What is Prostate Cancer?
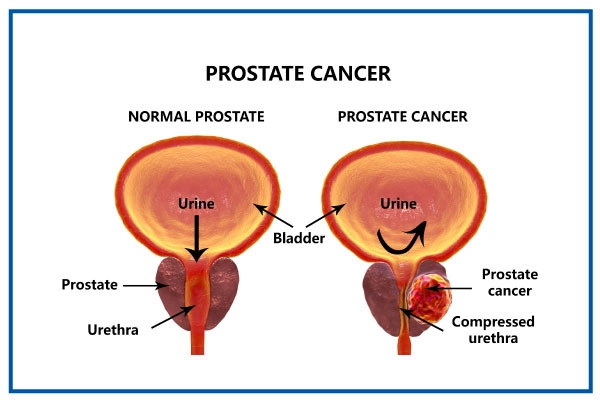
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate. In males, the prostate is a small walnut-shaped gland that generates seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
One of the most common types of cancer is prostate cancer. Many prostate cancers grow slowly and are restricted to the prostate gland, where they may not cause significant harm. While some types of prostate cancer develop slowly and may require little or no therapy, others are severe and spread quickly.
<
Prostate Cancer Symptoms:
It’s symptoms are not very much visible during the initial stage.
The advanced stage may show symptoms such as:
- Discomfort during urinating
- Less force in the stream of urine
- Hematuria - Blood in the urine
- Bone pain
- Blood in the semen
- Loss of weight for no reason
- Erectile dysfunction
- Fatigue
Causes
According to doctors, when the prostate gland cells develop changes in their DNA, they can result in cancer of the prostate gland. The cells' DNA controls the cells' functions and the mutated DNA causes the cells to grow and divide more rapidly than what normal cells do. The accumulation of unhealthy abnormal cells forms a mass called a tumor that can metastasize to the surrounding tissues.
Risk factors
Risks for prostate cancer includes the following factors:
- Older age: The risk of cancer increases in old age.
- Family history: If parents or any close relative had prostate cancer, the chances of getting this cancer also increase.
- Obesity: Obese people may have a higher risk of this cancer than people with healthy weight.
Complications
Complications of prostate cancer include:
- Urinary incontinence: Urinary incontinence:Prostate cancer and its treatment can lead to urinary incontinence.
- Prostate cancer metastasizes: Prostate cancer cells can spread to the surrounding organs, such as the urinary bladder, or get transported through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to other body parts.
- Erectile dysfunction: The dysfunction is due to the cancer or its treatment methods such as surgery, radiation or hormonal treatments.
Diagnosis
If the doctor suspects cancer of the prostate gland, he or she will enquire about related prostate problems such as urinary or sexual issues and other risk factors like family history. Following tests would be recommended to diagnose the condition.
- PSA blood test: A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test is done to evaluate the PSA levels, the proteins produced by both normal and cancerous prostate cells.
- Digital rectal examination (DRE): It is a routine screening test to monitor a patient’s lower rectum, pelvis, and lower abdomen. This test can help a doctor check a prostate gland's health.
- Biopsy test: A prostate biopsy test is done to remove tissue samples from the prostate gland for microscopic examination.
- Ultrasound scan (USG scan): Prostate ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of a prostate gland and find any abnormal mass in the organ.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A multi-parametric MRI (mpMRI) scan can help the doctor detect prostate gland malignancy and its capacity to grow.
Prostate Cancer Treatment
Prostate cancer treatment methods are as follows:
Prostate Cancer Surgery:
- Radical prostatectomy: A radical prostatectomy is recommended for prostate cancer patients whose cancer is in its initial phase. This operation may not be suitable if the malignancy has spread outside the prostate gland.
- Types of radical prostatectomy are:
- Retropubic prostatectomy
- Perineal prostatectomy
- Laparoscopic prostatectomy
- Robotic prostatectomy
- Radiation therapy (radiotherapy): Radiation therapy (radiotherapy)Radiation therapy (radiotherapy) is recommended in patients with the is in its cancer early stage or if surgery is not an option.
Radiotherapy can be done with external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) or by implanting radioactive seeds (brachytherapy). - Hormonal therapy for prostate cancer: Hormone therapy or androgen suppression therapy helps to decrease male hormone levels, called androgens, or to inhibit them from increasing prostate cancer cells.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy: Hormone therapy or androgen suppression therapy helps to decrease male hormone levels, called androgens, or to inhibit them from increasing prostate cancer cells.
- Minimal dysplasia or low-grade dysplasia: Cryoablation or cryotherapy uses a special probe to freeze and kill the malignant cells.
- Chemotherapy: This therapy may be a treatment option for curing metastasized prostate cancer, and it also treats cancers that don't respond to hormonal therapy.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy for prostate cancer stimulates a patient's own defense (immune) system to counter-attack cancer cells. One such vaccine is sipuleucel-T (Provenge), which induces an immune system to fight back against cancer cells.
- Targeted drug therapy: Targeted drug treatments aim to treat certain abnormalities of the malignant cells. This therapy can cause cancer cells to die, and it is indicated to manage advanced or recurrent prostate cancer cases.
