- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
The Role of Public Health in Controlling Monkeypox Outbreaks
In recent years, monkeypox has emerged as a significant global health concern. Although it is a rare disease, the outbreaks of monkeypox have highlighted the need for effective public health strategies to control its spread. Public health authorities play a crucial role in managing contagious diseases like:
- Monkeypox through surveillance
- Vaccination
- Education
- Other outbreak management tactics.
Here we will explore the role of public health in controlling monkeypox outbreaks and discuss various strategies that can help mitigate the spread of this infectious disease.
The resurgence of monkeypox cases has drawn attention from health organizations worldwide. The increasing incidences underscore the importance of a coordinated response to prevent widespread transmission.
Effective public health strategies are not only vital for controlling the current outbreaks but also for preparing for potential future ones. A comprehensive understanding of these strategies can help in building robust health systems capable of tackling such infectious diseases efficiently.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionWhat is Monkeypox?
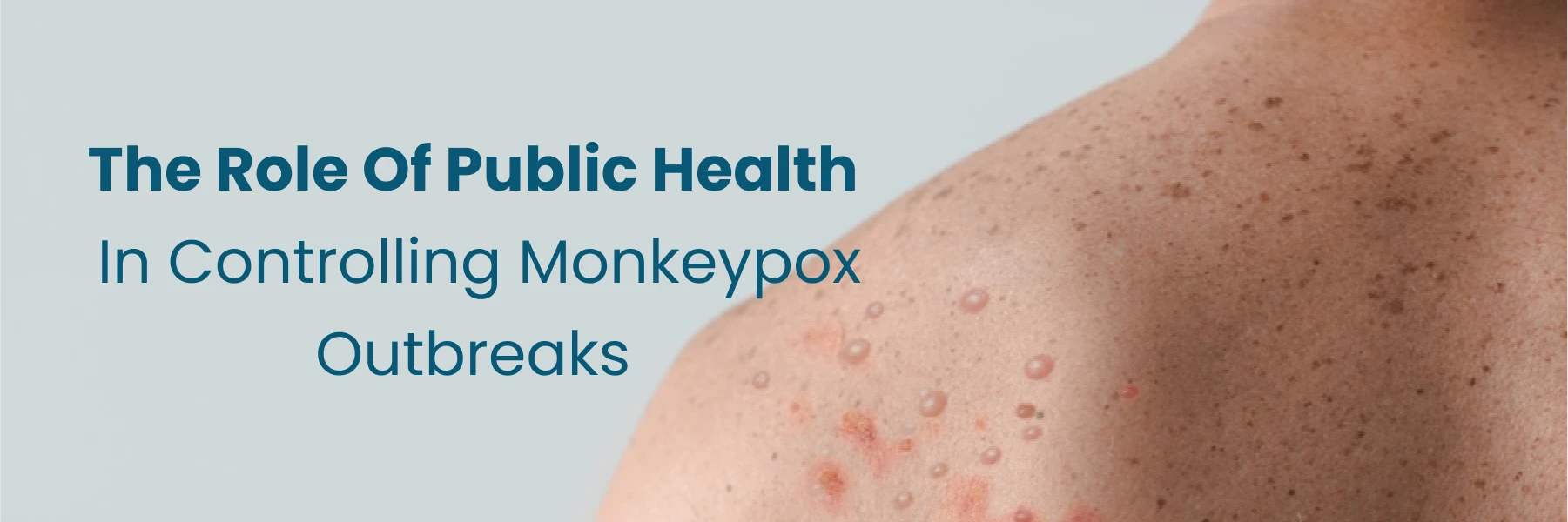
Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis, meaning it is transmitted from animals to humans. The virus responsible for monkeypox belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes smallpox. Monkeypox presents with symptoms similar to smallpox, such as:
- Fever
- Rash
- Swollen lymph nodes.
Understanding the epidemiology of monkeypox is crucial for public health planning. While it shares similarities with smallpox, the zoonotic nature of monkeypox adds complexity to its control.
The virus is primarily found in remote areas of Central and West Africa, often near tropical rainforests, where people may come into contact with infected animals. Recognizing these epidemiological factors helps in developing targeted public health interventions.
Transmission and Symptoms
Monkeypox can be transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, human-to-human transmission, or contaminated materials. The initial symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue.
Within a few days, a rash develops, starting on the face and then spreading to other parts of the body. The rash evolves into pustules before eventually crusting and falling off.
Human-to-human transmission primarily occurs through respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face contact, or through direct contact with body fluids or lesion material.
Additionally, the handling of contaminated items, such as bedding or clothing, can also facilitate the spread of the virus. Understanding these transmission dynamics is essential for implementing effective infection control measures.
Public Health Strategies for Monkeypox Control
Effective public health strategies are essential for controlling monkeypox outbreaks. These strategies include:
- Surveillance
- Vaccination
- Education
- Quarantine measures.
Implementing a multifaceted approach ensures that various aspects of disease control are addressed, minimizing the risk of widespread transmission.
Coordinated efforts from local, national, and international health bodies are necessary to tackle the disease comprehensively. Each strategy plays a unique role in the broader public health response, making it crucial to understand how they interconnect and support one another.
By leveraging these strategies, public health authorities can create a robust framework for outbreak management.
Surveillance and Monitoring
One of the first steps in controlling an outbreak is to detect it early. Public health authorities use surveillance systems to monitor the occurrence of monkeypox cases. This involves gathering data on new cases, tracking the spread of the disease, and identifying potential sources of infection.
Surveillance helps in understanding the epidemiology of monkeypox and enables timely interventions to prevent further spread.
Advanced surveillance technologies, such as geographic information systems (GIS) and real-time data analytics, enhance the ability to monitor and respond to outbreaks swiftly. These tools allow for the visualization of disease patterns and the identification of hotspots, facilitating targeted public health actions.
Effective surveillance is the backbone of any outbreak response, ensuring that interventions are both timely and efficient.
Vaccination Programs
Vaccination is a key tool in controlling monkeypox outbreaks. The smallpox vaccine has been shown to provide cross-protection against monkeypox. Public health authorities can implement targeted vaccination campaigns in areas experiencing outbreaks to protect high-risk populations and prevent the spread of the virus.
In addition to targeted campaigns, routine immunization programs can be adapted to include monkeypox vaccinations in endemic regions. This proactive approach not only protects individuals but also contributes to community immunity, reducing the overall risk of outbreaks. Continuous monitoring of vaccination coverage and effectiveness is necessary to adapt strategies as needed.
Role of Education and Communication
Education and communication are vital components of public health strategies for controlling monkeypox outbreaks. Public health authorities must educate the public about the disease, its symptoms, and preventive measures. Effective communication ensures that accurate information reaches the community, reducing misinformation and panic.
Engaging with community leaders and influencers can amplify the reach of educational campaigns. These figures often have the trust of the community and can help in disseminating information effectively. Collaboration with educational institutions and workplaces can further extend the impact of awareness initiatives.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns can help educate people about how monkeypox is transmitted and what they can do to protect themselves. These campaigns can use various media channels, such as:
- Television
- Radio
- Social media
- Print materials
- Reach a wide audience.
Clear and accurate information can help reduce fear and stigma associated with the disease.
Tailoring messages to different demographic groups ensures that the information is relevant and accessible. For instance, materials for healthcare workers may differ from those intended for the general public.
Utilizing local languages and culturally appropriate messaging can enhance the effectiveness of these campaigns.
Training Healthcare Workers
Healthcare workers are on the frontlines of managing monkeypox outbreaks. Public health authorities must provide training to healthcare workers on how to recognize and manage monkeypox cases. This includes proper infection control measures, case management, and reporting procedures. Well-trained healthcare workers can help in early detection and effective management of cases.
Regular refresher courses and simulations can help maintain a high level of preparedness among healthcare workers. Providing them with the latest guidelines and resources ensures they are equipped to handle evolving outbreak scenarios. Supporting healthcare workers with mental health resources is also crucial, as they often face significant stress during outbreaks.
Quarantine and Isolation Measures
Quarantine and isolation are critical components of outbreak management. Public health authorities may need to implement quarantine measures for individuals who have been exposed to the virus but are not yet symptomatic. Isolation is necessary for those who are already showing symptoms to prevent them from spreading the virus to others.
Establishing clear protocols for quarantine and isolation helps in managing these measures effectively. Providing support, such as food and medical care, to those in quarantine ensures compliance and reduces the burden on affected individuals. Transparent communication about the reasons for these measures can also foster public cooperation.
Contact Tracing
Contact tracing is a method used to identify and monitor individuals who have been in close contact with an infected person. By tracking and monitoring these contacts, public health authorities can quickly identify new cases and prevent further transmission. Contact tracing requires thorough investigation and cooperation from the public.
Digital tools and mobile applications can enhance the efficiency of contact tracing efforts. These technologies can help in quickly identifying and notifying contacts, thereby speeding up the response time. Privacy concerns must be addressed to ensure public trust and cooperation with contact tracing initiatives.
International Collaboration
Monkeypox is not confined to any one country; it can spread across borders. Therefore, international collaboration is essential for controlling monkeypox outbreaks. Countries must share information, resources, and expertise to effectively manage outbreaks. Collaborative efforts can strengthen global health security and improve outbreak response capabilities.
Bilateral and multilateral agreements can facilitate the sharing of critical resources, such as vaccines and medical supplies. Joint training programs and simulation exercises can help countries prepare for coordinated responses. International collaboration also includes harmonizing regulatory frameworks to expedite the approval and distribution of medical countermeasures.
Role of Global Health Organizations
Global health organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), play a crucial role in coordinating international efforts to control monkeypox. They provide guidelines, support research, and facilitate the sharing of information among countries. Collaboration with global health organizations can help countries strengthen their public health responses and improve outbreak management.
These organizations also play a pivotal role in mobilizing resources and coordinating international aid during outbreaks. By providing technical assistance and capacity-building support, they help countries enhance their public health infrastructure. Global health organizations can also advocate for sustained funding and political commitment to outbreak preparedness and response.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are necessary to improve our understanding of monkeypox and develop better tools for its control. This includes research on the virus itself, its transmission dynamics, and the effectiveness of various public health interventions. Continuous investment in research is essential for staying ahead of the evolving threat posed by monkeypox.
Collaborative research initiatives can accelerate the discovery of new interventions and enhance the global knowledge base. Sharing research findings through open-access platforms can facilitate the rapid dissemination of critical information. Engaging with the scientific community and fostering innovation are key components of a robust research strategy.
Development of New Vaccines
While the smallpox vaccine provides some protection against monkeypox, there is a need for specific vaccines that target monkeypox more effectively. Research efforts are underway to develop new vaccines that can provide better protection and be used in outbreak settings. These vaccines can enhance the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns and provide longer-lasting immunity.
Clinical trials and field studies are essential to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new vaccines. Collaboration with pharmaceutical companies and research institutions can expedite the development and distribution of these vaccines. Ensuring equitable access to new vaccines is also crucial for global health security.
Advancements in Diagnostic Tools
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for controlling monkeypox outbreaks. Advances in diagnostic tools can help in the rapid identification of cases, allowing for timely interventions. Research in this area focuses on developing more efficient and accessible diagnostic methods. Improved diagnostics can enhance surveillance efforts and support effective outbreak management.
Point-of-care diagnostic tests can facilitate early detection, especially in resource-limited settings. Innovations in molecular diagnostics and serological assays can provide more accurate and rapid results. Continuous validation and refinement of diagnostic tools are necessary to ensure their reliability and effectiveness.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Schedule Your AppointmentConclusion
Controlling monkeypox outbreaks requires a comprehensive approach involving surveillance, vaccination, education, quarantine, and international collaboration. Public health authorities play a vital role in implementing these strategies and ensuring effective outbreak management. By understanding the role of public health in controlling monkeypox, we can better prepare for and respond to future outbreaks, ultimately protecting public health on a global scale.
Strengthening public health infrastructure and fostering international cooperation are key to achieving these goals. Continuous investment in research and development, along with proactive public health policies, can mitigate the impact of monkeypox and other emerging infectious diseases. A united global effort is essential for safeguarding health and well-being in an increasingly interconnected world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Public health authorities are crucial in monitoring, controlling, and preventing Monkeypox outbreaks through surveillance, vaccination campaigns, public education, and containment strategies.
Agencies track Monkeypox through surveillance systems, case reporting, and laboratory testing to monitor outbreaks and implement timely interventions.
Measures include contact tracing, quarantine of exposed individuals, distribution of vaccines, and public awareness campaigns to educate the community.
Officials prioritize high-risk groups such as healthcare workers, contacts of infected individuals, and those in areas with active transmission when determining vaccine distribution.
Challenges include limited resources, public misinformation, vaccine hesitancy, and the need for international coordination in global outbreaks.
The public can assist by following health guidelines, reporting symptoms, getting vaccinated if eligible, and supporting public health initiatives to reduce the spread of the virus.

- Cardiology
- Case Studies
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- ENT
- Fertility
- Gastroenterology
- General
- General-Medicine
- Gynecology
- Hematology
- Infectious-Diseases
- Medical News
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Pediatrics
- Procedure
- Public-Health
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Second Opinion
- Urology
- Wellness
- Woman-and-child