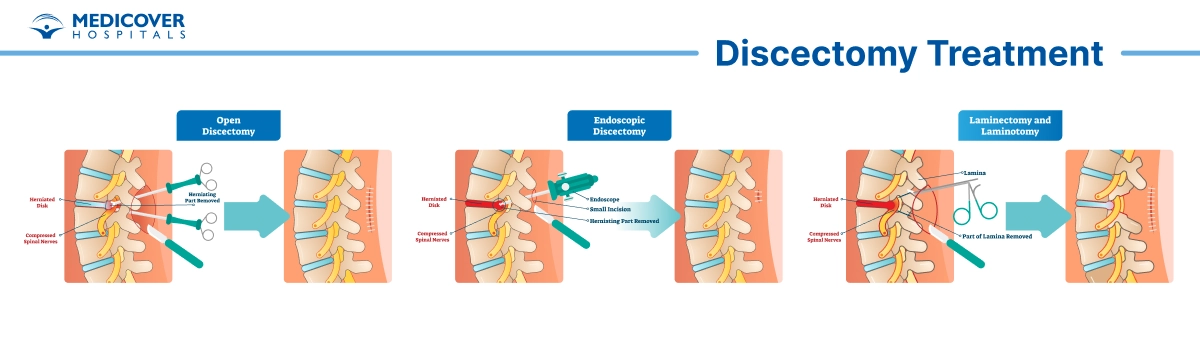
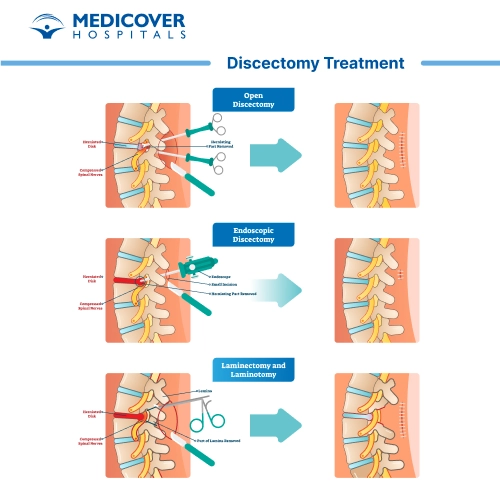
The Discectomy Procedure
A discectomy is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves the following steps:
- Incision: The surgeon makes a small incision near the affected disc, which is identified using imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans.
- Tissue Displacement: Muscles and other tissues are gently moved aside to access the spine.
- Disc Removal: The damaged portion of the disc, which might be causing nerve compression or irritation, is carefully removed. This can be done using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques.
- Closure: After removing the disc material, the incision is closed using stitches or surgical staples.
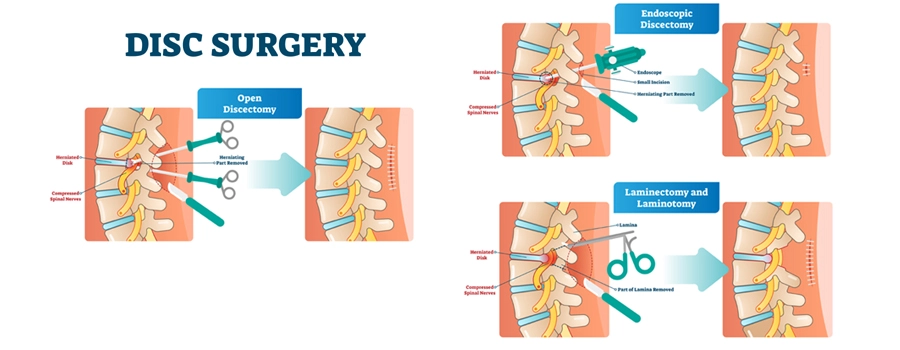
Benefits of Discectomy
- Pain Relief: The primary goal of a discectomy is to relieve pain caused by nerve compression. By removing the source of irritation, patients often experience significant pain reduction.
- Improved Mobility: Once the pressure on the affected nerve is relieved, patients may regain lost mobility and functionality.
- Quick Recovery: Minimally invasive discectomy techniques can result in shorter hospital stays, smaller incisions, and faster recovery times than traditional open surgery.
Potential Risks and Considerations: While discectomy is generally considered safe, some risks are associated with any surgical procedure. These might include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and the possibility of recurrent disc herniation. Patients must discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider and make an informed decision based on their unique circumstances.
Whom will treat for Discectomy
A discectomy is a surgical procedure to treat a herniated or bulging disc in the spine that is causing pressure on the nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness. This procedure is typically considered when conservative treatments like physical therapy, pain medications, and epidural injections have not provided sufficient relief.
The healthcare professional treating a patient with a discectomy is typically an orthopedic surgeon or a neurosurgeon. These specialists have the expertise and training required to perform the surgery and manage the associated conditions of the spine and nervous system. Before recommending a discectomy, the surgeon will thoroughly evaluate the patient's medical history, symptoms, imaging studies (such as MRI or CT scans), and overall health to determine if surgery is the appropriate course of action.
How to prepare for Discectomy
Before the Procedure
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Your journey begins with a consultation with a healthcare provider, usually a spine specialist or orthopedic surgeon. They will assess your condition, review your medical history, and recommend the appropriate treatment, which might be a discectomy.
- Medical Evaluation: You may need to undergo tests such as MRI, CT scan, or X-ray to provide the surgeon with a clear view of the affected area.
- Discussion with Surgeon: Have a detailed conversation with your surgeon about the procedure. Understand the benefits, risks, and potential outcomes. Address any concerns or questions you might have.
- Pre-Surgery Instructions: Your surgeon will provide specific instructions to follow in the days leading up to the surgery. This might include fasting before the surgery and stopping certain medications that could interfere with the procedure.
- Health Optimization: Prioritize a healthy lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise (within the limits recommended by your healthcare provider) can help optimize your overall health and prepare your body for surgery.
- Medication Review: Ensure to inform your surgeon about any medications you take, including prescription, over-the-counter, and supplements. They will advise you on which to continue or stop before the surgery.
- Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking. Smoking can hinder the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
- Arrange Support: You might need assistance after the surgery, so arrange for a friend or family member to help you with daily tasks during your recovery period.
- Prepare for Recovery: Set up a comfortable and organized recovery space at home. Gather supplies like pillows, blankets, loose-fitting clothing, and any equipment your surgeon recommends.
- Follow Post-Surgery Instructions: After the surgery, your surgeon will provide specific instructions for your recovery. These could include details about wound care, physical activity limitations, and medication management.
- Physical Therapy: Your surgeon might recommend physical therapy as part of your recovery plan. Attend sessions as scheduled and follow the exercises prescribed by the therapist.
Recovery Process
Recovery from a discectomy can vary depending on the extent of the surgery and the patient's overall health. However, some common aspects include:
- Hospital Stay: Minimally invasive procedures allow for shorter hospital stays, often just one or two days.
- Pain Management: Pain at the incision site is joint initially, but it typically improves within a few days. Pain medications and physical therapy may be prescribed.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy helps restore strength, flexibility, and proper posture.
- Return to Normal Activities: Patients are usually advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for a few weeks. Gradually, they can resume normal activities as guided by their surgeon.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process and address any concerns.
Lifestyle changes after Discectomy Procedure
Undergoing a discectomy procedure, which involves removing a herniated or damaged disc in the spine, can lead to various lifestyle changes during recovery and beyond. It's important to note that the specifics of these changes can vary from person to person, and you should always follow your doctor's advice and recommendations. Here are some typical lifestyle changes that individuals might experience after a discectomy procedure:
- Physical Activity: Initially, you'll need to limit your physical activity to allow your body to heal correctly. Your doctor will likely provide guidelines on when you can gradually resume activities like walking, stretching, and light exercises. High-impact activities and heavy lifting should be avoided for a certain period to prevent strain on the spine.
- Posture and Body Mechanics: Proper posture and body mechanics become crucial after a discectomy. Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can reduce the stress on your spine and prevent the recurrence of herniation.
- Exercise and Rehabilitation: Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are often recommended after a discectomy. These exercises strengthen the core muscles, improve flexibility, and support the spine. Following a structured rehabilitation plan can help you regain strength and mobility.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing stress on the spine. Excess weight can contribute to spinal problems, so a balanced diet and engaging in appropriate physical activities can help manage weight.
- Ergonomics: Ensuring your work environment, including your desk, chair, and computer setup, is ergonomically designed and can promote better spinal health. Proper ergonomics can help prevent strain and discomfort during extended periods of sitting.
- Smoking Cessation: If you're a smoker, quitting can improve your healing process and overall spinal health. Smoking can impede blood flow and delay healing, which can be particularly detrimental after surgery.
- Pain Management: While recovery from a discectomy can be uncomfortable, managing pain effectively is essential. Your doctor might prescribe pain medications for a limited period. Following their recommendations and communicating any pain concerns is necessary.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Staying hydrated and consuming a balanced, nutrient-rich diet can support healing. Proper nutrition can contribute to tissue repair and overall well-being.
- Gradual Return to Activities: As you progress in your recovery, you'll likely be able to reintroduce more activities into your daily routine gradually. Listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself too hard too quickly.
- Regular Check-ups: Follow up with your surgeon or healthcare provider as scheduled. They can monitor your progress, assess your healing, and provide further guidance on lifestyle adjustments.