- 3809
- 3.5 Minute
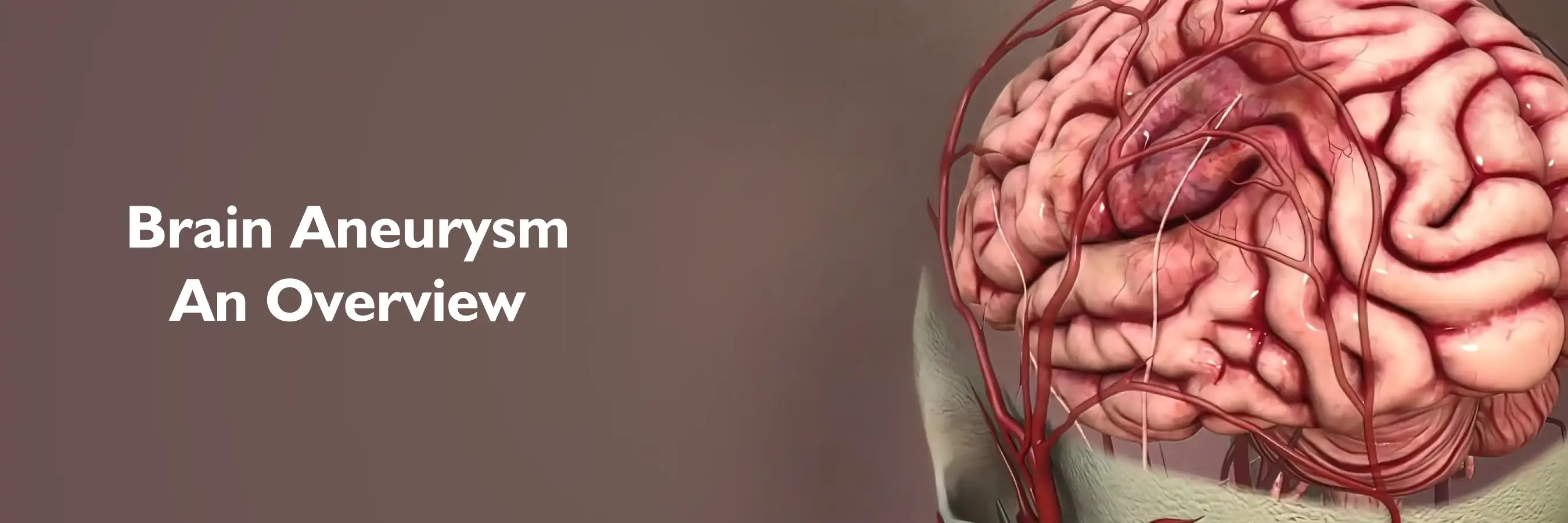
What is Brain Aneurysm?
Brain Aneurysm is a weak spot in a blood vessel in the brain that bulges out like a balloon. If this balloon bursts, it can cause serious bleeding in the brain and a life-threatening emergency. It can be deadly if it bursts, causing a severe headache or stroke. Many show no symptoms until it’s too late and early detection can save lives.
Types of Brain Aneurysms
Not all brain aneurysms are the same. They come in different shapes and sizes, and each type has its own risks. Here are the main types:
1. Saccular Aneurysm (Berry Aneurysm)
This is the most common type of brain aneurysm. It looks like a small, round sac or berry hanging off a blood vessel. Usually found at the base of the brain, it can break suddenly, causing bleeding in the brain. This is the easiest brain aneurysm to treat with surgery or coiling.
2. Fusiform Aneurysm
This type of brain aneurysm bulges out on all sides of the blood vessel, like a swollen tube. It is less common, but often more difficult to treat. Usually doesn’t burst, but may press on nearby brain tissue or nerves.
3. Dissecting Aneurysm
This brain aneurysm happens when there’s a tear in the inner wall of the artery. Blood enters the wall and splits it apart, forming a bulge. It is often caused by an injury or trauma, which can lead to a stroke if not treated quickly.
4. Mycotic Aneurysm
This brain aneurysm is caused by an infection in the artery wall. It is rare but serious and often needs antibiotics and sometimes surgery.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionSymptoms of Brain Aneurysm:
Brain aneurysms often have no symptoms until they get big or burst. But when they do show signs, it’s important to recognize them quickly. We can classify them into two categories as follows:
Early Symptoms: Most brain aneurysms don’t show symptoms until they grow large or rupture, but sometimes the body gives early warning signs. These may include a constant headache (often around or behind the eyes), blurred or double vision, a drooping eyelid, facial numbness, or trouble speaking or thinking clearly.
While these signs can be subtle, they shouldn’t be ignored. Spotting the early symptoms of a brain aneurysm and seeking medical attention promptly can make a big difference and, in some cases, save a life.
Even without rupture, early signs of a brain aneurysm are serious and require urgent medical attention. Delaying diagnosis can increase the risk of a sudden rupture, leading to a life-threatening emergency.
If the Aneurysm Hasn’t Burst (Unruptured)
Most unruptured aneurysms are silent, but large ones may press on nearby nerves and cause:
If the Aneurysm Bursts (Ruptured)
This is an acute medical emergency marked by the quick and intense appearance of symptoms:
- Sudden, severe headache (often called the “worst headache of your life”)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Stiff neck
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred or double vision
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion or trouble speaking
- Drooping eyelids or weakness in limbs
Common Causes and Risk Factors of Brain Aneurysms
1. Congenital Defects (Present at Birth): Some people are born with weak blood vessels or problems with the body's support tissues, which makes them more likely to get aneurysms
2. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Having high blood pressure for a long time can make the walls of blood vessels weaker, which raises the chance of an aneurysm forming or bursting
3. Atherosclerosis (Hardening of the Arteries): Buildup of fatty deposits inside blood vessels can lead to wall damage and aneurysm formation
4. Head Trauma: Severe injury to the head can sometimes damage brain blood vessels and cause aneurysms
5. Smoking: Smoking significantly increases the risk by damaging blood vessels and raising blood pressure
6. Family History: Having a close relative (parent, sibling) with a brain aneurysm increases your risk
7. Age and Gender: More common in adults over 40 and slightly more prevalent in women than in men
8. Drug Use: Especially cocaine or amphetamines, which can cause sudden spikes in blood pressure and damage vessel walls
9. Infections: Rarely, infections that affect the arterial walls (called mycotic aneurysms) can lead to aneurysm formation
10. Polycystic Kidney Disease: This inherited condition is associated with an increased risk of brain aneurysms
11. Connective Tissue Disorders: Conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome can weaken blood vessel walls
Diagnosis of Brain Aneurysm
Diagnosing a brain aneurysm often begins with a neurological examination and detailed evaluation of the symptoms. If a rupture is suspected, emergency imaging tests are performed to identify bleeding in the brain.
Common diagnostic tests include:
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Helps detect bleeding in the brain and locate the aneurysm.
- MRI or MRA (Magnetic Resonance Imaging/Angiography): Offers detailed images of brain blood vessels and can detect unruptured aneurysms.
- Cerebral Angiogram: A catheter is inserted into an artery to inject contrast dye and take X-rays of blood vessels.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): May be done if a rupture is suspected but a CT scan is inconclusive, to check for blood in cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatments Options
Treating a brain aneurysm really depends on the situation. If it hasn’t burst and looks low-risk, doctors might just keep an eye on it with regular scans, along with medication and lifestyle changes to reduce pressure on the blood vessels.
But if there’s a higher risk, they may suggest procedures like clipping or coiling to stop it from bursting. In some cases, surgery isn’t needed at all. It all comes down to what’s safest for you, and your doctor will help decide the best way forward.
Early detection of unruptured aneurysms is critical for preventing life-threatening complications.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Schedule Your AppointmentConclusion
A brain aneurysm can be a serious health risk, but early diagnosis and timely treatment can save lives. Whether it's a minor bulge being monitored or a critical case needing surgical intervention, being informed and proactive is key. Recognizing symptoms, understanding aneurysm causes, and knowing available brain aneurysm treatments are essential for making informed health decisions. If you or your loved one experiences symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Citations
Analysis of the mechanical parameters of human brain aneurysmComputational fluid dynamics in brain aneurysms
Aneurysm
Brain aneurysm
Frequently Asked Questions
Early symptoms may include a sudden, severe headache, vision problems, neck pain, and drooping eyelids. In many cases, unruptured aneurysms show no symptoms.
Yes, brain aneurysm treatment without surgery is possible in select cases through medication, lifestyle changes, and close monitoring of small, unruptured aneurysms.
Common aneurysm causes include high blood pressure, smoking, genetic factors, and trauma or injury to blood vessels in the brain.
The survival rate is high for unruptured aneurysms, especially if treated early. Ruptured aneurysms have a lower survival rate, but outcomes improve significantly with fast medical care.
You can reduce your risk by managing blood pressure, avoiding smoking and alcohol, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting routine health checkups.

- Cardiology
- Case Studies
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- ENT
- Fertility
- Gastroenterology
- General
- General-Medicine
- Gynecology
- Hematology
- Infectious-Diseases
- Medical News
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Pediatrics
- Procedure
- Public-Health
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Second Opinion
- Urology
- Wellness
- Woman-and-child