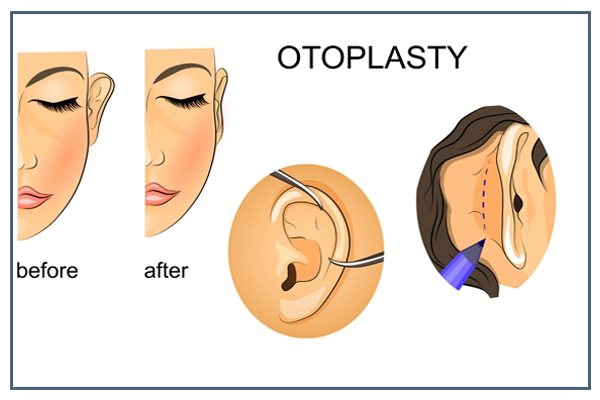
What is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty surgery, also known as ear surgery or ear pinning, is a cosmetic surgical procedure designed to reshape and reposition the ears. Otoplasty aims to improve the appearance of the ears by addressing issues such as prominent ears, ear deformities, or asymmetry. This surgical procedure can significantly impact a person's self-confidence and overall appearance.
Understanding Otoplasty Surgery
Otoplasty surgery is a specialized procedure that aims to modify the ears' shape, size, or position. While Otoplasty is often sought for cosmetic reasons, it can also address congenital deformities or ear injuries. The surgery is commonly performed on children and adults, and its primary objectives include:
- Prominent Ears: Otoplasty is often sought by individuals with ears that stick out prominently from the sides of the head. The surgery can create a more balanced and natural ear position.
- Ear Asymmetry: If there is a noticeable difference in the size, shape, or position of the ears, Otoplasty can help achieve better symmetry.
- Congenital Deformities: Otoplasty can address congenital ear deformities, such as lop ear, cupped ear, or shell ear, to improve the overall appearance of the ears.
- Injury Correction: Ear injuries or trauma can result in deformities that affect the appearance of the ears. Otoplasty can help restore a more natural look.
Steps involved in Otoplasty Surgery?
Otoplasty Surgery Procedure
Here's an overview of what happens during an otoplasty surgery:
- Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed under local anaesthesia with sedation or general anaesthesia, depending on the patient's age and preferences. This ensures that the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the surgery.
- Incision Placement: The surgeon makes an incision behind the ear, in the natural crease where the ear is attached to the head. This placement ensures that any resulting scars are discrete and well-hidden.
- Cartilage Reshaping: The surgeon gains access to the ear's cartilage through the incision. The cartilage is then carefully sculpted, reshaped, or trimmed to achieve the desired appearance. Sutures might be used to hold the cartilage in its new shape.
- Ear Positioning: If the goal is to correct prominent ears, the surgeon will reposition the ear closer to the head. Sutures secure the ear in its new position, creating a more natural contour.
- Skin Excision (if needed): In some cases, excess skin might be present, contributing to the appearance of prominent ears. The surgeon may excise a small amount of skin to achieve the desired result.
- Closing Incisions: After the cartilage has been reshaped and the ear repositioned, the incisions are carefully closed using sutures. These sutures are typically hidden within the natural creases behind the ear.
- Dressing and Bandaging: A dressing or bandage is applied over the ears to provide support and protection during the initial healing phase. This dressing helps maintain the new ear shape and reduces swelling.
- Recovery and Follow-Up: After the surgery, patients are monitored in a recovery area as they wake up from anaesthesia. Pain management medications are provided to manage any discomfort. A headband or bandage might be worn to protect the ears as they heal.
- Results: As swelling subsides, the final results of the otoplasty surgery become more apparent. The ears should appear more proportionate, natural, and balanced about the rest of the face.
Indications of Otoplasty Surgery
Here are the primary indications for Otoplasty:
- Prominent Ears: Prominent ears, commonly referred to as "bat ears," stick out noticeably from the sides of the head. Otoplasty can reposition the ears closer to the head, creating a more balanced and natural appearance.
- Asymmetrical Ears: When there is a noticeable difference in the size, shape, or position of the ears, Otoplasty can help achieve better symmetry and a more harmonious overall look.
- Congenital Deformities: Some individuals are born with congenital ear deformities that affect the appearance of the ears. Otoplasty can correct conditions such as lop ear (folding of the top of the ear), cupped ear (shallow ear cup), or shell ear (missing natural folds).
- Overcorrected Previous Surgery: Individuals who have undergone previous ear surgery might occasionally experience overcorrection or unsatisfactory results. Otoplasty can help improve the appearance in such cases.
- Protruding Ears After Trauma: Trauma or injury to the ears can lead to deformities that cause them to stick out. Otoplasty can correct these deformities and restore a more natural look.
- Earlobe Reduction or Reshaping: Otoplasty can also address concerns related to the shape or size of the earlobes, including reducing the size of large earlobes or reshaping them for aesthetic balance.
- Aesthetic Enhancement: Some individuals seek Otoplasty for purely aesthetic reasons, wishing to achieve a more proportionate and aesthetically pleasing ear appearance.
Who will treat for Otoplasty?
Here are the key professionals who may treat or perform Otoplasty:
- Plastic Surgeon: Plastic surgeons are medical doctors with specialized training in plastic and reconstructive surgery. They are the primary healthcare providers who perform otoplasty surgeries. Plastic surgeons have the skills to reshape and reposition the ears to achieve a more aesthetically pleasing and natural appearance.
- Facial Plastic Surgeon: A subset of plastic surgery, facial plastic surgery focuses specifically on procedures involving the face, head, and neck. A facial plastic surgeon can also perform Otoplasty to enhance facial symmetry and balance.
- Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Surgeon: ENT surgeons, also known as otolaryngologists, specialize in disorders of the ear, nose, and throat. They may have the expertise to perform Otoplasty, mainly if the procedure is related to correcting medical conditions affecting the ears.
- Pediatric Plastic Surgeon: Pediatric plastic surgeons specialize in performing plastic and reconstructive surgeries on children. They have experience addressing congenital ear deformities and other issues in pediatric patients.
- Cosmetic Surgeon: Cosmetic surgeons are trained in various cosmetic procedures, including Otoplasty. They can help individuals achieve their desired ear appearance for aesthetic reasons.
Preparing for Otoplasty Surgery?
Preparing for otoplasty surgery, also known as ear surgery or ear pinning, involves several essential steps to ensure a smooth and successful procedure and a comfortable recovery period. Here's a guide on how to prepare:
- Choose a Qualified Surgeon: Research and choose a board-certified plastic surgeon with experience in performing Otoplasty. Schedule a consultation to discuss your goals and expectations.
- Consultation and Medical Evaluation: During the consultation, your surgeon will assess your ears, discuss your desired outcomes, and explain the procedure. A comprehensive medical evaluation will also ensure you're a suitable candidate for surgery.
- Open Communication: Be open and honest with your surgeon about your medical history, medications, allergies, and any previous surgeries. This information is crucial for your safety during the procedure.
- Understand the Procedure: Gain a clear understanding of the otoplasty procedure, including its risks, benefits, and potential outcomes. Ask any questions you have to alleviate concerns and make informed decisions.
- Quit Smoking: If you're a smoker, consider quitting or minimizing smoking before and after surgery. Smoking can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
- Medication Review: Discuss any medications you take with your surgeon. Some medications, including blood-thinning drugs and herbal supplements, may need to be temporarily stopped before the surgery.
- Fasting Instructions: Your surgeon will provide specific fasting instructions for the night before the surgery. You'll need to avoid eating or drinking anything after a particular time.
Recovery After Otoplasty Surgery
Recovery after otoplasty surgery, also known as ear surgery or ear pinning, is a crucial phase that requires proper care and attention to ensure optimal healing and the best possible results. While individual experiences may vary, here's a general overview of what you can expect during the recovery period:
- Immediate Post-Operative Phase: You'll be monitored in a recovery area as you wake up from anaesthesia. Pain management medications will be administered as needed to keep you comfortable.
- Dressing and Bandages: Your ears will be covered with a dressing or bandage to support and protect the surgical area. The sauce helps maintain the new ear shape and minimizes swelling.
- Discomfort and Swelling: After surgery, some discomfort, swelling, and bruising around the ears are expected. Cold compresses can help reduce swelling during the initial days.
- Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Follow your surgeon's instructions carefully for cleaning and caring for the surgical site. Avoid touching, scratching, or manipulating the ears.
- Headband or Bandage Use: Your surgeon might recommend wearing a headband or bandage to hold the ears in their new position during the initial healing period. Follow their guidance on how long to wear it.
- Medications: Take prescribed medications as directed for pain relief and to prevent infection.Avoid taking medicines that can increase bleeding risk unless approved by your surgeon.
- Restricted Activities: Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and vigorous exercise for a few weeks. Be cautious with activities that could affect the surgical area.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. These appointments are essential for monitoring healing progress and addressing any concerns.
- Gradual Return to Normal Activities: As you heal, you can gradually resume daily activities as your surgeon advises. Avoid activities that put excessive pressure on the ears.
- Results and Healing Time: While initial results are visible soon after surgery, complete healing and resolution of swelling can take several weeks to a few months. Final results may take time to develop fully.
Lifestyle changes after Otoplasty Surgery
Lifestyle changes after otoplasty surgery, also known as ear surgery or ear pinning, are generally temporary and aim to support a smooth recovery and optimal healing. These adjustments help protect the surgical area, minimize discomfort, and promote the best possible results. Here are some lifestyle changes to consider during the postoperative period:
- Careful Handling of the Ears: Avoid touching, scratching, or manipulating the surgical area to prevent disrupting the healing process.Be gentle when washing your hair or performing daily hygiene routines.
- Protecting the Ears: If your surgeon recommends using a headband or bandage, wear it consistently as instructed. It helps maintain the new ear position and protects the surgical site.
- Sleep Position: Sleep on your back during the initial healing phase to avoid putting pressure on the ears.
- Avoiding Strenuous Activities: Refrain from vigorous exercises, heavy lifting, and activities that could strain the ears for a few weeks after surgery.
- Gradual Return to Normal Activities: As you heal, gradually reintroduce normal activities, but do so cautiously and within the guidelines provided by your surgeon.
- Sun Protection: If you're going outside, protect your ears from direct sun exposure by wearing a wide-brimmed hat or using sunblock with your surgeon's approval.