Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
When stomach acid runs back into the tube that connects your mouth and stomach, it's called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) might irritate your esophageal lining. Acid reflux affects a large number of people at some point in their lives. GERD is defined as mild acid reflux occurring at least twice a week or moderate to severe acid reflux occurring at least once a week. The majority of the people may manage their GERD symptoms with a combination of lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter drugs.
Symptoms of GERD
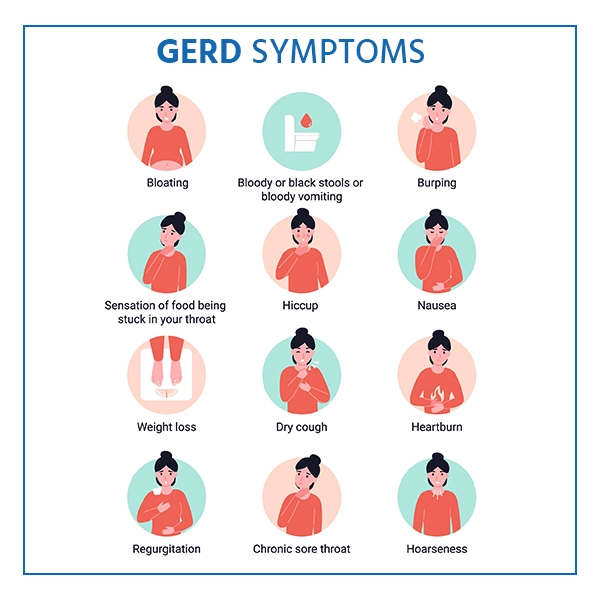
The following are some of the most common GERD indications and symptoms:
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest that occurs after eating and is often worse at night.
- Pain in the chest
- Swallowing problems
- Food or sour liquid regurgitation
- Feeling like you have a lump in your throat
- Neck lymph nodes that are swollen and painful
You may also encounter the following symptoms if you have acid reflux at night:
- Coughing for a long time
- Laryngitis
- Asthma that is new or worsening
- Sleep disturbances
Causes
GERD is caused by acid reflux on a regular basis. When you swallow, the lower esophageal sphincter (a circular band of muscle around the bottom of your esophagus) relaxes, allowing food and drink to flow into your stomach. The sphincter then closes again. Stomach acid might run back up into your esophagus if the sphincter relaxes or weakens abnormally. The lining of your esophagus is irritated by the continual backwash of acid, and it commonly becomes inflamed.
Risk Factors
The following conditions can raise your risk of GERD:
- Obesity
- Hiatal hernia in which the stomach bulges up into the diaphragm
- Pregnancy
- Scleroderma and other connective tissue disease
- When stomach emptying takes longer than usual
Complications
Chronic esophageal inflammation can lead to the following symptoms over time:
- Esophageal stricture : It is a condition in which the esophagus narrows. Scar tissue forms when stomach acid damages the lower esophagus. The scar tissue narrows the food channel, causing swallowing difficulties.
- Esophageal ulcer : It is an esophageal sore that hasn't healed. Stomach acid can eat away at esophageal tissue, resulting in an open sore. Bleeding, pain and difficulty swallowing are all symptoms of an esophageal ulcer.
- Barrett's esophagus : It is a precancerous alteration in the esophagus. Acid damage can lead to abnormalities in the tissue that lines the lower esophagus. These modifications have been linked to a higher risk of esophageal cancer.
Diagnosis of GERD
Based on a physical examination and a history of your signs and symptoms, your doctor may be able to diagnose GERD. Your doctor may suggest the following tests to confirm a diagnosis of GERD or to check for complications:
- Endoscopy of the upper intestine : A thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) is inserted down your throat by your doctor to inspect the inside of your esophagus and stomach. When reflux is present, test results may be normal, but an endoscopy may reveal esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus) or other consequences. An endoscopy can also be used to take a biopsy of the tissue to check for issues like Barrett's esophagus.
- Ambulatory acid pH probe test : A monitor is inserted into your esophagus to determine when and how long stomach acid regurgitates. The display is connected to a little computer that you carry around your waist or over your shoulder with a strap. A tiny, flexible tube (catheter) put through your nose into your esophagus, or a clip placed in your esophagus during endoscopy and passed into your stool after about two days, could be used as a monitor.
- Manometry of the esophagus : When you swallow, this test monitors the rhythmic muscular contractions in your esophagus. The coordination and force exerted by the muscles of your esophagus are also measured using esophageal manometry.
Treatment of GERD
Your doctor would most likely advise you to start with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter drugs. If you don't feel better after a few weeks, your doctor may prescribe medication or suggest surgery. Certain medications such as antacids are prescribed for treating GERD and its symptoms. If medications do not show any result then after seeing your condition doctor will advise surgeries in very rare cases.
