Inherited disorder leading to crescent-shaped red blood cells, causing stickiness and impaired blood flow.
- Normocytic Anemia: Normal-shaped red blood cells are insufficient, resulting from impaired production or chronic infections and diseases.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Low hemoglobin from red blood cell destruction, increased catabolism, reduced production, and heightened bone marrow efforts.
- Fanconi Anemia: Rare inherited disorder impacting bone marrow, leading to the failure to produce various blood cells, serious birth defects, and a risk of leukemia.
- Megaloblastic Anemia (MA): Macrocytic type with unusually large, structurally abnormal red blood cells (megaloblasts), primarily caused by deficiencies in folic acid or vitamin B12.
- Pernicious Anemia (PA): Megaloblastic Anemia resulting from vitamin B12 deficiency, an autoimmune disorder affecting absorption due to the lack of intrinsic factors.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second Opinion
Anaemia symptoms
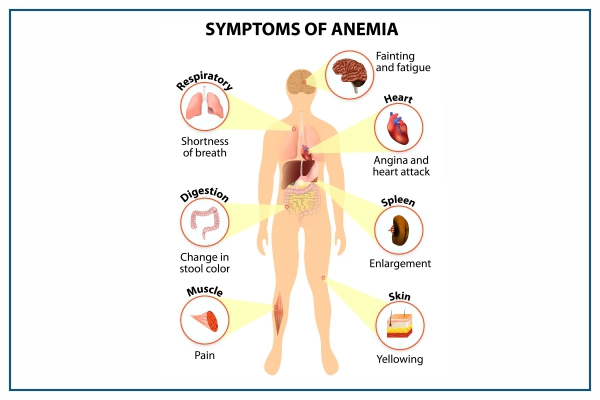
Anemia symptoms are signs that show up when your body doesn't have enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin to carry oxygen properly. Knowing these signs is important for finding out if you have anemia and getting the right help. In this guide, we'll talk about what to look for if you think you might have anemia and what you can do to feel better.
- Weakness
- Tiring easily
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Frequent headaches
- Palpitations
- Irritational behaviour
- Difficulty concentrating
- Cracked or reddened tongue
- Loss of appetite
- Strange food cravings
Causes of Anaemia
Anaemia can be congenital or due to a condition you develop (acquired). Anaemia is observed when the blood has insufficient red blood cells.
The reasons are -
- Less red blood cell production
- The most common type of Anemia is iron-deficiency Anemia. It occurs due to low levels of iron in the body.
- Nutrition is devoid of vitamin B12, or the body is unable to absorb Vitamin B12 in case of pernicious Anemia.
- Foods do not have folic acid or folate, or the body is unable to utilize folic acid properly resulting in folate-deficiency Anemia.
- Genetic blood disorders like sickle cell Anemia or thalassemia.
- Conditions that cause red blood cell destruction cause hemolytic Anemia.
- Chronic diseases involve fewer hormones that do not produce enough red blood cells.
- Loss of blood due to other health conditions like hemorrhoids, ulcers or gastritis.
Anaemia Risk factors
- Poor nutrition: A nourishment deficient in certain vitamins and minerals increases the risk of Anemia.
- Gastrointestinal problems: A gastrointestinal disorder that affects the absorption of the nutrients in your small intestines, for example, Crohn's disease and celiac disease increase Anemia risks.
- Menstruation: Menstrual women who haven't yet reached menopause have a greater risk of iron deficiency Anemia. Menstruation results in the loss of red blood cells.
- Pregnancy: Anemia in pregnancy is due to not taking a multivitamin with folic acid and iron.
- Genetic factors: If you're having a family history of inherited Anemia, for example, sickle cell Anemia, your chances of being anemic increase.
- Age: Elderly people mainly over age 65 face an increased risk of Anemia.
Diagnosis of anaemia
A complete blood count (CBC) test will provide counts of your white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in a sample of your blood. If you have anaemia, your doctor will suggest additional tests to determine its type and whether it has a serious cause.
The normal haemoglobin levels are
- Men: 13.8 to 17.2 gm/dl
- Women: 12.1 to 15.1 gm/dl
- Children: 11 to 16 g/dl
- Pregnant women: 11 to 15.1 g/dl.
Treatment of anaemia
Anemia treatment depends on the specific diagnosis and its severity. Anemia treatment includes
- Iron deficiency Anemia: Taking iron supplements and medications, iron-rich food, blood transfusions, surgery, or even cancer treatment. Iron is given through an intravenous (IV) infusion mostly in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Vitamin deficiency Anemia: Suggesting dietary supplements with folic acid and vitamin C. Increasing intake of these nutrients in the diet. If your digestive system is unable to absorb vitamin B-12 from the food you eat, your doctor might suggest vitamin B-12 shots.
- Chronic disease-related Anemia: Managing the underlying disease, blood transfusions, or synthetic hormone injections to increase the production of red blood cells.
- Aplastic Anemia: The only treatment for aplastic Anemia is a bone marrow transplant. Certain medications and blood transfusions are preferred to enhance red blood cell production.