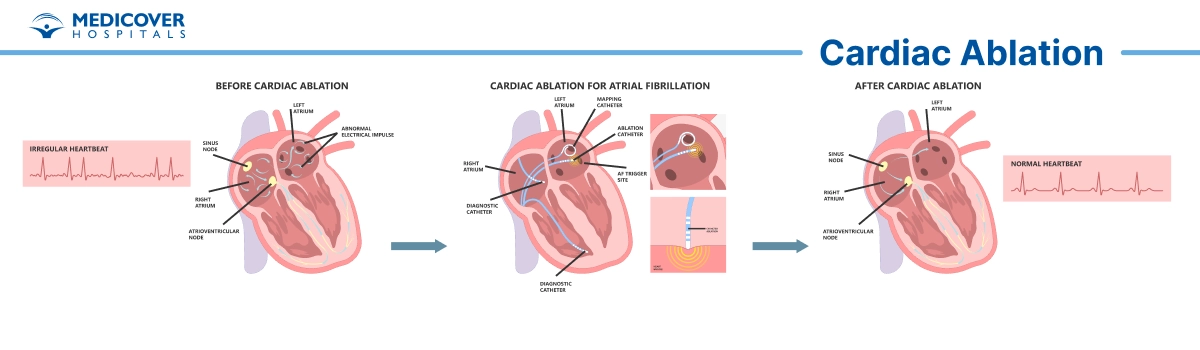
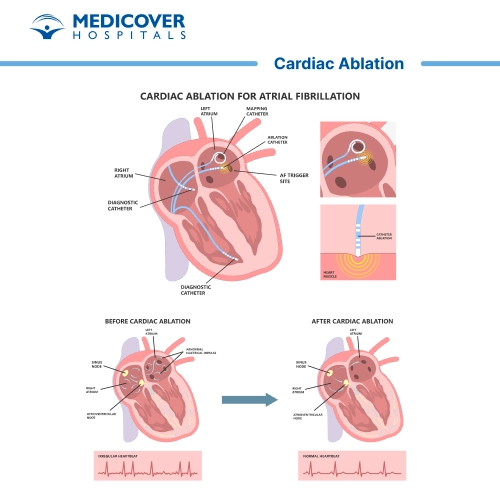
Indications
Cardiac ablation is recommended for individuals with specific types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) that haven't responded well to medications or other treatments. Common indications include:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Atrial fibrillation is a rapid and irregular heartbeat originating in the heart's upper chambers (atria). Ablation may be considered to restore normal heart rhythm when medications are ineffective.
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT): SVT refers to various rapid heart rhythms originating above the ventricles. Ablation can correct abnormal electrical pathways causing SVT.
- Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Ventricular tachycardia is a rapid heartbeat originating in the heart's lower chambers (ventricles). Ablation may be used to treat certain types of VT.
- Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT): AVNRT is a common type of SVT that involves abnormal pathways within the heart's electrical system. Ablation can eliminate these pathways.
- Accessory Pathways: Some individuals have extra electrical pathways (accessory pathways) in the heart that can cause abnormal rhythms like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Ablation can remove these pathways.
- Ventricular Fibrillation Risk: In some cases, ablation may be considered to reduce the risk of ventricular fibrillation, a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia.
Steps involved in Cardiac Ablation
During a cardiac ablation procedure, several steps are taken to diagnose and treat abnormal heart rhythms, also known as arrhythmias. Here's an overview of what happens during a cardiac ablation:
- Patient Evaluation: Before the procedure, the patient's medical history, symptoms, and previous diagnostic tests (such as electrocardiograms and Holter monitoring) are reviewed to identify the specific arrhythmia.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia or mild sedation is administered to ensure the patient's comfort during the procedure.
- Catheter Insertion: Catheter (thin, flexible tube) is inserted through a blood vessel, typically in the groin area. It's threaded up to the heart under X-ray guidance.
- Mapping: Specialized mapping catheters with electrodes are used to record the heart's electrical activity and identify the precise location of abnormal electrical signals.
- Energy Application: Once the abnormal sites are located, the catheter's electrode emits energy (such as radiofrequency or cryotherapy) to create controlled scar tissue or lesions. This disrupts the faulty electrical pathways causing the arrhythmia.
- Monitoring and Testing: Throughout the procedure, the patient's heart rhythm is monitored to ensure that the ablation is successfully eliminating the abnormal signals.
- Verification: After each energy application, the medical team verifies whether the arrhythmia has been successfully corrected by observing changes in the heart's electrical patterns.
- Completion: Once the necessary ablations are performed and the heart's rhythm is restored to a more regular pattern, the catheters are removed.
- Recovery: After the procedure, the patient is closely monitored in a recovery area for a few hours to ensure stability. Most patients can go home on the same day.
- Follow-Up: Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the patient's progress, assess the success of the procedure, and make any necessary adjustments to medications or further treatments.
Who will Treat for Cardiac Ablation Procedure
- Cardiac electrophysiologist:Cardiac ablation is a specialized procedure performed by a cardiac electrophysiologist. A cardiac electrophysiologist is a cardiologist who has undergone additional training and expertise in the field of electrophysiology, which focuses on the electrical activities of the heart and the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias. These highly trained medical professionals have extensive knowledge of the heart's electrical system, the various types of arrhythmias, and the techniques used in cardiac ablation procedures.
Preparing for Cardiac Ablation Surgery
Preparing for cardiac ablation surgery involves several important steps to ensure a safe and successful procedure. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to prepare:
- Consultation with a Cardiac Electrophysiologist: Schedule a consultation with a board-certified cardiac electrophysiologist to discuss your arrhythmia, medical history, and treatment options.
- Medical Evaluation: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation, including physical examination, blood tests, and imaging, to assess your overall health and determine if you're a suitable candidate for cardiac ablation.
- Medication Review: Provide a list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. Your specialist will advise you on which medications to continue or temporarily stop before the procedure.
- Allergies and Sensitivities: Inform your medical team about any allergies or sensitivities you have, especially to medications, anesthesia, or medical supplies.
- Fasting Instructions: Your doctor will provide fasting instructions for the night before the procedure. Typically, you'll be asked not to eat or drink anything after midnight.
- Arrangements for Transportation: Arrange for someone to drive you to and from the hospital on the day of the procedure, as you may not be able to drive after receiving anesthesia.
- Stop Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting or reducing smoking before the procedure. Smoking can impact your heart's health and healing.
- Hygiene: Shower or bathe the night before or the morning of the procedure to minimize the risk of infection.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to the hospital. You may need to change into a hospital gown for the procedure.
- Medication Instructions: Follow your doctor's instructions regarding which medications to take or avoid on the day of the procedure. Some medications may need to be adjusted.
- Personal Belongings: Leave valuables and jewelry at home. Bring only essentials like identification, insurance information, and a list of your medications.
- Consent Forms: Sign any required consent forms after thoroughly discussing the procedure with your doctor and understanding the risks and benefits.
- Questions and Concerns: Use the consultation to ask any remaining questions about the procedure, recovery, and postoperative care.
- Mental Preparation: Mentally prepare for the procedure by understanding its purpose, potential outcomes, and the care you'll receive.
- Follow Preoperative Instructions: Adhere to all preoperative instructions provided by your medical team, as they are tailored to your specific situation.
- Emotional Support: Seek emotional support from friends, family, or support groups to alleviate any anxiety or concerns you may have about the procedure.
Recovery after a cardiac ablation:
Recovery after a cardiac ablation procedure is a gradual process that involves rest, monitoring, and adherence to your medical team's postoperative instructions. The duration and specifics of your recovery can vary based on the type of arrhythmia treated, your overall health, and the approach used during the procedure. Here's what you can generally expect during the recovery period:
- Immediate Postoperative Period:
- After the procedure, you'll be monitored in a recovery area as you wake up from anesthesia.
- You may have dressings over the catheter insertion site(s) and monitoring electrodes on your chest.
- Observation and Monitoring:
- Medical staff will observe your vital signs and heart rhythm to ensure a stable recovery.
- Depending on the specifics of your procedure, you might need to stay in the hospital for a few hours or overnight.
- Pain and Discomfort: You may experience mild discomfort or soreness at the catheter insertion site(s) or in the chest area. Pain is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Activity Restrictions: During the initial recovery period, it's important to rest and avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and intense physical exertion.
- Follow-Up Appointments:
- Your medical team will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your recovery and assess the success of the procedure.
- These appointments also allow for any necessary adjustments to your medication regimen or treatment plan
- Wound Care: Follow your medical team's instructions for caring for the catheter insertion site(s). Keep the area clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Medications: Continue taking prescribed medications as directed by your medical team. They may adjust your medications based on your progress.
- Resuming Normal Activities:
- Most individuals can return to light activities within a few days after the procedure.
- Strenuous activities and heavy lifting may need to be avoided for a longer period, typically around one to two weeks
- Driving: You may need to refrain from driving for a day or two, especially if sedation or anesthesia was used during the procedure.
- Diet and Hydration: Maintain a Proper balanced diet and stay hydrated to support your healing process.
- Work: Depending on your job and the nature of the procedure, you might be able to return to work within a few days to a week.
- Gradual Return to Exercise: Gradually reintroduce exercise and physical activities as guided by your medical team. Avoid strenuous activities initially.
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to all postoperative instructions provided by your medical team, including any medication adjustments or lifestyle recommendations.
- Contact Your Medical Team: If you experience any abnormal symptoms such as excessive bleeding, swelling, signs of infection, chest pain, or irregular heartbeats, contact your medical team promptly.
Lifestyle changes after Cardiac Ablation procedure:
After undergoing a cardiac ablation procedure, certain lifestyle changes can contribute to your overall heart health, promote healing, and decrease the risk of future heart rhythm issues. Here are some lifestyle changes to consider:
- Follow Medical Recommendations: Adhere to your doctor's instructions regarding medications, activity level, and any restrictions.
- Healthy Diet: Take an heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink sufficient water to stay hydrated, which supports overall cardiovascular health.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular, moderate-intensity exercise as advised by your doctor. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can improve heart health.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing ways such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or mindfulness to support your heart health.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Excess weight can strain the heart.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting. Smoking is a major risk factor for heart diseases & can interfere with your healing process.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. Excessive alcohol can negatively impact heart health.
- Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: Keep track of your BP and cholesterol levels, and work with your doctor to manage them within healthy ranges.
- Diabetes Management: If you have diabetes, manage your blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Sleep Well: Prioritize quality sleep to support your overall health and healing process.
- Stay Hygienic: Follow proper hygiene practices to prevent infections and maintain overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Engage in activities you enjoy, spend time with loved ones, and consider stress-relieving practices to enhance your emotional well-being.
- Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications consistently and as directed by your doctor to prevent recurrences of arrhythmias.
- Regular Follow-Up: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your heart rhythm and discuss any concerns with your medical team.
- Learn About Your Condition: Educate yourself about your specific arrhythmia and heart health to make informed decisions and advocate for your well-being.
- Support Network: Seek support from family, friends, and support groups to navigate any emotional or lifestyle changes.