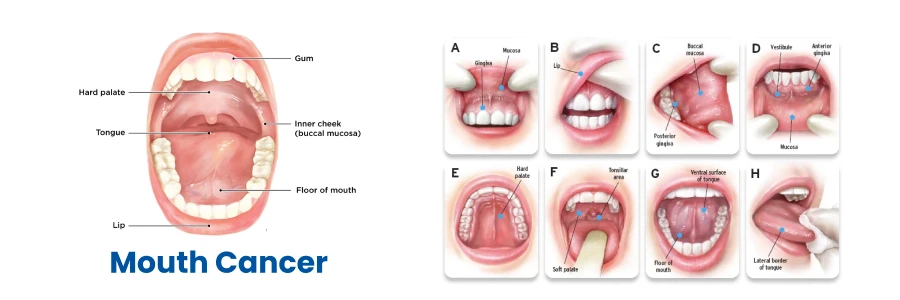
Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, is considered a head and neck cancer subtype. Oral cancer is any cancerous tissue. The growth occurs in the oral cavity. It can arise as a primary injury originating in any of the tissues of the oral cavity. There are several types of oral cancers, but about 90% are squamous cell carcinomas, originating in the tissues that line the mouth and lips. Mouth or mouth cancer more commonly involves the tongue.
Mouth Cancer Symptoms
In the early stages of oral cancer, symptoms are difficult to detect. A word from Caution for both smokers and heavy drinkers: it would be advisable to go for regular checkups at your nearest dentist. When the signs and symptoms eventually, begin to manifest themselves, they may include the following:
- Patches on the lining of the mouth or tongue, usually red or
- Red and white in color
- Mouth ulcers that refuse to go away
- Swelling in the mouth that persists for over three weeks
- A lump or thickening of the skin or lining of the mouth
- Pain when swallowing
- Lose teeth (tooth) for no clear reason
- Jaw pain
- Jaw stiffness
- Sore throat
- Painful tongue
- A hoarse voice
- Pain in the neck that does not go away
- Unexplained weight loss
- Unusual changes in the sense of taste
- The lymph nodes (glands) in the neck become swollen
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Unexplained numbness, loss of feeling, or pain/tenderness
Mouth Cancer Causes
Smoking and Drinking
Smoking and drinking contain substances that are naturally carcinogenic, meaning they contain chemicals that can damage the DNA of cells, eventually making them cancerous. The risk of mouth cancer is significantly increased in someone who is a chain smoker and heavy drinker. Someone who smokes 40 cigarettes per day and consuming an average of 30 pints of beer a week is 38 times more. You are likely to develop oral cancer compared to other people.
Betel nuts
Betel nuts are mildly addictive seeds extracted from the betel palm tree. They have a stimulating effect similar to coffee. Betel nuts also have a carcinogenic effect that can increase the risk of mouth cancer. Due to the tradition of using betel nuts, the rates of mouth cancer are very high.
Smokeless tobacco
A variety of lung diseases, including lung cancer, can be caused by asbestos. There is a synergistic impact of smoke and asbestos on the formation of lung cancer. Asbestos can cause pleural cancer as well (a thin lining between the lung and the chest wall). An aggressive cancer of the pleura is called mesothelioma and affects the lungs, heart, or abdomen.
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
It is the name of a family of viruses that affect your skin and the moist membranes that line your body, such as your cervix, anus, mouth, and throat. You can get HPV infection by having sexual contact with an already infected person, it is not necessary to have sex simply close skin-to-skin contact. Infection with some types of HPV can cause abnormal tissue growth and other changes in cells, which can lead to the development of cervical cancer.
Diet
There is evidence that a diet rich in red meat, processed foods and fried foods can increase your risk of developing mouth cancer.
GERD (gastro-oesophageal reflux disease)
People with this digestive A condition in which acid from the stomach leaks backs up through the esophagus. (esophagus) has an increased risk of oral cancer. Exposure to certain minerals and chemicals, especially asbestos, sulfuric acid, and formaldehyde, increases the risk of mouth cancer
Poor oral hygiene
There is evidence that poor oral hygiene, such as having cavities, gum disease, not brushing your teeth regularly, and having ill-fitting dentures (dentures) can increase your risk of mouth cancer
Diagnosis
To determine if a lesion is cancerous, the doctor will need to remove a small sample of affected tissue to check for the presence of cancer cells. This procedure is known as a biopsy. The three main methods used to perform a biopsy in cases of suspected mouth cancer are:
Punch biopsy
A punch biopsy is used when the suspected area of tissue is an accessible place, such as the tongue or the inside of the mouth. The area is injected with a local anesthetic to make you numb. The doctor will then remove a small section of the affected tissue and remove it with forceps. The procedure is not painful.
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
A fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a type of biopsy that is used if suspected that neck swelling is the result of mouth cancer. During an FNA, the doctor inserts a sharp needle into the lump and removes a small tissue and fluid sample. The sample is then tested for cancer cells.
Panendoscopy
A panendoscopy is a procedure used to obtain a biopsy when the suspected tissue in the back of the throat or within one of the cavities of the nasal passage. The doctor uses an instrument called a panendoscope. This is a long, thin tube that contains a camera and a light source. The panendoscope is guided through the nose and then used to remove a small section of tissue for biopsy. The panendoscope can also check for cancer.
Other tests
If the biopsy results are positive, further tests will need to be done to check how far along it is and how far it has spread. These tests will include any of the following:
MRI scan
It is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize internally body structures in detail. MRI can create more detailed images of the human body than is possible with X-rays. An MRI scanner is a device in which the patient is inside a large and powerful magnet where the magnetic field is used to align the magnetization of some atomic nuclei in the body, and radiofrequency magnetic fields are applied systematically to alter the alignment of this magnetization. This causes the nuclei to produce a rotating magnetic field detectable by the scanner and this information is etched to build an image of the scanned area of the body. By using Gradients can be obtained in different directions, 2D images, or 3D volumes in any arbitrary orientation. MRI provides good contrast between different soft tissues of the body, which makes it especially useful in Images of the brain, muscles, heart, and cancers compared to other medical imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) or x-rays. Unlike CT scans or traditional X-rays, MRI does not use ionizing radiation.
CT scan
A CT scanner emits a series of narrow beams through the human body as it moves through an arc, unlike an X-ray machine that sends out only one radiation beam. The final image is much more detailed on a CT scan than on an X-ray. Inside the CT scanner, there is an X-ray detector that can see hundreds of different density levels. You can see tissues within a solid organ. These dates transmitted to a computer, which creates a 3D cross-section image of the body part and displays it on the screen. Sometimes a contrasting tint is used because it looks so much more clearly on the screen. If a three-dimensional image of the abdomen is required, the patient can have to drink a barium meal. Barium appears white on a scan as travels through the digestive system. If the images of the lower body are necessary, such as the rectum, the patient may receive a barium enema.
PET scan
IPET scanning is a nuclear medical imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or image of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide (tracer), which gets into the body into a biologically active molecule. Tracer 3D Imaging the concentration within the body is then built up by computer analysis
Mouth Cancer Treatment
Depending on the stage of mouth cancer, the doctor will recommend any of the following methods to treat cancer cells:
Surgery
The most common treatment used to treat mouth cancer is surgery. the The type of operation depends on the size of cancer and its site. Sometimes surgery is aimed at slowing down cancer by removing everything. It is sometimes used to relieve symptoms if the cancer is in an advanced stage. stage (palliative surgery). Laser surgery can sometimes be used to remove small mouth cancers. This can be combined with a light-sensitive drug in The treatment is known as photodynamic therapy (PDT).
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy, also known as radiation therapy, is a treatment that uses high-energy radiation beams that are focused on cancerous tissue. This kills the cancer cells or stops the cancer cells from multiplying.
1.External radiation therapy: This is where the radiation is directed to the cancer of a machine. (This is the common type of radiation therapy used for many types of cancer).
2.Internal radiation therapy: This treatment involves placing small radioactive wires next to the cancer site for a short time and deleting them later.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses anticancer drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them to multiply. Chemotherapy can be used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy It may also be recommended if cancer has spread to other areas of the body. The extent of treatment for oral cancer depends on several factors. These include the location, size, type, and extent of the tumor, and the stage of the disease. Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, or a combination.
