- Cardiology 84
- Dermatology 45
- Endocrinology 33
- ENT 16
- Fertility 190
- Gastroenterology 78
- General-Medicine 81
- Gynecology 80
- Hematology 19
- Infectious-Diseases 33
- Neurology 52
- Oncology 34
- Ophthalmology 23
- Orthopedics 69
- Pediatrics 31
- Procedure 23
- Public-Health 144
- Pulmonology 59
- Radiology 8
- Urology 68
- Wellness 161
- Woman-and-child 77
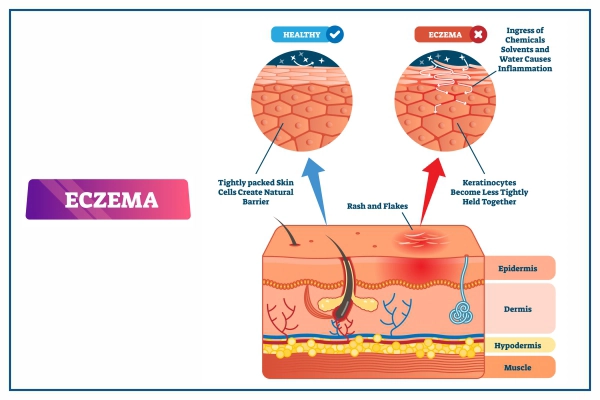
Understanding Eczema: Types, Causes and Treatments
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a common skin disorder causing itchy, inflamed patches. It often appears on infants’ faces but can affect children, teenagers, and adults in various ways. This chronic condition can flare up periodically and may be associated with asthma or hay fever.
There is no cure for atopic dermatitis, but treatments and self-care can relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks. Key steps include avoiding harsh soaps, regularly moisturizing the skin, and using medicated creams or ointments.
Types
The people usually mean atopic dermatitis, which they characterize as dry, itchy skin that often appears with a red rash. This is the most common and chronic type of eczema.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is induced by irritant contact. It induces burning, scratching, and redness. When the irritant is removed, the inflammation goes away.
Dyshidrotic Dermatitis
The fingers, hands, and soles of the feet are affected by dyshidrotic dermatitis. It causes itchy, scaly patches of flaking or red, broken, and painful skin.
In women, the disorder is more common.Nummular Dermatitis
In the winter months, nummular dermatitis causes dry, round patches of skin. The legs are commonly affected by it. In men, it’s more popular.
Get a second opinion from trusted experts and makeconfident, informed decisions.
Get Second OpinionCauses
- It is caused by an overactive immune system, which, when exposed to irritants, responds aggressively.
- An irregular reaction to proteins that are part of the body also causes eczema. The immune system usually rejects proteins that are part of the human body and instead targets invaders’ proteins, such as bacteria or viruses.
- The immune system loses the ability to tell the distinction between the two in eczema, which induces inflammation. An eczema flare-up is when the skin displays one or more signs of eczema.
Common triggers of eczema flare-ups are:
- Synthetic fabrics
- Raised body temperature
- Sweating
- Temperature changes
- A sudden drop in humidity
- Stress
- Food allergies
- Animal dander
- Upper respiratory infections
- Chemicals used in detergents and cleaners that dry the skin out
Symptoms
The symptoms of Eczema vary depending on the age of the person. Eczema is more common in infants, rubbing and scratching lead to skin infections. The symptoms in children and adults are different.
Your health is everything - prioritize your well-being today.
Schedule Your AppointmentSymptoms In Infants
The following eczema symptoms are most common in infants under the age of 2
- Rashes on skin
- Bubble-up rashes before fluid leaking
- Rashes that cause extreme itchiness and interfere with sleeping
Symptoms In Children
The following eczema symptoms are most common in children with age 2 and above
- Rashes that appear behind elbows or knees’ creases
- Rashes that occur between the buttocks and legs on the front, wrists, feet, and the crease
- Bumpy rashes
- Skin thickening
Symptoms In Adults
The Following are the symptoms that are common in adults
- Skin Infections
- Dry skin on the affected area
- Rashes on the body
- Rashes on the elbows and knees
Complications
Asthma And Hay Fever
These symptoms are also followed by eczema. Asthma and hay fever occurs in more than half of young children with atopic dermatitis by the age of 13
Chronic Itchy, Scaly Skin
With a patch of itchy skin, a skin disorder called neurodermatitis begins. You are scratching the place, which makes it even itchier. Eventually, purely out of habit, you can itch. The affected skin can become discolored, thick, and leathery because of this condition.
Skin Infections
Open sores and cracks may be caused by frequent scratching that damages the skin. These raise the risk of bacteria and viruses, including the herpes simplex virus, causing infection.
Irritant Hand Dermatitis
This particularly affects individuals whose work requires their hands to be wet and exposed to harsh soaps, detergents, and disinfectants.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This is the most common in people with atopic dermatitis.
Sleep Problems
The itch and scratch cycle can cause poor sleep quality.
Eczema Prevention
- Moisturize skin twice a day
- Identify and avoid triggers
- Shorter baths or showers
- Bleach bath
- Using gentle soaps
- Dry the skin soft towel and apply moisturizer
Foods To Eat
Eating such foods can cause the body to release immune system compounds that cause inflammation in people with eczema, which in turn leads to an eczema flare-up. A diet for anti-eczema is equivalent to an anti-inflammatory diet. Anti-inflammatory foods may include:
Fish
A natural source of fatty acids containing omega-3 that can combat inflammation in the body. Salmon, Albacore tuna, mackerel, sardines, and herring are examples of fish rich in omega-3s.
Foods High In Probiotics
Bacteria encourage the good health of the gut. Yogurt with living and active communities, miso soup, and tempeh are examples. Probiotics are also present in other fermented foods and beverages, such as kéfir, kombucha, and sauerkraut.
Foods High In Inflammation-Fighting Flavonoids
It includes fruits and vegetables such as apples, broccoli, cherries, spinach, and kale.
Foods To Avoid
- Citrus Fruits
- Eggs
- Tomatoes
- Wheat
- Dairy products
- Soy
Treatments
Frequently, eczema comes and goes. You may need to try various medications and other remedies to get rid of the rash when it occurs.
- The itch can be controlled by Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine
- The itch can be reduced by corticosteroid cream or ointment
- Steroids like prednisone can be taken to reduce swelling
- Skin infections are treated by Antibiotics
- Rashes can be healed by light therapy
Conclusion
A common inflammatory skin disorder is eczema. The most prevalent type is called atopic dermatitis. In adolescents, eczema is most prominent, but the majority develop out of it by the time they reach puberty. While there is currently no remedy, using home remedies, moisturizers, medications, and lifestyle changes, people can treat and avoid eczema outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Eczema itself doesn't spread from person to person, but it can spread to different parts of the body. It's not contagious.
During pregnancy, treating eczema involves using moisturizers and topical steroids deemed safe by healthcare providers. Consult a doctor for specific recommendations.
There is no known permanent cure for eczema, but treatments like moisturizers, topical steroids, and lifestyle changes can manage symptoms effectively.
It is safe to touch someone with eczema. However, they may be sensitive to certain fabrics, chemicals, or allergens, so it's best to ask them about their preferences.
Eczema can worsen at night due to lower humidity levels and increased itching. Using moisturizers, avoiding triggers, and maintaining a cool room temperature can help.
To manage eczema, use gentle cleansers, moisturize regularly, avoid triggers like harsh soaps and allergens, and follow a skincare routine recommended by a dermatologist.
Underlying inflammation triggers eczema. Substances that cause negative immune reactions are involved in the development of this inflammatory skin condition. These include multiple allergens as well as factors that are genetic and environmental. Allergies are one common cause of eczema.
Citrus Fruits, Eggs, Tomatoes, Wheat, Dairy products, Soy.
In people with normal immune systems, common skin disorders such as eczema or psoriasis are seen. Skin disease is also one of the first signs of primary immunodeficiency disease and can lead to more clinical or laboratory assessments to determine an immune deficiency.

- Cardiology
- Case Studies
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- ENT
- Fertility
- Gastroenterology
- General
- General-Medicine
- Gynecology
- Hematology
- Infectious-Diseases
- Medical News
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Pediatrics
- Procedure
- Public-Health
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Second Opinion
- Urology
- Wellness
- Woman-and-child