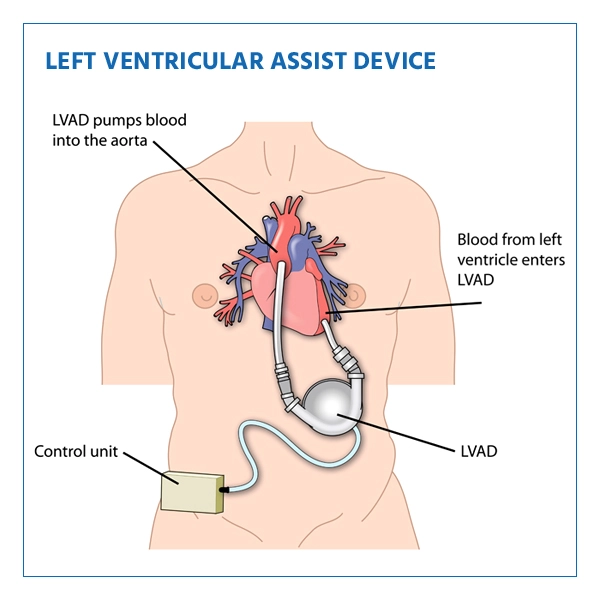
Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs)
A Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) is a mechanical pump that is surgically implanted into the patient's chest to help a weakened or failing heart pump blood more effectively. It assists the left ventricle in pumping oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. The procedure involves attaching the LVAD to the heart's left ventricle and aorta, and it can be used as a bridge to heart transplantation or as destination therapy for patients who are not eligible for a heart transplant.
Indications of LVAD-Implantation Procedure:
LVAD implantation is indicated for individuals with advanced heart failure whose heart is unable to pump blood effectively. Some common indications include:
- End-stage heart failure
- Severe cardiomyopathy
- Ineligible for heart transplant due to various reasons
- Temporary support while waiting for a suitable heart transplant (bridge to transplant)
- Destination therapy for patients who are not candidates for heart transplantation
- The primary purpose of an LVAD is to provide mechanical circulatory support, improving blood flow, relieving symptoms of heart failure, and enhancing the patient's quality of life.
Who Will Treat for LVAD Implantation Procedure:
LVAD implantation is performed by cardiothoracic surgeons who specialize in heart surgeries and advanced heart failure treatments. These surgeons have specific training and expertise in implanting LVADs.
If you or a loved one requires information about LVAD implantation, you should consider contacting:
-
Cardiologists and Cardiothoracic Surgeons: These medical professionals specialize in heart health and surgeries. They can assess your condition, determine if you are a candidate for an LVAD, and discuss the procedure and potential benefits.
- Heart Failure Clinics or Heart Transplant Centers: These specialized centers have experience in managing advanced heart failure patients and may offer LVAD implantation as a treatment option.
- Referring Physicians: If you're already under the care of a primary care physician or cardiologist, they can provide guidance and referrals to specialists who can assess your need for an LVAD.
- Hospitals with Advanced Heart Failure Programs: Research hospitals or medical centers with advanced heart failure programs, as they are more likely to have experienced surgeons and comprehensive facilities for LVAD implantation.
Preparing for LVAD Implantation Procedure:
Preparing for LVAD implantation surgery involves careful planning, medical evaluations, and discussions with your healthcare team. Here's what you can expect:
- Consultation: You will have thorough discussions with your cardiologist, cardiothoracic surgeon, and the LVAD team. They will assess your medical history, heart condition, and overall health to determine if you are a suitable candidate for the surgery.
- Medical Evaluation: You may undergo various tests such as blood tests, imaging scans (like echocardiograms and angiograms), and a comprehensive physical examination. These tests provide crucial information about your heart's function and overall health.
- Educational Sessions: You and your caregivers will receive comprehensive education about the LVAD, its benefits, potential risks, and how to manage it post-surgery. This education is essential to ensure that you're fully prepared for life with the device.
- Nutrition and Medications: Your healthcare team will provide guidelines on maintaining a healthy diet and managing your medications. Some adjustments might be necessary before and after surgery.
- Physical Conditioning: Depending on your condition, your healthcare team might recommend specific exercises to help you build strength and endurance before surgery.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: The emotional and psychological aspects of undergoing such a procedure are crucial. You may have discussions with mental health professionals to ensure you are mentally prepared for the surgery and the post-implantation period.
- Advanced Directives and Planning: Discuss your wishes for medical interventions and care with your healthcare proxy or family members. Having an advance directive in place can ensure your preferences are respected.
- Social Support: Ensure you have a support system in place for your recovery period. Having family members, friends, or caregivers who understand the procedure and its demands can make a significant difference.
What will happens during LVAD Implantation Surgery:
The LVAD implantation surgery is a complex procedure performed by a team of specialized cardiothoracic surgeons and support staff. Here's an overview of the steps involved:
- Anesthesia: You will be given general anesthesia to ensure you are asleep and pain-free during the surgery.
- Surgical Incision: The surgeon will make an incision in your chest to access your heart. The incision is typically made in the middle of your chest or on the left side.
- Connection to Heart: The surgeon will expose your heart and make connections to the left ventricle, aorta, and possibly the right atrium. Tubes are attached to these areas to facilitate blood flow.
- Implantation of LVAD: The LVAD device is implanted near the heart. One end of the device is connected to the left ventricle, while the other end is connected to the aorta. The device will assist your heart in pumping blood.
- Driveline Placement: A driveline, a thin cable that powers the LVAD, is tunneled through your skin and attached to the device. It exits your body, allowing connection to an external power source.
- Suturing and Closure: The incision is carefully sutured and closed, and sterile dressings are applied.
- Post-Surgery: After surgery, you will be closely monitored in the intensive care unit (ICU). The LVAD team will ensure the device is functioning properly and that your body is adapting to the new setup.
Recovery After LVAD Implantation Surgery Procedure:
Recovery after LVAD implantation surgery is a significant process that involves adjusting to the new device and regaining strength. Here's what to expect during your recovery:
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Stay: After the surgery, you'll be closely monitored in the ICU. The medical team will check your vital signs, ensure the LVAD is functioning properly, and manage pain and discomfort.
- Gradual Awakening: As the effects of anesthesia wear off, you'll gradually wake up. You might feel groggy initially.
- Pain Management: Pain and discomfort are common after surgery. Your medical team will provide pain relief medications and manage any discomfort.
- LVAD Function Assessment: The LVAD team will monitor the performance of the device, making sure it's pumping blood effectively and that there are no complications.
- Physical Therapy: You'll start with gentle physical therapy sessions to gradually increase your strength and mobility. Physical therapists will guide you in safe movements and exercises.
- Driveline Care: Proper care of the driveline exit site is crucial to prevent infection. Your healthcare team will educate you and your caregivers on how to clean and dress the site.
- Learning Device Management: You and your caregivers will receive extensive training on managing the LVAD, including changing batteries, alarms, troubleshooting, and emergency response.
- Nutrition and Medication: Your healthcare team will provide guidance on maintaining a proper diet and managing medications to support your recovery and overall health.
- Psychosocial Support: Emotional support is essential during this period of adjustment. Counselors or support groups can help you and your caregivers cope with the changes.
- Hospital Discharge: Once you've reached certain recovery milestones, you'll be discharged from the hospital. This doesn't mean your recovery is complete; it's a transition to the next phase of your journey.
- Regular Follow-Up: You'll have frequent follow-up appointments with your LVAD team to monitor your progress, manage any complications, and make any necessary adjustments.
Lifestyle Changes After LVAD Implantation Surgery Procedure:
After receiving an LVAD, certain lifestyle changes are necessary to ensure your well-being and the longevity of the device. Here are some considerations:
- Medication Adherence: Follow your medication regimen as prescribed. Medications are crucial to prevent blood clots, infections, and to manage heart function.
- Physical Activity: Engage in light to moderate physical activity as advised by your medical team. Regular activity can improve your overall health and support recovery.
- Dietary Modifications: Follow a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sodium intake and manage fluid consumption as advised.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated, but monitor fluid intake to prevent excess strain on your heart.
- Driveline Care: Maintain proper hygiene and care for the driveline exit site to prevent infections.
- Device Monitoring: Learn how to monitor the LVAD's alarms and indicators and respond appropriately to any alerts.
- Emotional Well-being: Coping with the emotional aspects of living with an LVAD is important. Seek support from mental health professionals, support groups, and your healthcare team.
- Regular Follow-Ups: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your LVAD team to ensure the device's proper function and address any concerns.
- Travel Precautions: If you plan to travel, discuss the arrangements and precautions with your healthcare team in advance.
- Emergency Preparedness: Have a plan in place for power outages, emergencies, and device alarms.