What is Pulmonary Valve Surgery?
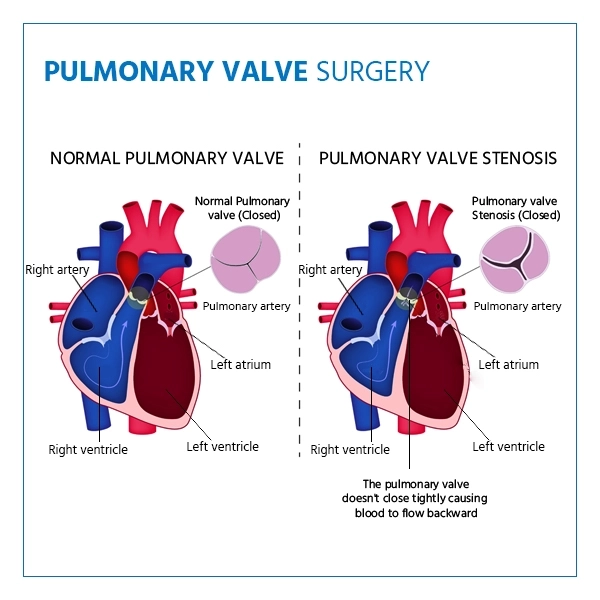
Pulmonary valve surgery is a specialized procedure aimed at treating issues related to the pulmonary valve, which controls blood flow from the heart to the lungs. This procedure is performed to address conditions such as pulmonary valve stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage), which can hinder the efficient circulation of oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
During pulmonary valve surgery, skilled cardiac surgeons meticulously repair or replace the valve, restoring proper blood flow. The surgery can involve various approaches, including traditional open-heart surgery or minimally invasive techniques, depending on the patient's condition and the surgeon's assessment.
In cases of severe valve damage, a replacement valve may be used. This can be a mechanical valve, which offers durability but requires lifelong blood-thinning medication, or a biological valve, derived from human or animal tissue, which might not last as long but eliminates the need for blood-thinning drugs.
The goal of pulmonary valve surgery is to enhance the heart's functionality, improve blood oxygen levels, and alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. This procedure plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by pulmonary valve issues.
As with any surgical procedure, the decision to undergo pulmonary valve surgery is based on a thorough evaluation by a medical team. Factors such as the patient's overall health, the severity of the valve condition, and potential risks are carefully considered. Post-surgery, a period of recovery and rehabilitation is essential to ensure the best possible outcome.
Innovations in medical technology and surgical techniques continue to refine pulmonary valve surgery, offering safer and more effective treatment options. Patients undergoing this procedure can look forward to improved cardiovascular health and an enhanced quality of life, thanks to the dedication and expertise of the medical professionals who specialize in pulmonary valve surgery.